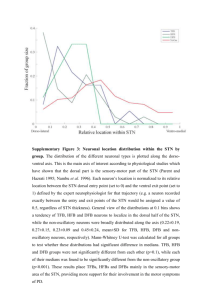
Eco- Routing Using Spatial Big Data

Lagrangian Xgraphs: A logical data-model for Spatio-temporal Network Data
Venkata Gunturi, Shashi Shekhar
University of Minnesota, Minneapolis
Acknowledgement:
Outline of the Talk
What is Spatio-temporal Network (STN) data?
Value addition potential of STN data
Problem Definition
Challenges
Limitations of Related Work
Proposed Lagrangian Xgraphs
Concluding Remarks
What is Spatial-temporal
Network (STN) Data?
STN data is result of interactions (across time) of entity(s) with a network embedded in space.
Large number of urban sensors produce a variety of datasets.
E.g., GPS navigation devices, Loop detector data, Social media etc.
Some are mobile, some are stationary,
All of them capture diverse characteristics of a network in a urban scenario
Motivation: Collective wisdom from these datasets could support valuable use-cases, e.g., eco-routing
Sample STN datasets over Transportation Network
Temporally detailed roadmaps.
Traffic signal and coordination data.
GPS tracks annotated with engine measurement data .
From Traditional Roadmaps
Dinky town Roadmap
Intersection between 5 th Ave
SE and 5 th St
Corresponding Digital Representation
5 th Ave SE edge
Intersection between 5 th Ave
SE and 4 th St
Source: Google Maps
Attributes of 5 th
Ave SE road segment between
N4 and N7
N7 N4
To Temporally Detailed (TD) Roadmaps
Contains typical travel-time under traffic equilibrium conditions
Per minute speed/travel time values
100 million road segments in US
NAVTEQ’s highly compressed weekly speed profile data
Source: ESRI and NAVTEQ
GPS traces
Sources: Mobile devices
Smart phones, in car/truck GPS devices,
GPS collars
Coupled with engine measurements
VGI Commuter preferred routes under non-equilibrium conditions
Estimate traffic signal delays?
Ramp meters
Coordinated signals
Left turn delays
Waiting at signals
Outline of the Talk
What is Spatio-temporal Network (STN) data?
Value addition potential of STN data
Problem Definition
Challenges
Limitations of Related Work
Proposed Lagrangian Xgraphs
Concluding Remarks
McKinsey Conjecture and Preliminary Evidence
U.P.S.
Embraces High-Tech Delivery Methods (July 12, 2007)
By “ The research at U.P.S. is paying off. ……..— saving roughly three million gallons of fuel in good part by mapping routes that minimize left turns .
”
Outline of the Talk
What is Spatio-temporal Network (STN) data?
Value addition potential of STN data
Problem Definition
Challenges
Limitations of Related Work
Proposed Lagrangian Xgraphs
Concluding Remarks
P ROBLEM D EFINITION
Input
– A collection of Spatio-temporal Network datasets
– Use case queries (e.g. compare candidate routes)
Output
– A unified logical model across these datasets
Objective
– Travel related concepts are expressed upfront
– Suitable for common routing algorithms e.g. Dijsktra’s, A*
P
ROBLEM
I
LLUSTRATION
: A
T
C
ONCEPTUAL
L
EVEL
GPS DATA Delay Data
TD roadmaps
Logical Model for STN datasets over Transportation Network
Usually entities like Roads, Signals, Streets are modeled using lines strings and polygons.
Queried through OGIS operators
Not suitable for comparing candidate routes.
Modeling as Spatial/Spatio-temporal networks?
Outline of the Talk
What is Spatio-temporal Network (STN) data?
Value addition potential of STN data
Problem Definition
Challenges
Limitations of Related Work
Proposed Lagrangian Xgraphs
Concluding Remarks
C HALLENGES OF
“S
EQUENCE OF
” R
ELATION
What if M >2?
Logical Model for STN datasets over Transportation Network
Current spatial/spatio-temporal models work for M=2
What if M>2? e.g. GPS traces and Traffic signal coordination
Outline of the Talk
What is Spatio-temporal Network (STN) data?
Value addition potential of STN data
Problem Definition
Challenges
Limitations of Related Work
Proposed Lagrangian Xgraphs
Concluding Remarks
Limitations of Related Work:
Non-decomposable Properties of N-ary relations
Sample N-ary relation: Typical delay experienced in series of coordination signals
Holistic Property: Properties measured over a larger instance loose their semantic meaning when broken down into properties of small instances
After waiting at SG1, SG2 and SG3 become wait-free!
Non-local interactions (SG1 not a neighbor of SG2)
Typical delay measured over S-B-C-E-D will have wait only at SG1
Not true for journeys starting after intersection B or intersection C
Limitations of Related Work:
Non-decomposable Properties of N-ary Relations
Current related work not suitable for representing holistic properties network databases, e.g., Oracle spatial,
ArcGIS etc.
Query: What is the typical travel-time experienced on Hiawatha Ave (between S and D)?
Result: Between 21mins – 25mins 30secs
Cannot represent signal coordination upfront!
Outline of the Talk
What is Spatio-temporal Network (STN) data?
