Unit 1 Flashcards [Biochemistry]
advertisement
![Unit 1 Flashcards [Biochemistry]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009271654_1-35a16c23e7f5950979b14d5b44b6987d-768x994.png)
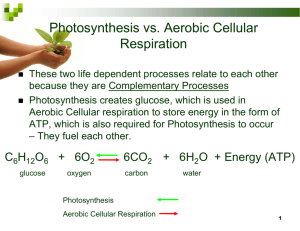
Unit 1 Flashcards [Biochemistry] What are the 6 Biological Elements? • • • • • • C H O N P S What are the 4 Biomolecules? • • • • Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids What is ATP? • Adenosin Triphosphate • Energy storing molecule How do you release energy from ATP? • Remove a phosphate How do you store energy in ATP? • Bond / Add a phosphate What are all of the Characteristics of Life? • Maintain homeostasis • Metabolize nutrients + Excrete Waste • Respond + Adapt • Contain a Genetic Code + Reproduce Are Viruses Living? • No • They cannot… –Reproduce –Maintain Homeostasis –Metabolize / Excrete … on their own What are atoms? • Basic units of matter What are cells? • Basic units of life What is Kinetic Energy? • Energy being used right now in a cell What is Chemical Potential Energy? • Energy stored in the bonds of molecules What element is an organic molecule made of? • carbon What is a Monomer? • The basic unit / building block that makes up larger molecules. What are Polymers? • Larger molecules (made of monomers) List out the levels of biological organization: • • • • • • Atoms / Molecules Organelles / Cells Tissue Organ Organ System Organism What is the Monomer of a Carbohydrate? • monosaccharide What is the Polymer of a Carbohydrate? • polysaccharide What is the function of Carbohydrates? • Provide immediate / intermediate energy Why do Polysaccharides provide more energy for you? • They have more bonds What are the Monomers for Lipids? • Fatty Acids + Glycerol What are some Lipid Polymers? • Phospholipid • Neutral Fat What is the function of a Lipid? • Provide long term energy storage What is the Monomer for a Protein? • Amino acid What is the Polymer of an Amino Acid? • Polypeptide • Enzymes What is the Function of Proteins? • Express DNA code • Catalyze reactions What does it mean to denature a protein? • Change the shape, and function of the protein… • …the protein stops working! What denatures a protein? • Heat • Acid What happens when you mix Liver and Hydrogen Peroxide? • Bubbles • Enzyme in Liver (Catalase) breaks down Hydrogen Peroxide What is the Monomer for a Nucleic Acid? • nucleotide What are the Polymers of Nucleic Acids? • DNA • RNA What is the Function of a Nucleic Acid? • Store the genetic code of a cell What does “polar” mean? • The molecule has an uneven distribution of charges across its length…. • … One end is more positive … One end is more negative Unit 2 Flashcards [Cells & Cell Processes] What are the 3 parts of the Cell Theory? • Cell are the basic units of life • All living things are made of cells • Cells come from other cells What is the Endosymbiotic Theory? • Modern eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells living symbiotically with one another. • Chloroplasts + Mitochondria were once free-living bacteria that then lived inside larger cells. What is a Prokaryotic Cell? • Cell without a nucleus What is a Eukaryotic Cell? • A cell with a nucleus What is a Unicellular Organism? • An organism made of only one cell What is a Multicellular Organism? • An organism made of many specialized cells What is diffusion? • The movement of particles from high to low concentration. • NO Energy • Goes until it reaches equilirium What is Osmosis? • The movement of Water particles from high to low concentration. • NO Energy • Goes until reaching equilibrium What is Active Transport? • The forced movement of particles across the cell membrane. • USES ENERGY What is Facilitated Diffusion? • The assisted movement of larger particles across the cell membrane. • Through protein channels. • No Energy. What is Endocytosis? • Pinching off of cell membrane… • Bringing materials INTO cell What is Exocytosis? • Pinching off of cell membrane… • Pushing OUT waste Describe a Hypertonic Cell… • There is MORE water inside the cell, than outside. How will water move in a Hypertonic cell? • Water will move from HIGH LOW. • Water will leave / exit the cell. Describe a Hypotonic Cell… • There is LESS water inside the cell, than outside. How will water move in a Hypotonic cell? • Water moves HIGH LOW. • Water will move INTO the cell. Describe an Isotonic Cell… • There is an equal amount of water inside and outside the cell. • The cell will not fill or lose water… What is a cell membrane made of? • Phospholipid Bilayer Name the Organelles in this picture: 1- golgi body 2- endoplasmic reticulum 3- lysosome / peroxisome 4- ribosomes 5- ribosomes 6- mitochondria 7- lysosome / peroxisome 8- cell membrane 9- nucleus 10- centrioles Name the Function of the Organelles in this picture: 1- Package + Ship proteins 2- Fold proteins 3- Lysosomes use Lysozyme to break down cell parts / toxins Peroxisomes use Catalase to break down Hydrogen Peroxide 4- Assemble amino acids to make a protein 5- (same as #4) 6- Complete cellular respiration to make ATP 7- (see #3) 8- Control what enters / exits 9- Store DNA / genetic code 10- Organize DNA during division 1- Nucleus Name the 2- endoplasmic Organelles in this reticulum picture: 3- vacuole 4- mitochondria 5- chloroplast 6- cell membrane 7- cell wall #3 Which of the organelles below #5 #7 are unique to PLANTS? Name the Function of the Organelles in this picture: 1- store DNA / genetic code 2- fold proteins 3- store water + maintain cell shape 4- Complete cell. Respiration to make ATP 5- Complete Photosynthesis to convert SUNlight into Sugar + Oxygen 6- Control what enters / exits 7- Extra support + protection What is Hydrolysis? • A cell process in which water is ADDED… • Polymer Monomer • Energy released from broken bonds What is Dehydration Synthesis? • A cell process in which water is REMOVED… • Monomers Polymer • Energy stored in new bonds What does this diagram show? • • • • Dehydration Synthesis Water is being removed Monomers Polymers Energy stored in new bonds What does this diagram show? • Hydrolysis • Water added • Polymer Monomers • Energy released from broken bonds Unit 3 Flashcards [Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration] What is the chemical equation for Photosynthesis? Sun + CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + O2 In words, What is Photosynthesis? • The reacting of sunlight, carbon dioxide and water… • …. Producing glucose and oxygen. What are the reactants for Photosynthesis? • Sunlight • Carbon dioxide • water What are the products for Photosynthesis? • Glucose • oxyge Which organelle completes Photosynthesis? • chloroplast How is energy transferred during Photosynthesis? • Energy is transferred from the Sun to the bonds of Glucose How is energy converted during Photosynthesis? • Energy is converted from electromagnetic energy chemical potential energy What is the overall purpose of Photosynthesis? • Convert the un-useable energy from the Sun useable energy in the form of sugar / glucose What is the chemical equation for Cellular Respiration? C6H12O6 + O2 H2O + CO2 + ATP In words, what is Cellular Respiration? • The reacting of glucose and oxygen.. • …producing carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. What are the reactants for Cellular Respiration? • Glucose • Oxygen What are the products for Cellular Respiration? • Carbon dioxide • Water • ATP Which organelle completes Cellular Respiration? • Mitochondria How is energy transferred during Cellular Respiration? • Energy is transferred from the bonds of glucose bonds of ATP How is energy converted during Cellular Respiration? • Energy is not converted • It stays in the form of chemical potential energy What is the overall purpose of Cellular Respiration? • To release the energy from glucose, and store it in the bonds of ATP. How do we rely on plants? • We rely on plants to produce: –Glucose / sugar –Oxygen How do plants rely on us? • They rely on us to produce: –Carbon dioxide –Water Unit 4 Flashcards [Cell Division] What is asexual reproduction? • Reproduction with only 1 organism • Offspring are identical to parent What is sexual reproduction? • Reproduction with 2 parents • Offspring are genetic variants of parents What is Binary Fission? • A type of asexual reproduction • Bacteria copy themselves + divide in half What is Conjugation? • When bacteria exchange plasmids. • Can lead to antibiotic resistance. What is the Cell Cycle? • Process in which cells prepare for division… –Grow –Copy organelles –Copy DNA … AND actually divide What are the 4 phases in the Cell Cycle? • • • • G1 S G2 M Which phases are in Interphase? • G1 •S • G2 What takes place during G1 and G2 phases? • The cell… –Grows –Copies organelles What happens during the S phase? • DNA is copied What happens during the M phase? • The cell actually divides Identify each stage in the Diagram Below: [This shows the Cell Cycle] • A = G1 phase • B = S phase • C = G2 phase • D = M phase Identify each stage in the Diagram Below: [This shows the Cell Cycle] • A = G1 phase • B = S phase • C = G2 phase • D = M phase What is Mitosis? • Cell Division for nonsex / somatic cells What is Meiosis? • Division for sex / gamete cells Mitosis starts 2n / Diploid, and ends… • 2n / Diploid Identify the Mitosis Stages in the diagram: • A – Metaphase • B-Telophase & Cytokinesis • C—Anaphase • D—Prophase What happens during Prophase of Mitosis? • Nucleus dissolves • Chromosomes form • Spindle fibers prepare What happens during Metaphase of Mitosis? • Sister chromatids line up in the center of the cell. What happens during Anaphase of Mitosis? • Sister chromatids separate. What happens during Telophase & Cytokinesis of Mitosis? • Chromosomes unwind • Nuclei reform • Cytoplasm splits Meiosis starts 2n / Diploid, and ends… • 1n / Haploid What happens during Prophase 1 of Meiosis? • Nucleus dissolves • Chromosomes form • Spindle fibers prepare What happens during Metaphase 1 of Meiosis? • Pairs of homologous chromosomes line up in the center of the cell • Crossing over What happens during Anaphase 1 of Meiosis? • Homologous pairs of chromosomes separate What happens during Metaphase 2 of Meiosis? • Sister chromatids line up in the center of the cell What happens during Anaphase 2 of Meiosis? • Sister chromatids separate What happens during Telophase & Cytokinesis of Meiosis? • Chromosomes unwind • Nuclei reform • Cytoplasm splits How many cells do you end up with in Meiosis? •4 What is Crossing Over? • Exchange of alleles between nearby homologous chromosomes • Happens during Metaphase1 of Meiosis What is the Law of Segregation? • Each sex cell ends up with only ½ genetic info… • OR • Each sex cell ends up with only 1 allele per gene What is the Law of Independent Assortment? • Each sex cell ends up with a random combination of alleles What is happening in this picture? • Crossing Over What is happening in this picture? • A-C = Meiosis 1 • D-G = Meiosis 2 • G = 1N cells What is cancer? • Uncontrolled cell growth and division. How many chromosomes should a normal human have? • 46 total • 23 pairs What are the sex chromosomes of a male? • XY What are the sex chromosomes of a female? • XX What is shown in this diagram? • Karyotype • Error #23 has too many sex chromosom es! XXY!!