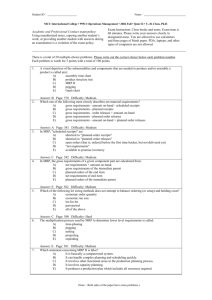
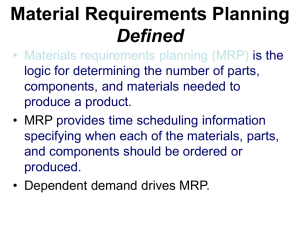
1) One of the differences between Enterprise Resource Planning
advertisement

311 Review 3 (Chapters 11,12,14) 1. The MRP input stating which end items are to be produced, when they are needed, and what quantities are needed, is the: a. master schedule b. bill-of-materials file c. inventory record file d. assembly-time chart e. net-requirement chart 5. A basic requirement for operating with low inventories in JIT systems is 2. The MRP input storing information on the status of each item by time period (e.g., scheduled receipts, lead time, lot size) is the: 6. Which of the following statements about ERP is true? a. b. c. d. e. master production schedule bill-of-materials file inventory record file assembly-time chart net-requirement chart 3. Which one of the following most closely describes net requirements? a. Gross requirements – amount onhand – scheduled receipts b. Gross requirements – planned receipts c. Gross requirements - order releases + amount on-hand d. Gross requirements – planned order release e. Gross requirements – amount onhand + planned order releases a. b. c. d. e. inventory space must be saved inventory investment must be saved major problems must be uncovered major problems must have been solved inventory must be reduced rapidly a). ERP is limited to operations internal to the enterprise b). ERP is similar to MRPII, except that t extends to service operations. c). ERP allows customers and suppliers to access the system d). Both ERP and MRPII are linked to the external supply chains. 7. Which of the following statements about lotsizing rules for MRP is true? a). The L4L rule generates a high level of average inventory b). Fixed order quantity (FOQ) reduces the amount of inventory on hand c). the L-4-L rules minimize inventory investment, but increases the number of orders d). all lot-sizing rules seek to minimize inventory levels. 4. In MRP, “scheduled receipts” are: a. identical to “planned order receipts” b. identical to “planned order releases” c. open orders (that is, ordered before the first time bucket but not delivered yet) d. “net requirements” e. none of the above 8. Which one of the following is an advantage of JIT? a). JIT systems reduce equipment needs by using larger lot sizes b). JIT systems result in an increase in manufacturing lead time c). JIT systems result in a decrease in safety stock and WIP inventory d). JIT systems reduce WIP inventory by adopting a push system 1. Use the following MPS, BOM, and inventory data, fill out the MRP tables provided in the next page to answer questions 1 to 3. 311 Review 3 (Chapters 11,12,14) a) Master Production Schedule: The following table shows the MPS release dates already offset for item A's lead time. Week Week 1 MPS 2 3 60 4 5 70 6 40 b) Bill of Material -End item A uses 1 each of component D and 2 each of subassembly C. -Subassembly C uses 2 each of component E and 1 each of component F. c) Selected Inventory Data Item Data Category C D E Lot-sizing rule FOQ=50 L4L FOQ=70 Lead time (weeks) 1 1 1 Beginning (on-hand) inventory 30 0 30 Safety stock 0 0 20 50 (wk 1) 30 (wk 1) 90 (wk 1) Scheduled receipts 1. What is the largest quantity of projected on-hand inventory for any of the weeks for item D? a. 0 units b. greater than 0, but less than or equal to 25 units c. greater than 25, but less than or equal to 50 units. d. Greater than 50 2. How many planned order releases are there for item C? a. none b. one c. two d. more than two 3. Which of the following statements concerning item E is true? a. The projected on-hand inventory quantity in week 4 is 0 units b. The planned order receipt in week 3 is 280 units c. There are three planned order releases. d. There are planned order receipts needed in weeks 3 and 5. Item: Lead time: Lot size: 311 Review 3 (Chapters 11,12,14) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Gross requirements Scheduled receipts On-hand Inv. Net Requirements Planned receipts Planned releases Item: Lead time: Lot size: Gross requirements Scheduled receipts On-hand Inv. Net Requirements Planned receipts Planned releases Item: Lead time: Lot size: Gross requirements Scheduled receipts On-hand Inv. Net Requirements Planned receipts Planned releases