Value addition potential of STN data
Problem Definition
Challenges
Limitations of Related Work
Proposed Lagrangian Xgraphs
Concluding Remarks
3mins
Proposed Approach: Lagrangian Xgraphs
Summary of proposed approach
8mins
5mins
5mins
Holistic properties are modeled as series of overlapping “sub-journeys”
Each “sub-journey” is contains one nonlocal interaction
Suitable for non-decomposable properties of N-ary relations.
Travel Related Concepts:
Lagrangian vs Eulerian frame of reference
Eulerian Frame: Perspective of a fixed observe, e.g., traffic observatory
What is cost of following routes at 5:00pm
• I-35W
• Hiawatha Route
Digital Road Map
Legend:
A-I-D: UMN-I35W-Airport
A-H-D : UMN-Hiawatha-Airport
Path
A-I-D
A-H-D
Cost from
Traveler Pers.
27 mins
25 mins
Cost at 5:00pm
Fixed Obs.
20 mins
25 mins
Travel Related Concepts:
Lagrangian vs Eulerian frame of reference
Lagrangian Frame: Perspective of a traveler travelling through the network
What is cost of following routes at 5:00pm
• I-35W
• Hiawatha Route
Digital Road Map
Legend:
A-I-D: UMN-I35W-Airport
A-H-D : UMN-Hiawatha-Airport
Path
A-I-D
A-H-D
Cost from
Traveler Pers.
11+
??
Cost at 5:00pm
Fixed Obs.
20 mins
25 mins
Travel Related Concepts:
Lagrangian & Eulerian frame of reference
Lagrangian Frame: Perspective of a traveler travelling through the network
What is cost of following routes at 5:00pm
• I-35W
• Hiawatha Route
Digital Road Map
Legend:
A-I-D: UMN-I35W-Airport
A-H-D : UMN-Hiawatha-Airport
Path
A-I-D
A-H-D
Cost from
Traveler Pers.
Cost at 5:00pm
Fixed Obs.
11+16 =27 20 mins
??
25 mins
Travel Related Concepts:
Lagrangian & Eulerian frame of reference
What is cost of following routes at 5:00pm
• I-35W
• Hiawatha Route
Digital Road Map
Legend:
A-I-D: UMN-I35W-Airport
A-H-D : UMN-Hiawatha-Airport
Path Cost from
Traveler Pers.
A-I-D 27 mins
A-H-D 25 mins
5:00PM
Snapshot
20 mins
25 mins
Travel Related Concepts:
Decomposable vs Holistic Properties
Decomposable: Property measured over a larger instance can be broken down into properties of small instances
Distance inferred from a GPS track can be decomposed into distances along individual road segments
Travel Related Concepts:
Decomposable vs Holistic Properties
Holistic Property: Properties measured over a larger instance loose their semantic meaning when broken down into properties of small instances
What about travel-time inferred from a GPS track?
Time spent on a segment depends on the initial velocity attained before entering the segment!
Taxonomy of Travel Related Concepts
Captured in STN Datasets
Signal Delay Data
GPS DATA
TD roadmaps
All STN datasets capture data along two dimensions.
Traveler’s Frame of Reference For
Comparing Candidate Routes
Candidate routes are evaluated from the perspective of a person moving through the transportation network.
A-C-D is shorter for t=1 :
Lagrangian Frame needs to be upfront
Langrangian Xgraph: Formal Definition
Lagrangian Xgraph: {Xnodes, Xedges}
Xnodes: Underlying entities at specific space-time coordinates.
– Xv1, Xv2, Xv3…
Xedges: Express a Lagrangian relation ( i.e.,’as-traveled’ or ‘typicalexperience-intravel’) relationship among a group a Xnodes
– Xei = { Xvs , Xv1, Xv2, Xv3…, Xvk, Xvd1, Xvd2,..,Xvdj }
First and Last set of Xnodes in an
Xedge are marked separately
TD roadmaps Shoot Xedges
GPS Traces Shoot and Stem Xedges
Trafffic Signal Delays Bush and
Flower Xedges
Get, Set and Join operators (only
Xedges) For Xndoes and Xedges
Sample Langrangian Xgraph for Signal
Coordination (1/2)
Xnodes: Underlying road segments between two road intersections at specific departure-times.
Xedges: Express a ‘as-traveled’ or ‘typical-experience-in-travel’ relationship among a group a Xnodes
3mins
8mins
5mins
Xnode ED6:
Road segment ED for departure-time 7:03am at E
Sample Langrangian Xgraph for Signal
Coordination (2/2)
Xedge SB0 and (ED32, ED33, ED34, ED 35) as first and last Xnodes:
– An Xedge representing: “If one leaves at S at 7:00am he/she can start traversing segment E-D at times 7:16, 7:16:30, 7:17, or 7:17:30”
Outline of the Talk
What is Spatio-temporal Network (STN) data?
Value addition potential of STN data
Problem Definition
Challenges
Limitations of Related Work
Proposed Lagrangian Xgraphs
Concluding Remarks
Conclusion
Increased proliferation of sensors
– Spatio-temporal datasets capturing diverse phenomena on a transportation network
Collectively they can add significant value to societal use-cases.
However, they pose modeling challenges due to holistic nature of properties captured in these datasets.
Proposed Lagrangian Xgraphs
– can model both decomposable and holistic properties