Protista 1
advertisement

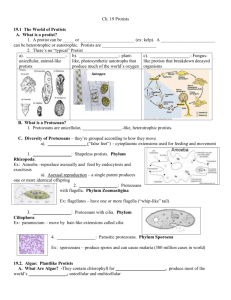
The most diverse eukaryotes… Techno Protists Some vocab before we start… Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Some vocab before we start… Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Pro = before Eu = good/true Karyo = nucleus Karyo = nucleus Lack a nucleus Has a nucleus Does not have membrane Has membrane bound bound organelles Eg. Monerans - bacteria organelles Eg. Plant and animal cells Unifying Characteristics Eukaryotic Most are unicellular and microscopic (some are colonial) Most reproduce asexually (binary fission) Lives in almost any environment that contains water Move in a variety of ways Obtain food in a variety of ways How do protists obtain food? Autotroph Heterotroph Saprotroph • Auto = self • Hetero = other • Troph = nutrition • Using light energy • Ingest organic or inorganic substances that chemicals to will be broken make its own food down for energy • Sapro = decaying E.g. algae (photoautotroph) E.g. slime molds E.g. amoeba, paramecium • Absorbs nutrients from decaying organic matter As they are presented in our textbooks… 3 Categories of Protists Plant-like Protists Animal-like Fungi-like Protists Protists (Protozoa) 1. Euglenophyta 1. Sarcodina 1. Slime molds 2. Chrysophyta 2. Mastigophora 2. Water molds 3. Pyrrophyta 3. Ciliophora 4. Sporozoa Mnemonic Time! Plant-like Protists contain chlorophyll and carry out photosynthesis commonly called algae four phyla: euglenophytes, chrysophytes, diatoms, dinoflagellates accessory pigments help absorb light, give algae a variety of colors Phylum Euglenophyta Eugleno = good eye / Phyta = plant Single cells One or more flagella No cell walls Elastic layer called the pellicle Has chloroplast Autotrophic (photosynthesis) but becomes heterotropic in the absence of light E.g. – Euglena (euglenoid flagellates) Phylum Chrysophyta Chrys = gold / Phyta = plant Single cells or grouped (colonies) Motile and free floating Cell walls (often with silica) Chlorophyll and yellow pigment in plastids Food stored as oil or complex carbohydrates E.g. golden algae and diatoms Phylum Pyrrophyta Pyrro = fire / phyta = plant Single cells with 2 flagella Thick cell wall Chlorophyll and other pigments in plastids Food stored in starch or oil Causes “red tide” E.g. - dinoflagellates Flagella Animal-like Protists (PROTOZOA) No cell wall Heterotrophic (free living or parasitic) Classified according to means of locomotion into 4 phyla Phylum Sarcodina Sarco = flesh Locomotion by protoplasmic extensions called pseudopodia Many with shells Reproduces by fission Can become cysts when in harsh conditions E.g. amoeba, foraminifera Phylum Ciliophora Cilio = eyelash / phora = bearing Locomotion by beating of cilia Cilia also help in feeding Has a macronucleus and micronucleus Reproduces by binary fission or conjugation E.g. paramecium, vorticella, and stentor Phylum Sporozoa Sporo = seed / Zoa = animal Lack locomotive structures Lack contractile vacuoles Mostly parasitic Have sexual and asexual life cycle stages and may infect multiple hosts e.g. plasmodium (malaria) Phylum Mastigophora Mastigo = whip / phora = bearing Locomotion by flagella Absence of chlorophyll Parasitic and saprophytic E.g. trypanosoma (sleeping sickness) 9 m Kingdom Protista – The Protists Homework 1. Read front page of coloring sheet “Introduction to Protozoans” and color protozoans on back side. 2. Memorize names of 7 Phyla in Protista and know the literal translation of their phylum name. Entry Slip next class on reading content AND phylum names. REMINDER: DISEASE PROJECTS DUE NEXT CLASS!!!`