kingdom_protista
advertisement

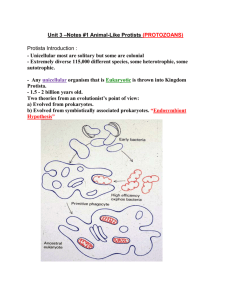
Biology 112 • Includes more than 200,000 species • Easier to classify protists by what characteristics they don’t possess • It is not a plant, animal, fungi, or prokaryote • They are eukaryotic cells that contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles • They are mainly unicellular but are also multicellular • They were the first eukaryotic organisms on Earth • Appeared nearly 1.5 billion years ago • Probably evolved from a symbiosis of several cells • • • • One possible way is how they obtain their nutrition Heterotrophs are animal-like protists Autotrophs are plant-like protists External digesters (decomposers and parasites) are fungus-like protists • A shortcoming of this classification is that it does not reflect their evolutionary history • Classified according to their movement • Zooflagellates (Phylum Zoomastigina) • Possess flagella, which are whip-like structures used for movement through water • May have one to many flagella • Absorb food through their cell membranes • Reproduce asexually by mitosis and cytokinesis or sexually though meiosis where two organisms fuse together and produce a new organism with a recombination of genetic material • Sarcodines (Phylum Sarcodina) • Possess temporary cytoplasmic projections called pseudopods for both movement and feeding • Most common example are amoeba • Cytoplasm moves into the pseudopods and propels the organism forward • Amoeboid movement • Encapsulate their food and form a food vacuole • digested food is used by the cell and undigested remains in vacuole until it can be eliminated • Reproduce by mitosis and cytokinesis • Ciliates (Phylum Ciliaphora) • Contain cilia, short hair-like structures similar to flagella used for movement and feeding • Found in both salt and fresh water • Most are free-living and do not exist in symbiotic relationships • Paramecium are the most common ciliates • They contain trichocysts below their surface • Stiff projections that can be released which will protect the cell • Possess two nuclei – macronucleus and micronucleus • Macronucleus contains exact copies of genetic information responsible for daily function • Micronucleus contains a reserve copy of all the cell’s genes • Sweep food with cilia into a gullet, an indentation on the side of the organism • Food gets trapped and absorbed into a food vacuole • Waste material gets fused with an anal pore • Water moves into the organism through osmosis • Excess water moves into contractile vacuoles which is then expelled by the organism • Most reproduce asexually through mitosis and cytokinesis • While experiencing an external stress, may reproduce by conjugation • Two organisms fuse together and exchange genetic information once they undergo meiosis • This is not technically reproduction since no new organisms are produced • Only new combination of genetic material occurs • It is referred to as a sexual process instead • Sporozoans (Phylum Sporozoa) • • • • Do not move on their own and are parasitic Found in many different organisms Many times, they have more than one host They reproduce by sporozoites