Supplementary Materials:
advertisement

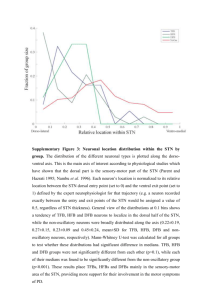
Supplementary Materials: 1. Supplemental text 2 Tables S1-3 3. Figure S1 1. STN localization All patients suffering from OCD and referred to our institution are operated under the same surgical procedure routinely used for the implantation of DBS leads in patients with movement disorders 30. Briefly, 2 days before the surgical implantation, a stereotactic digital televentriculography (Pixray; BioScan, Geneva, Switzerland) is performed under general anaesthesia. Then, for each patient, T1- and T2-contrasted three-dimensional cerebral magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are obtained in stereotactic conditions before the surgical implantation of the leads. The targeting of anterior STN is performed on the ventriculographic X-ray fused with the MRI scans using stereotactic imaging software (Voxim; IVS Solutions, Chemnitz, Germany). In patients with PD, the following coordinates are frequently used to target the STN: 6/12 of the anterior-posterior commissural (AC-PC) length posterior to the AC, 12mm lateral to the midline, and 3 mm below the AC-PC line. In patients with OCD, the anterior STN is targeted 2 mm anterior and 1 mm medial to the previous target. It is then adjusted during surgical implantation by using multiunit recordings. In patients with OCD, the anterior STN is identified by the lack of sensorimotor side effects such as contralateral paresthesias or motor contractions induced by microstimulations. STN location was confirmed in six patients (P1-P6) by a combined approach that included intraoperative microelectrode recordings, direct micro and macro-stimulation and postoperative stereotactic MRI (Fig. S1) with fusion to the preoperative MRI (cases 1–6). In case 7, STN was localized using preoperative MRI and direct macrostimulation. The final DBS electrode coordinates are reported in Table S2 and Figure S1. 2. Supplemental Table S1-3 Table S1. Clinical characteristics of OCD patients at time of surgery. OCD type (1;2;3) corresponded to the main type of symptom observed: contamination/cleaner (1), doubt/checker (2) and miscellaneous OCD + repeating (3); YBOCS = Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (with Obsessions + Compulsions subscores); GAF = Global Assessment of Functioning; CGI = Clinical Global Impression; SNRI = serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors; SRI = serotonin reuptake inhibitors; FGA = first-generation antipsychotics; SGA= second-generation antipsychotics. Clinical scales Sex Age, years Duration of symptoms, years OCD type YBOCS P1 M 36 17 1 P2 F 38 11 P3 F 40 P4 F P5 Medication, Total Daily Dose (mg) CGI GAF 17+15 5 40 1 18+18 6 32 15 1 19+17 6 34 54 22 2 17+16 5 30 M 34 13 2 16+16 6 35 P6 M 27 10 3 17+17 6 30 P7 F 30 23 2 16+18 6 35 SNRI and SRI paroxetine 40mg sertraline 100mg fluvoxamine 200mg clomipramine 75mg paroxetine 50mg clomipramine 187,5mg sertraline 150mg Venlafaxine 75mg FGA and SGA Other Medications clonazepam 4mg gabapentin 600mg clonazepam 3mg lorazepam 3mg zopiclone 7,5mg cyamemazine 150mg amisulpride 300mg oxazepam 150mg Levothyrox 125µg Table S2. Summary of task-responsive and non-responsive (NR) units in the associative STN. Each line corresponds to one unit (Su and MU; for example, c26 corresponds to a single cell 26 whereas MU9 corresponds to a multi-unit 9). For each unit type (task responsive: GO, SS, US cells or nonresponsive cells, NR), each column describes the patient (Pat) that contributed to each recording, the hemisphere recorded (STN side, left L and right, R), the recording depth (in mm below CA-CP line) and the baseline firing rate of this unit (computed during visual fixation epochs). Note that most of the NR units showed no response at all to task events (79 %) whereas the