Seed review
advertisement

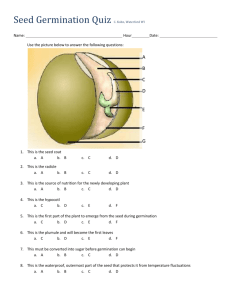
Station1 a. Name the structures with arrow. b. Give the function of the above structure. c. Why is proper sowing depth of seeds important? Station 2 Name the 4 types of seed / fruit dispersal. a. b. c. d. Station 3 Label the diagram. A. B. C. A B C Station 4 a. Name the structure with arrow. b. What is the function of this structure? c. Name 2 ways to artificially speed up germination. Station 5 a. Name the structure labeled A. b. It is also known as “little ______” c. Give the function of this structure. Station 6 Name 4 environmental factors that affect seed germination. a. b. c. d. Station 7 a. Is this plant a monocot or a dicot? b. Which number on the diagram represents the food storage structure? c. Give the name of this food storage structure. 2 1 3 Station 8 a. Name the structure labeled A. b. Name the structure labeled B. c. Describe the difference between structures A and B. B A Station 9 a. A plant embryo consists of the ___________ and the __________. b. The first root to emerge from a seed is the ___________ which develops into the ____________ root. Station 10 a. The ___________ is a scar on the seed coat from where it was attached to the ovary wall. b. The _________ is a scar on the seed coat from where the sperm entered the ovule. Station 11 a. The result of fertilization of an ovule is a _____________. b. Seeds are the product of sexual or asexual reproduction. c. Pollen develops into the male gamete (sex cell) called__________ d. Fertilization of the egg occurs in the _________ enclosed in the ovary. e. A fertilized flower develops into a ___________ which contains seeds. Station 12 a. Explain how light affects germination. a. Give an example of a plant that requires light for germination. a. Give an example of a plant that requires dark to germinate. a. Explain how compacted soil affects seed germination. Station 13 a. Give the definition of a seed. b. Give the definition of germination. c. Explain why a tomato seed will not germinate while inside the tomato fruit. Station14 Give the method of dispersal for each. a. cocklebur b. sea heart vine c. dandelion d. coconut e. impatiens f. maple g. berries h. mangrove mangrove sea heart vine impatiens Station 15 Label the diagram. A. B. C. D. E. F. F Station 16 a. Is the plant in the diagram a monocot or a dicot? b. Name the 2 food sources for the embryo in the diagram. c. Give to 2 differences between a monocot seed and a dicot seed. Station 17 a. Name the structure labeled A. b. Give the function of this structure. c. Name the structure labeled B. d. Give the function of this structure. A B