Lecture 1 Title: MIS Concept and Definition
advertisement

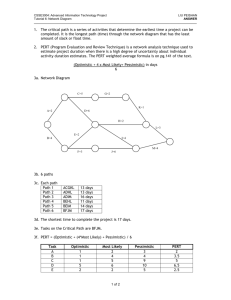
Lecture 5 Title: Project Time Management By: Mr Hashem Alaidaros MIS 434 Main Points Activity Definition Project Network Diagrams Activity on the Node (AON) Critical Path Analysis Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) Precedence Diagramming Method (PDM) Lead and Lag Time Activity Resource Estimation Activity Duration Estimation Schedule Management Introduction Project time management is often cited as the main source of conflict on projects, and most IT projects exceed time estimates. Some people prefer to follow schedules and meet deadlines while others do not. Different cultures and even entire countries have different attitudes about schedules. Project Time Process Management Activity definition: Identifying the specific activities that the project team members and stakeholders must perform to produce the project deliverables. Activity sequencing: Identifying and documenting the relationships between project activities. Activity resource estimating: Estimating how many resources a project team should use to perform project activities. Activity duration estimating: Estimating the number of work periods that are needed to complete individual activities. Schedule development: Analyzing activity sequences, activity resource estimates, and activity duration estimates to create the project schedule. Schedule control: Controlling and managing changes to the project schedule. Project Planning Framework Activity Definition An activity or task is an element of work normally found on the WBS that has an expected duration, a cost, and resource requirements. Project schedules grow out of the basic documents that initiate a project. The project charter includes start and end dates and budget information. The scope statement and WBS help define what will be done. Activity definition involves developing a more detailed WBS and supporting explanations to understand all the work to be done, so you can develop realistic cost and duration estimates. Activity list and Attributes An activity list is a tabulation of activities to be included on a project schedule. The list should include: The activity name An activity identifier or number A brief description of the activity Activity attributes provide more information about each activity, such as predecessors, successors, logical relationships, leads and lags, resource requirements, constraints, imposed dates, and assumptions related to the activity. Activity Sequences Involves reviewing dependencies. activities and determining A dependency or relationship relates to the sequencing of project activities or tasks. You must determine dependencies in order to use critical path analysis. Activity on the Node (AON) Activity Description Estimated Duration (Days) Predecessor A Evaluate current technology platform 2 None B Define user requirements 5 A C Design Web page layouts 4 B D Set-up Server 3 B E Estimate Web traffic 1 B F Test Web pages and links 4 C,D G Move web pages to production environment 3 D,E H Write announcement of intranet for corp. newsletter 2 F,G I Train users 5 G J Write report to management 1 H,I AON Network Diagram Possible Activity Paths on AON Possible Paths Path Path 1 A+B+C+F+H+J 2+5+4+4+2+1 Path 2 A+B+D+F+H+J Total 18 17 Path 3 2+5+3+4+2+1 A+B+D+G+H+J 2+5+3+3+2+1 16 Path 4 A+B+D+G+I+J 19* Path 5 2+5+3+3+5+1 A+B+E+G+I+J 17 2+5+1+3+5+1 * The Critical Path Critical Path A Critical Path (CP) for a project is the series of activities that determines the earliest time by which the project can be completed. The CP is the longest path through the network diagram and has the least amount of slack or float. Slack (or float) is the amount of time an activity can be delayed before it delays the project The CP must be monitored and managed! Project manager can expedite or crash by adding resources Fast tracking – running activities in parallel which were originally planned as sequential The CP can change If one or more of the activities on the critical path takes longer than planned, the whole project schedule will slip unless the project manager takes corrective action. Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) PERT is a network analysis technique used to estimate project duration when there is a high degree of uncertainty about the individual activity duration estimates. PERT uses probabilistic time estimates: Duration estimates based on using optimistic, most likely, and pessimistic estimates of activity durations, or a three-point estimate. PERT analysis Activity Predecessor Optimistic Estimates (Days) Most Likely Estimates (Days) Pessimistic Estimates (Days) Expected Duration (a+4b+c) 6 A None 1 2 4 2.2 B A 3 5 8 5.2 C B 2 4 5 3.8 D B 2 3 6 3.3 E B 1 1 1 1.0 F C,D 2 4 6 4.0 G D,E 2 3 4 3.0 H F,G 1 2 5 2.3 I G 4 5 9 5.5 J H,I .5 1 3 1.3 Possible Paths on PERT Possible Paths Path Total Path 1 A+B+C+F+H+J 18.8 2.2+5.2+3.8+4.0+2.3+1.3 Path 2 A+B+D+F+H+J 18.3 2.2+5.2+3.3+4.0+2.3+1.3 Path 3 A+B+D+G+H+J 18.6 2.2+5.2+3.3+3.0+2.3+1.3 Path 4 A+B+D+G+I+J 20.5* 2.2+5.2+3.3+3.0+5.5+1.3 Path 5 A+B+E+G+I+J 18.2 2.2+5.2+1.0+3.0+5.5+1.3 * The Critical Path Precedence Diagramming Method (PDM) Relationships Task B cannot start before A finishes Task B cannot start before A starts Task B cannot finish before A finishes Task A cannot start before B finishes Lead and Lag Times Lead is starting the next task before the first task is complete Example: Begin installing the operating systems when half of the PCs are set up Lag (or negative lead) is the adding of a buffer of time before the next task begins Example: Once the walls have been painted, wait one day before laying the carpet so that the walls have had a chance to dry Activity Resource Estimation Before estimating activity durations, you must have a good idea of the quantity and type of resources that will be assigned to each activity. Consider important issues in estimating resources: How difficult will it be to complete specific activities on this project? What is the organization’s history in doing similar activities? Are the required resources available? Activity Duration Estimation Duration includes the actual amount of time worked on an activity plus the elapsed time. Effort is the number of workdays or work hours required to complete a task. Effort does not normally equal duration. People doing the work should help create estimates, and an expert should review them. Schedule Development The project’s schedule can be determined based upon the tasks and time estimates in the WBS The schedule will also depend on how these activities are sequenced Ultimate goal is to create a realistic project schedule that provides a basis for monitoring project progress for the time dimension of the project. Project Management Tools Gantt Charts Project Network Diagrams Activity on the Node (AON) Critical Path Analysis Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) Precedence Diagramming Method (PDM) Project Schedule The project schedule and budget may require several iterations before it is acceptable to the sponsor, the project manager, and the project team. Once the project schedule and project plan are accepted, the project plan becomes the baseline plan. Once accepted, the project manager and project team have the authority to execute or carry out the plan. Schedule Control Goals are to know the status of the schedule, influence factors that cause schedule changes, determine that the schedule has changed, and manage changes when they occur. Tools and techniques include: Progress reports. A schedule change control system. Project management software, including schedule comparison charts, such as the tracking Gantt chart. Variance analysis, such as analyzing float or slack. Performance management, such as earned value. Free MS Project Tutorial http://www.profsr.com/msproject/msproj01.htm http://office.microsoft.com/en- us/training/FX100565001033.aspx http://www.project-blog.com/