The Nervous System
advertisement

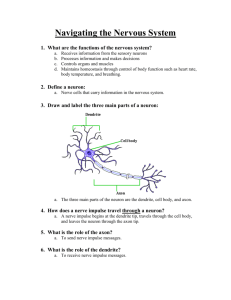
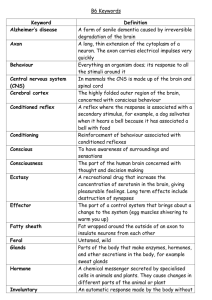
The Nervous System Function: Recognizes and coordinates the body's __________ to changes in its internal and external environments. Structures: Neurons: The nervous system carries messages as _______________ signals (__________). The nerve cells that carry these impulses are called _________. 1. The 3 types of neurons: a. _______________: carry messages from sensory organs (such as the ear or eye) to the brain or spinal cord. B: ________________: carry impulses from the brain or spinal cord to the muscles or glands. c. ____________________: connect sensory and motor neurons. 2. The parts of the neuron: Although there are numerous types of neurons, they have the following parts in common: a. ______________: contains nucleus, cytoplasm; most metabolic activities take place here. b. ___________: short extensions of the cell body; carry impulses from the body or other neurons to the cell body. c. ____: a long fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body. d: ___________________:found at the end of the axon; contain hundreds of vesicles that contain neurotransmitters. e. ____________________: found in longer neurons, this is a fatty membrane that insulates the neuron; this speeds the transmission rate of impulses. Nerve impulse: 1. The nerve at rest: the neuron has a net ________ charge outside the cell and a net _____________ charge inside the cell. This is caused by the active transport of ions across the cell membrane. The cell pumps Na+ out of the cell and K+ ions in (the sodium-potassium pump). This causes a higher concentration of K+ in the cell and a lower concentration of Na+ out. The cell membrane allows more K+ to leak out of the cell which produces a negative charge on the inside. This electrical charge is known as the ______________________. 2. The moving impulse: neurons stay at rest until a ________ (from the environment or another neuron) starts a nerve __________. This causes ions to move across the membrane. The impulse moves from the cell body to the axon terminals. This causes a reversal in the charges along the membrane (see transparency). The cell membrane of the neuron contains numerous protein channels that allow ions to move through it. As an impulse moves along a neuron, these channels open, allowing Na+ ions in. This switches the charges of the membrane... the inside becomes positive while the outside becomes negative. This reversal of charge is called the __________________________. Once the impulse passes, potassium gates open allowing K+ out. This restores the resting potential. 3. Threshold: the threshold is the _______ level of stimulus to activate a neuron. A stimulus that is lower than the threshold will not produce an impulse. 4. The synapse: the impulse arrives at the end of the neuron, the axon terminal. Here it passes the impulse to another cell, such as a muscle cell. The location at which a neuron can transfer an impulse to another cell is called the______________. The axon terminal contains vesicles filled with _______________________, chemicals that transmit an impulse from one cell to another. Types of neurotransmitters: a. ____________: functions include learning, sleep, and control of mood. It is similar to drugs that cause mental aberrations such as LSD; ________________ has been linked to low levels of serotonin. b. ____________: stimulates muscles; some poisons block its transmission; nerve gas breaks it down. c. ________________: increases heart rate and blood pressure in response to short term stress (activates “fight or flight”); low levels associated with _______________. d. _________________: high levels are associated with ___________________. Divisions of the Nervous System: 1. _____________________________________: a. Functions: relays _____________, processes information, and analyzes information. b. Structures: composed of the ______, __________, _________ (connective tissue covering the brain and spinal cord), _____________________ (fluid that bathes brain and spinal cord; acts as shock absorber; allows for nutrient and waste exchange). 1. The ________: composed of 100 _________ neurons. a. cerebrum: largest region; responsible for voluntary activities, intelligence, learning , and judgment; divided into left and right hemispheres connected by tissue called the _____________. Each hemisphere deals mainly with the opposite side of the body (left hemisphere controls right side of body); right hemisphere associated with creativity and artistic ability; left hemisphere associated with analytical skills and mathematical ability. Composed of two layers: gray matter (cerebral cortex) that processes information and controls body movement; white matter that connects the cerebral cortex to the brain stem. b. __________________: coordinates and balances muscle movement to allow for grace and efficiency. c. ____________: connects the brain to the spinal cord; composed of the pons and the medulla oblongata; controls functions such as blood pressure, heart rate, breathing and swallowing. d. __________: receives sensory information and relays it to cerebrum for processing. e. ______________: control center for recognition of hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger and body temperature; controls the coordination of the nervous and endocrine systems. 2. The ________________: major link between the brain and the body; ___ pairs of nerves branch from it to the rest of the body; many ______ (quick, automatic response such as sneezing or blinking) are processed directly in the spinal cord. 2. The ___________________________________: A. Composed of: 1. the ________ and supporting cells that are not part of the brain and spinal cord. 2. May be divided into two parts: a. _________: sends impulses from sense organs to CNS. b. ________: sends impulses from CNS to muscles or glands; May be divided into ______________ nervous system (conscious control): example: stepping on sharp object →sensory neuron→spinal cord→motor neuron causing foot to pull away from object. This is called a ____ _____. The second division is called the __________ nervous system: regulates automatic or involuntary activity such as heart rate or contraction of the smooth muscle in the digestive system. The autonomic nervous system slows activity with the _____________________ nervous system and increases activity with the _____________________ nervous system.