MRP System Structure: BOM, MPS, and Planning
advertisement

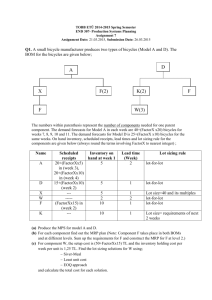
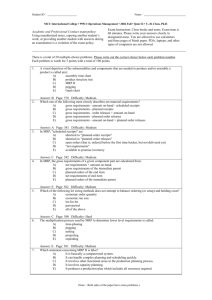
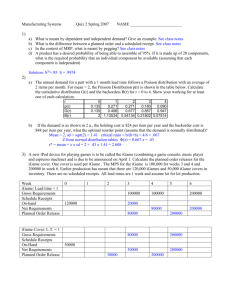
Structure of the MRP System BOM (Bill-of-Material) Master Production Schedule Lead Times (Item Master File) MRP by period report MRP by date report MRP Programs Planned orders report Inventory Data Purchase requirements Purchasing data Exception reports Master Production Schedule Drives MRP process with a schedule of finished products Quantities represent production not demand Quantities may consist of a combination of customer orders & demand forecasts Quantities represent what needs to be produced, not what can be produced Master Production Schedule MPS Period Item 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Clipboard 86 93 119 100 100 100 100 100 Lapboard 0 50 0 50 0 50 0 50 Lapdesk 75 120 47 20 17 10 0 0 Pencil Case 125 125 125 125 125 125 125 125 Product Structure Tree Clipboard Clip Assembly (10) Rivet (2) Top Clip (1) Bottom Clip (1) Pivot (1) Spring (1) Sheet Metal (8 in2) Sheet Metal (8 in2) Spring Steel (10 in.) Iron Rod (3 in.) Level 0 Board (1) Pressboard (1) Level 1 Finish (2oz.) Level 2 Level 3 Indented Bill of Material LEVEL 0----1----2----3--2----3--2----3--2----3-1---1----2---2-- ITEM Unit of Measure Clipboard Ea Clip Assembly Ea Top Clip Ea Sheet Metal In2 Bottom Clip Ea Sheet Metal In2 Pivot Ea Iron Rod In Spring Ea Spring Steel In Rivet Ea Board Ea Press Board Ea Finish Oz Quantity 1 10 1 8 1 8 1 3 1 10 2 1 1 2 The MRP Matrix Lot size: LT: Gross requirements Scheduled receipts Projected on hand Net requirements Planned order receipts Planned order releases PD 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Item • name or number identifying scheduled item LLC • low-level-code; lowest level at which item appears in a product structure 9 10 Parts Of MRP Matrix Lot size • order multiples of this qty; can be min/max qty LT (lead time) • time from order placement to receipt PD (past-due) • orders behind schedule Gross requirements • demand for item by time period Scheduled receipts Projected on hand • quantity already on order & receipt date • released orders become scheduled receipts • expected on-hand inventory at beginning of period Net requirements Planned order receipts Planned order releases • net amount needed after on-hand adjustments • net requirements adjusted for lot-sizing • planned order receipts offset by lead time The Alpha Beta Company A LT=3 C(3) LT=4 Item On Hand B LT=2 D(2) LT=2 D(3) LT=2 Scheduled Receipts Lot Size MPS A 10 0 1 100, period 8 B 5 0 1 200, period 6 C 140 0 150 --- D 200 250, period 2 250 --- MRP Matrices For A & B Item: A LLC: 0 Lot size: 1 LT: 3 Gross requirements Scheduled receipts Projected on hand Net requirements Planned order receipts Planned order releases Item: B LLC: 0 Lot size: 1 LT: 2 Gross requirements Scheduled receipts Projected on hand Net requirements Planned order receipts Planned order releases PD 10 1 2 10 10 Period 3 4 10 10 5 6 7 8 100 10 10 10 10 90 90 90 PD 5 1 2 Period 3 4 5 5 5 5 195 5 6 200 7 8 5 5 195 195 0 0 MRP Matrices For C & D Item: C LLC: 1 Lot size: 150 LT: 4 Period PD 1 2 3 4 Gross requirements 5 6 7 8 20 20 20 270 Scheduled receipts Projected on hand 140 140 140 140 140 140 Net requirements 130 Planned order receipts 150 Planned order releases Item: D LLC: 1 Lot size: 250 LT: 2 Gross requirements Scheduled receipts Projected on hand Net requirements Planned order receipts Planned order releases 150 PD 200 Period 3 4 585 1 2 200 250 450 450 250 250 450 135 250 5 180 6 7 8 115 65 250 185 185 185 Alpha Beta Planned Order Report Period 1 2 3 4 5 Item C D D B A Quantity 150 250 250 195 90 MRP and The Production Planning Process Forecast & Firm Orders Aggregate Production Planning Material Requirements Planning Master Production Scheduling Resource Availability No, modify CRP, MRP, or MPS Capacity Requirements Planning Realistic? Yes Shop Floor Schedules MRP Benefits Increased customer satisfaction due to meeting delivery schedules Faster response to market changes Improved labor & equipment utilization Better inventory planning & scheduling • Reduced inventory levels without reduced customer service Mechanism for communication between departments MRP Requirements Computer system Mainly discrete products Accurate master production schedule Accurate inventory status Stable lead times • 99% inventory accuracy © 1984-1994 T/Maker Co. Inventory Accuracy 1. Maintain orderly stockrooms 2. Control access to stockrooms 3. Establish & enforce procedures for inventory withdrawal 4. Ensure prompt and accurate entry of inventory transactions 5. Take physical inventory count on a regular basis 6. Reconcile inventory discrepancies in a timely manner (use cycle counting)