The Strategy Environment
advertisement

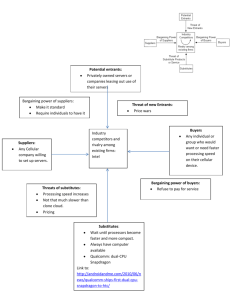
The Strategy Environment Session 2 Business Strategy The Strategy Environment • Analyse the broad macro-environment of organisations in terms of political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors (PESTEL) • Identify key drivers in this macroenvironment and use these key drivers to construct alternative scenarios with regard to environmental change The Strategy Environment • Use five forces analysis in order to define the attractiveness of industries and sectors for investment and to identify their potential for change • Identify strategic groups, market segments, and critical success factors, and use them in order to recognise strategic gaps and opportunities in the market Business Environment The Organisation PESTEL Framework Political Economic Social Technological Environmental Legal Key Drivers for Change Key drivers for change are environmental factors that are likely to have a high impact on the success or failure of strategy. The Five Forces Framework Potential entrants Suppliers Competitive rivalry Substitutes Buyers The Threat of Entry: Barriers to Entry Scale and experience Access to supply and distribution channels Expected retaliation Legislation or government action Differentiation Why Are Substitutes a Threat? Substitutes can reduce demand for a particular class of products as customers switch to alternatives. • Price/performance ratio • Extra-industry effects The Power of Buyers Are buyers concentrated? What are the costs of switching? Does backward vertical integration exist? The Power of Suppliers Are suppliers concentrated? What are the costs of switching? Does forward vertical integration exist? Degree of Competitive Rivalry • • • • • Competitor balance Industry growth rate High fixed costs High exit barriers Low differentiation Implications • Which industries should we enter or leave? • What influence can we exert? • How are competitors differently affected? The Industry Life Cycle Strategic Groups Strategic groups are organisations within an industry with similar strategic characteristics, following similar strategies or competing on similar bases. Characteristics for Identifying Strategic Groups Scope of activities • Extent of product diversity • Extent of geographic coverage • Number of segments served • Distribution channels Resource commitment • Extent of branding • Marketing effort • Extent of vertical integration • Product quality • Technological leadership • Organisational size Benefits of Identifying Strategic Groups Understanding competition Analysis of strategic opportunities Analysis of mobility barriers Market Segment A market segment is a group of customers who have similar needs that are different from customer needs in other parts of the market. Market Segment Managerial Issues in Market Segmentation • How do customer needs vary by market? • What is the relative market share within market segments? • How can market segments be identified and ‘serviced’? Strategic Customer A strategic customer is the person(s) at whom the strategy is primarily addressed because they have the most influence over which goods or services are purchased Critical Success Factors Critical success factors (CSFs) are those product features with which a organisation must outperform the competition because they are particularly valued by a group of customers. Strategic gap A strategic gap is an opportunity in the competitive environment that is not being fully exploited by competitors. Case Example: The European Brewing Industry • Complete a PESTEL analysis of the European brewing industry. • Complete a five forces analysis for the industry. • How will the environmental trends affect these companies? • What are the relative strengths and weaknesses of each?