March 20 - Axis determination in frog embryos
advertisement

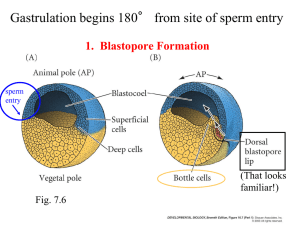
Axis determination in frog embryos How are embryonic axes set up? What signaling events regulate embryo development? Time-lapse videos of Xenopus gastrulation: By David Shook : http://faculty.virginia.edu/shook/ShowMovies/index.htm By Mike Danilchik: http://worms.zoology.wisc.edu/frogs/gastxen/gastxen_sagview.html Overview of frog gastrulation Future Ventral Side (belly) Sperm entry in animal hemisphere Future Dorsal side (back) Vg1 mRNA (in situ hybridization) A 3’ UTR sequence element localizes Vg1 mRNA i) Inject RNA molecules into oocyte ii) Isolate animal and vegetal RNAs iii) Northern blot using Vg1 probe (From Mowry and Melton (1992) Science 255: 991-993) A 3’ UTR sequence element localizes Vg1 mRNA (depends on microtubules, mRNA-binding proteins) (From Mowry and Melton (1992) Science 255: 991-993) Sperm entry provides the asymmetric cue to set up the dorsal-ventral axis of Xenopus embryos Cortical rotation requires the microtubules – may be nucleated by the centriole delivered by sperm. UV irradiation on vegetal side prevents cortical rotation. No dorsal axis forms, no gastrulation occurs. Embryo is ventralized. Rotate zygote in a new plane at time of first cleavage: two blastopores form Rotated zygotes after gastrulation and hatching Rotate zygote in a new plane at time of first cleavage: two blastopores form Prevent normal cortical rotation by UV-irradiating vegetal side of zygote: No dorsal axis or gastrulation Cortical rotation creates asymmetry of cytoplasm Asymmetric cell divisions – a general way to create distinct cell fates in daughter cells. (Relies on asymmetry in mother cell = cell polarity) Fate map of late blastula Are cell identities determined (in developmental sense) as shown in the fate map? Experimental test of specification. Specification map: shows what the cells have been instructed to become early Explant early blastula tissues: don’t get mesoderm Transplanting dorsal vegetal cells restores axis formation in embryos from UVirradiated embryos (32-64 cell stage) Figure 10.11 Transplanting dorsal vegetal cells to the ventral vegetal side causes a second axis to form Transplant organizer just before gastrulation Transplanted organizer Mesoderm induction ~64-cell stage late blastula Signals 3 and 4 induce further specialization of mesoderm cells. Additional signaling events act at later stages. Different parts of the dorsal mesoderm signal differently Source of transplant: Anterior mesoderm Posterior mesoderm Dorsal blastopore lip signals differently at different times (Actually different cells at different times) Transplanting presumptive epidermis Transplant presumptive neural ectoderm Transplant later, get different result: Cells have become determined (or, perhaps an epidermal signal is missing later).