Chapter 5
advertisement

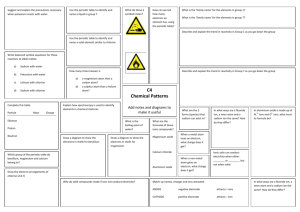
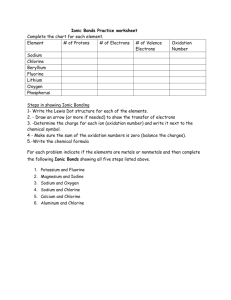
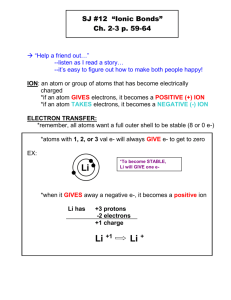
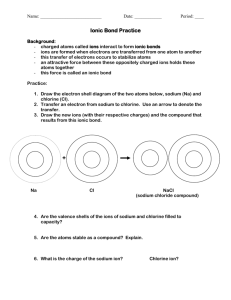
Ionic Compounds Chapter 5 What are ions? ► An ion is an atom or group of atom that has an electric charge because it has gained or lost electron. ► [Na]= 1s2 2s² 2p6 3s1 ► [Na+] = 1s2 2s² 2p6 ► When a sodium atom loses its outermost electron, it becomes positively charged ion called as sodium ion. Cations and anions ► Ions with a positive charge are called as cations. They have more protons than electrons. ► Negatively charged ions are called as anions. They have more electrons than protons. ► [Cl-] = 1s²2s²2p63s²3p6 =[Ar] ► [Cl] = 1s²2s²2p63s²3p5 ► Collection of cations are never found without the formation of similar number of anions. The concept of having equal number of positive charges is called electroneutrality. Class Practice ► What will be the electronic configuration of ► [Ca] and [Ca2+] Write down the number of protons and electrons. Transition metals ► Not all simple ions are isoelectronic with noble gas atoms. The transition metals do not fit this pattern. Lanthanides and actinides elements form cations, mostly with +3 charges, hence they are not isoelectronic with noble gases. Octet rule ► The tendency of atoms of elements to gain or lose electrons so that their outer s and p orbitals are full with eight electrons. The tendency of atoms to match the electron configuration of the s and p orbitals of a noble gas is called the octet rule. Binary ionic compound ► An ionic compound composed of simple cation and simple anion is called a binary ionic compound. ► Common table salt NaCl is composed of equal number of sodium ions, Na+ and chloride ions Cl-. Naming Binary Compounds ► The name consists of two words: the name of the cation followed by the name of the anion. ► NaCl sodium chloride ► Mg3N2 magnesium nitride ► The magnesium ion,Mg2+ has two positive charges, and the nitride ion, N3- has three negative charges. We must combine in such a way that there are as many negative charges as there are positive charges. ► Three Mg2+ cations are needed for every two N3- anions to produce electrically neutral compounds. Subscripts denote 3 magnesium ions and 2 nitride ions. Home work ► Page 164 Section review ► Q1) b and c. ► Q2) a, d, e and h. ► Q3) e, c and d. Ionic Bonding ► Sodium a very reactive Group I metal combines with chlorine a reactive Group 17 non metal ( a poisonous yellowish green gas that consists of molecules with two chlorine atoms bonded together) react a violent exothermic reaction occurs. The white residue formed from two dangerous elements is the salt we eat every day. Crystal structure of NaCl ► The coulombic force of attraction of oppositely charged ions is greater than the coulombic force of repulsion from the ions of like charges. Coulombic force is the attraction or repulsion between two objects that have electric charges. Energy aspects of salt formation. ► Ionization energy is the energy that must be supplied to remove the outermost electron from an atom. Atoms always resist having their electrons removed so their ionization energies are always positive. ► Na(g) +495 kJ/mol -- Na+(g) +e- (g) ► Electron affinity is the energy needed to put an extra electron into a neutral atom. Most electron affinities are negative indicating that the recipient atom easily accepts another electron. ► Cl(g) +e-(g) -349 kJ/mol -- Cl-(g) ► Adding the above two equations we find that the electron transfer from sodium to chlorine atom is an endothermic reaction. ► Na(g) +Cl(g) +146 kJ/mol -- Na+(g) + Cl-(g) ► This is very different from what happens in the flask. The formation if ions is only a part of the reation. ► 1. The energy must be added to convert 1 mol of sodium from a solid to a gas. Na(s) + energy -- Na(g) 2. More energy must be added to remove one electron from each sodium atom. Na(g) +energy -- Na+ (g) +e- ► ► ► 3. No energy is needed to convert chlorine into gaseous state because it is already a gas. However energy must be added to break up ½ mole of Cl2 molecules to produce 1 mol of chlorine atoms. ½Cl2(g) + energy --- Cl(g) 4. Some energy is given off when an electron is added to each chlorine atom to form Cl- ion. This is an exothermic reaction. Cl(g) + e- -- Cl- (g) + energy 5. Much more energy is given off when Na+ and Cl- ions come together to form ionic crystal of NaCl. Na +(g) + Cl- (g) -- NaCl (s) +energy. Properties Of Binary ionic compounds ►A simple cation combined with a simple anion results in binary compounds. ► Since they form strong ionic bonds they have higher melting and boiling points. ► Since they have strong ionic bond these solids are not good conductors of electricity. ► However in solution they form ions which help in conducting electricity. Polyatomic ions ► An electrically charged group of two or more chemically bonded atoms that functions as a single ion. Charges of poly atomic ions. Oxidation numbers ►A number assigned to an atom in a polyatomic ion or molecular compound based on complete transfer of electrons. ► Some guide lines: ► 1. The oxidation number of any free or combined element is zero. ► 2. Oxidation number for mono atomic ion is the charge on the ion. ► 3.The oxidation number on hydrogen is +1 unless combined with a metal when it has a charge -1. ► The oxidation number of halogen is -1 since more electro negative. ► Oxygen has an oxidation number -2 except in peroxides it is -1 and when combined with fluorine it is +2. ► In compounds the metals in Group I,II and Al have oxidation numbers +1,+2 and +3. ► The sum of the oxidation number for all the atoms in a compound is zero. ► The sum of the oxidation number for all polyatomic ion is equal to the charge on that ion. Homework ► Page 181 ► # 1-5 Silicates and Hydrates Silicates are any compounds containing silicon, oxygen, one or more metals, and possibly hydrogen ► Ionic compounds like copper sulfate CuSO4 with water molecules incorporated into their crystal lattices are called hydrates. Some salts form hydrates. E.g CuSO4.5H2O ► When a hydrated compound is heated to get rid of the water molecule the remaining salt is anhydrous. Homework ► Page 184 ► Q.3 a, c, e, f, i ,j ► Q.4 all ► Q.5. a, c, d, e, h. Class work ► Test prep page 191.