remaining 21 % were modulated non-specifically by different trial-types (i.e., these units did not fulfill criteria used to define SS, US and GO units). Pat Side Depth Cell Type cell number FR (Hz) P1 P1 P1 P2 P2 P3 P4 P5 P5 P6 P1 P2 P2 P2 P3 P3 P3 P4 P5 P6 P1 P1 P2 P2 P2 P2 P4 P4 P5 P6 P6 P6 P1 P1 P1 P1 P1 P1 P2 P2 P2 P2 P2 P2 P2 P2 P2 P2 P2 R L R L L L R L L L L L R R L L L R R R R L R R L L R R R L R L R R L L R R L L L L L R R L L L R -3,751 -7,718 -2,535 -5,484 -8,258 -4,468 -5,395 -5,025 -5,025 -7,240 -6,536 -5,484 -3,769 -4,899 -4,468 -5,988 -4,468 -4,978 -6,359 -7,086 -2,535 -7,718 -3,769 -4,899 -7,429 -8,258 -6,146 -4,978 -4,673 -4,251 -6,247 -6,472 -2,535 -2,535 -5,934 -7,718 -3,751 -3,751 -5,484 -6,410 -6,410 -6,410 -7,429 -4,899 -4,899 -7,429 -7,429 -8,258 -3,769 GO GO GO GO GO GO GO GO GO GO SS SS SS SS SS SS SS SS SS SS US US US US US US US US US US US US NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR c26 c30 MU9 MU13 MU19 c43 MU3 C5 C6c c16 c28 c31 c37 c40 c45 c46 MU22 C2 MU5 MU7 c25 MU12 c38 c42 MU16 MU18 C3 MU1 c7 c13 c18 MU6 c23 c24 c27 c29 MU10 MU11 c32 c33 c34 c35 c36 c39 c41 MU14 MU15 MU17 MU20 18,4 49,1 9,0 2,7 11,8 16,3 36,4 26,7 53,5 39,8 32,0 6,6 29,3 3,4 13,1 4,1 4,2 21,0 29,5 36,2 7,4 32,1 13,7 11,3 3,8 7,6 2,8 13,5 27,8 14,9 8,3 38,3 17,0 10,2 30,6 33,4 35,8 19,1 8,1 24,3 25,3 16,8 15,0 14,2 10,5 37,9 36,6 41,1 7,7 P2 P3 P3 P3 P3 P3 P3 P4 P4 P4 P4 P5 P5 P5 P5 P5 P5 P5 P6 P6 P6 P6 P6 P6 P6 P6 R L R R R R L L R R R R R R L L R R L L L R R R R R -4,899 -4,468 -6,183 -6,183 -6,183 -6,183 -5,988 -4,940 -6,146 -5,395 -6,146 -5,334 -6,359 -6,359 -5,025 -5,025 -5,334 -5,334 -5,768 -5,768 -7,240 -6,962 -6,962 -7,086 -7,409 -7,409 NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR NR MU21 c44 c47 c48 c49 c50 MU23 C1 C4 MU2 MU4 c10 c11 c12 C6 C6b c8 c9 c14 c15 c17 c19 c20 c21 c22 MU8 14,9 17,6 16,7 32,6 19,1 13,2 14,4 11,5 15,3 6,3 6,7 24,2 3,5 27,8 29,6 21,9 32,9 5,1 24,6 27,2 9,4 26,4 20,4 10,5 20,2 20,1 Table S3. Final DBS electrode coordinates where the maximal level of 15-30 Hz activity was recorded during the stop-signal task. For each side, the coordinates of the two adjacent electrode contacts defining the bipole are shown. Coordinates are given in millimetres relative to each patient ventricular landmarks (Anterior/posterior Commissures (AC, PC) and midline). These coordinates were determined offline using the televentriculography and the final intraoperative X-Ray scan, as described previously 1, 30, 31. X coordinates: laterality relative to the midline. Z coordinates: depth relative to the AC-PC line. Y coordinates: anteriority relative to the anterior border of PC. By convention, DBS contacts are labelled contacts 0,1,2,3 on the right side and contacts 4,5,6,7 on the left side. P1 P1 P1 P1 P2 P2 P2 P2 P3 P3 P3 P3 P4 P4 P4 P4 P5 P5 P5 P5 P6 P6 P6 P6 P7 P7 P7 P7 Left Left Right Right Left Left Right Right Left Left Right Right Left Left Right Right Left Left Right Right Left Left Right Right Left Left Right Right DBS contact 5 6 1 2 6 7 1 2 6 7 1 2 6 7 2 3 5 6 0 1 5 6 2 3 5 6 1 2 X (mm) 9,24 9,82 -8,89 -9,62 9,75 10,50 -8,89 -9,62 9,36 10,12 -10,09 -10,64 9,35 9,91 -10,84 -11,59 9,59 10,41 -8,15 -8,89 7,66 8,22 -10,84 -11,78 9,39 9,88 9,22 9,63 Y (mm) 10,85 12,10 9,30 10,62 12,58 13,55 9,30 10,62 10,40 11,36 11,60 12,75 12,37 12,74 12,37 12,74 13,68 14,37 8,18 9,30 11,41 12,48 13,13 14,20 11,19 12,48 11,58 12,79 Z (mm) -3,22 -1,32 -3,22 -1,70 -1,87 0,11 -3,22 -1,70 -1,64 -0,04 -3,31 -1,67 -3,39 -1,37 -3,39 -1,37 -3,55 -1,90 -4,71 -3,22 -4,21 -2,50 -2,70 -1,00 -3,49 -1,87 -3,74 -2,06 3. Figure S1 Figure S1. Final DBS electrode location superimposed on the preoperative MRI of each patient. Yellow spheres: individual DBS contacts. RN: red nucleus; GP: globus pallidus; SN: Substantia Nigra; CD: caudate nucleus; STN: subthalamic nucleus.