Nile River Basin – Case Study
advertisement
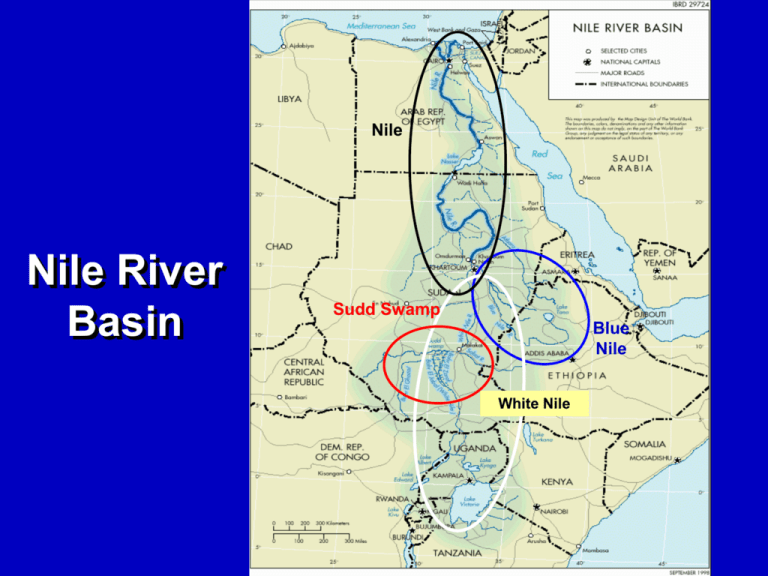
Nile Nile River Basin Sudd Swamp Blue Nile White Nile Basin Population Eritea 1% • Ten Riparian States – – – – – – – – – – Egypt Sudan Ethiopia Uganda Rwanda Tanzania Kenya D.R. Congo Eritrea Burundi Burundi 2% Congo 16% Egypt 22% Kenya 9% Tanzania 10% Rwanda 2% Sudan 11% Uganda 7% Ethiopia 20% Issues in the Nile Basin Ethiopia Egypt •Generates 85% water reaching Egypt’s Aswah Dam •96% of population live in Nile Sudan •Second most populated Delta/Basin riparian statein Basin •60% of Land Mass •Entirely dependent on Nile waters – •“The Single most important Swamp – Evap loss of Only•Sudd 4% from underground reserves strategic interest striving 50% of all Wateris in Whiteto attain food in a •Considered thesecurity most powerful Nile chronically famine-prone riparian state in basin region…and scenarios •Civil all war [involve] more intense use of •Historically always sided the western Nile watershed” Waterbury with Egypt in Nile Issues Unique Issues to Nile Basin • Historic precedence – Colonial and Egyptian control • Egypt and Northern Sudan do not contribute to water generation in the Nile • Majority of the riparian states became independent nations since the 1960’s • Political and economic basis weak International Agreements • 1899 Anglo-Egyptian – No water withdrawn upstream of Egypt without Egyptian and British consent • 1929 – Egyptian and British Agreement – British represented Kenya, Tanzania and Sudan – 93% water of Nile allocated to Egypt, 7% to Sudan – All upstream projects approved by Egypt • 1959 – Egypt and Sudan – 75% to Egypt, 25% to Sudan – Rejected by all of the other riparian states when they became independent Water Allocation in the Basin 1959 Allocation Agreement between Egypt and Sudan Sudan 25% Egypt 75% Riparian States Interests • Status Quo – Egypt – Uganda • New Allocations – Ethiopia – Sudan – Eritrea • Indifferent – Kenya, Tanzania, Congo, Rwanda, Burundi How do you allocate the water in the Nile? Beaumont’s Proposal 50/50 Historical/Generation 80000 Million Cubic Meters/Year 70000 Proposed Allocation 60000 Current Proposed Allotment 50000 Sudan 27% 40000 30000 20000 10000 Ethiopia 44% 0 Egypt Ethiopia Sudan Egypt 29% Brichier-Colomba (1996) 33% weight to each factor Population of Riparian’s country in Basin 80000 70000 Riparian's Area of Basin Million Cubic Meters/Year 60000 50000 Current Allotment Proposed Allotment Average amount of water used 40000 30000 Sudan 27% 20000 10000 Egypt 54% 0 Egypt Ethiopia Sudan Ethiopia 19% What factors should be considered for allocations in the Nile Basin? Waterbury’s Criteria Equal Weighting for each factor • Ratio of water flowing across a riparian's border to the total discharge of the watercourse • Proportion of the ripairan's total population living in the basin • Total amount of irrigable land that could be farmed with watercourse water without extra-basin transfers • Amount of alternative, utilizable water available in aquifers, regionally appropriate rainfall and stored water (deductions) • Basin needs per capita to protect life and basic health • Allocation necessary to protect existing wetlands and ecosystems What’s Happening in the Basin? Recent History of Cooperation • 1992 – Council of Ministers of Water Affairs (Nile-COM) – All riparian states represented • 1995 – Nile River Basin Action Plan – Cooperative framework for management of the Nile – Endorsed by all riparians • 1997 – World Bank agrees to play a lead role in coordinating external finances • 1997 – Egypt announces (unilaterally) New Nile Valley Development • 1998 – NBI Shared Vision Plan developed • 1999 – Nile Basin Initiative formally established Nile Basin Initiative • Goal: – Achieve sustainable socioeconomic development through the equitable utilization of, and benefit from the common resources • Objectives: – Develop water resources in a sustainable and equitable way to ensure prosperity, security and peace for all its people – Ensure efficient water management and optimal use – Ensure cooperation and joint action between states – Target poverty eradication and promote economic integration – Ensure the program results in a move from planning to action Recent Developments, cont. • 2001 – Sub-Basin agreements between Egypt, Sudan and Ethiopia – Agreement to build dams and expand irrigation within Ethiopia with the plan to sell power to Sudan and Egypt • Sept. 28, 2005 – Largest ever dam to be built in Ethiopia at Kara Dobe on the Awash River with Sudan and Egypt providing financial support Questions • How did colonialism influence the development of water resources in the Nile basin? • What factors impinge on the reaching agreement among the Nile River Riparian nations? • Beaumont (2002) proposes a water allocation scheme to fit the “equitable and reasonable” call in the 1997 UN Convention on a 50% generation/50% historical split. Is this is applicable to the Nile River Basin? • The Nile Basin Initiative did not start with specific water projects, but rather education, development of skilled personnel and inclusiveness of all stakeholders. Will this work?