the nervous system - Dominican
advertisement

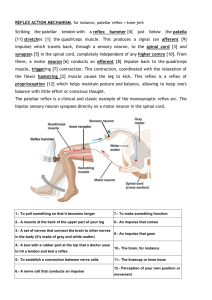
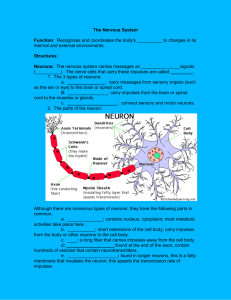
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The Nervous System Central Nervous Peripheral Nervous System System Brain Spinal cord Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Ganglia Neuron = Nerve cell • Sensory Neuron (afferent) • Carry electrical impulses from sense organs to the C.N.S • Cell body is outside C.N.S in ganglia • Motor Neuron (efferent) • Carry electrical impulses from the C.N.S to effector (muscle/Gland) • Cell body inside C.N.S Interneurons • Occur in the C.N.S only • May connect sensory to motor neurons Direction of impulse Diagrams • Draw diagram of sensory neuron and interneuron into notes Functions of parts • Dendrites – receive information and carry electrical impulses towards the cell body • Axons – carry impulses away from a cell body • Cell body – contains a nucleus and it forms neurotransmitter chemicals • Myelin sheath – is a fat rich material that insulates electrical impulses • Schwann cells – form myelin sheath • Neurotransmitter swellings (vesicles) – produce neurotransmitter chemicals. • Dendron – brings impulse to the cell body • Nodes of Ranvier – are gaps in the myelin sheath. Electrical impulse ‘jumps’ from one gap to the next Speeds up transmission of impulse Stimulus • A change in the neurons environment that, if strong enough, will generate an impulse e.g. red light at traffic lights Movement of an Impulse • Impulses travels along an neuron in the form of an electrical impulse • In order for the impulse to travel it is necessary for ions to move in and out of dendrites and axons • The movement of ions requires energy in the form of ATP Threshold level • The minimum intensity of stimulus needed to generate an impulse • It does not matter if the stimulus is above the required strength the same message is sent • Message sent in all neurons is the same All or nothing Law – an impulse is only generated if the stimulus is at or above the threshold. Functions of parts • Cerebrum – major sensory and motor control, language, memory, intelligence and consciousness. • Cerebellum – muscle co-ordination, movement and balance. Functions of parts • Medulla oblongata – regulates breathing and heart rate. • Hypothalmus – overall body homeostasis osmoregulation, temperature control regulates hormone secretion by the pituitary gland. • Pituitary gland – master gland - secretes 8 hormones which control other glands in the body The Spinal Cord • Bones of the backbone enclose the spinal cord. It carries impulses to and from the brain. • It is also involved in many reflex actions T.S. of spinal cord Functions of parts • The Meninges – are membranes that surround (the brain) and Spinal cord. • Spinal nerves – 31 pairs of spinal nerves carry impulses to and from the spinal cord. • Dorsal root – carries impulses into the spinal cord along sensory neurons. • Ganglion – (pl. Ganglia) located on the dorsal root is a swelling that contains cell bodies of sensory neurons Functions of parts • White matter – contains axons • Grey matter – contains cell bodies and dendrites. • Central canal – contains cerebrospinal fluid. • Ventral root – contains motor neurons that carry impulses out of the spinal cord Reflex Action A reflex action is an automatic, unconscious or involuntary response to a stimulus. The brain is NOT involved in reflex actions Examples – knee jerk reaction, blinking for protection, raising your hands when falling Significance/Benefit allows faster responses than normal REFLEX ACTION --- The Reflex Arc The path of a reflex action • The path taken by a reflex action is called a reflex arc. Example : Dropping a hot object Receptors in finger detect hot object Impulse travels along sensory neuron to spinal cord Impulse travels into spine via dorsal root In the spinal cord the impulse splits The path of a reflex action (a) It crosses a synapse onto an interneuron (b) It crosses another synapse and passes on up to the brain. From the interneuron the impulse crosses another synapse and travels out of the ventral root along a motor neuron The motor neuron connects to a muscle to a