Skeletal, Muscular, Integumentary and Nervous Systems
advertisement

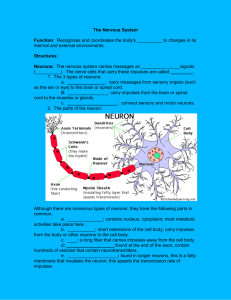
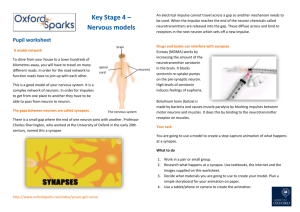
Skeletal, Muscular, Integumentary and Nervous Systems Quiz Study Guide Textbook Chapters 32-33 Review Book Topic 1 Skeletal System What is the difference between compact and spongy bone Compact – strength and support, solid Spongy – production of RBCs and fat storage, full of air pockets, “bone marrow” What does red bone marrow produce? Yellow bone marrow? Red blood cells Fat What are the five functions of bones? Protection, support, movement, red blood cell production, fat storage As a fetus, what were your bones made of? Cartilage What type of chemical is released when you break a bone to act as a natural pain killer? What else happens when you break a bone? Endorphins are released by the body as pain killers, blood clots form, site swells, cartilage forms at break, gradual ossification into bone What is a joint? Where two bones meet Are all joints moveable? No What is a ligament? Attaches two joints together What are the five types of joints we talked about? Know examples for each Ball and socket – hip, hinge – knee, gliding – wrist, suture – skull, pivot - neck Which joint has the widest range of movement? Ball and socket Which joint is not moveable? Where is it found in your body? Suture - skull Muscular System What is a tendon? Tissue connecting muscle to bone What are the three main types of muscle? Where do you find these types within your body? Skeletal – moves bones, cardiac – heart, smooth – organs: skin, stomach, uterus Which muscle types are involuntary? Cardiac and smooth Which muscle types are striated? What does striated mean? Cardiac and skeletal Has light and dark bands on muscle Majority of muscles in your body are what type? Skeletal Integumentary System What is the main organ of this system? Skin What are the four main tissues of this system? What are their functions? Muscular (movement), nervous (communication), connective (support/protection), epidermal (covers body) What are the functions of the system? Temperature regulation, vitamin production, sense organ, protection What are the two layers of skin? Epidermis, dermis What is keratin? Melanin? Waterproofing protein pigment protein which absorbs sunlight Nervous System What is a neuron? Specialized cell for communication Know the parts and functions of a neuron (be able to label a diagram) Dendrite – accepts impulse Cell body – contains nucleus and other cell organelles, helps pass impulse along Axon – extension off cell body which impulse travels down Terminal branches – contains synaptic knobs Synaptic knobs – impulse is released here across the synapse to another neuron Myelin sheath – layer of fat that insulates the axon to prevent losing impulses Synapse – space between two neurons where neurotransmitters are used to pass an impulse from the terminal branches of one neuron to the dendrites of another What are the three types of neurons? What are their functions? Where are they found in the body? Sensory – detects changes in the environment using your senses, found attached to sense organs Interneuron – passes impulses to brain/spinal cord and then onto motor neurons, found throughout the body connecting sense organs to brain/spinal cord and then back to muscles/glands Motor neurons – passes impulse to muscles or glands to respond to a stimulus, found attached to muscles or glands Describe a reflex arc. Does it involve the brain or the spinal cord? Voluntary or involuntary? Stimulus sensory neuron interneuron spinal cord interneuron motor neuron response Involuntary, does NOT involve the brain What is an impulse? A stimulus? What is a synapse? A neurotransmitter? Gap between neurons chemical which diffuses across the synapse and transmits the impulse to another neuron What are the two divisions of the nervous system? What parts of the body do they include? Stimulus – change in the environment which is detected using your senses (ex, pressure, temp change, etc.) Impulse – chemical/electrical message which is created as a result of the detection of a stimulus by a sensory neuron Central NS – brain and spinal cord Peripheral NS – all nerves that branch off of spinal cord throughout the body What are the functions of the following parts of the brain: cerebrum, cerebellum, medulla oblongata, pons, brain stem, hypothalamus, spinal cord Cerebrum – thought, senses, voluntary motor control, memory, language, etc. Cerebellum – coordination and muscle control Medulla oblongata (part of brain stem)– heart rate, breathing Pons (part of brain stem)- breathing Hypothalamus – fear, aggression, regulating homeostasis, water balance, temperature control, etc. Spinal cord – bundle of nerves, communication/relay of messages to/from brain to body What is the difference between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems Somatic – voluntary nerves, motor/sensory Autonomic – involuntary nerves, organs (heart contraction, uterus contraction, etc)