PNS Study Guide: Discussion 2 1. Organize the following
advertisement

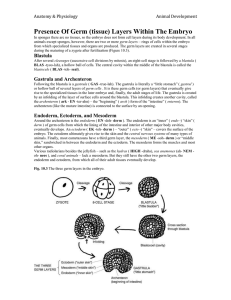
PNS Study Guide: Discussion 2 1. Organize the following developmental events in correct chronological order: fertilization, neurulation, blastulation, gastrulation. Define each. 2. What informational axis of a developing embryo is intrinsically set in the egg, pre-fertilization? How is this accomplished? 3. What is polyspermy, and how is it prevented after fertilization? 4. The site of sperm entry determines the (Dorsal / Ventral) pole of the developing blastula. 5. Organize the following developmental events/structures in the correct chronological sequence: (Nieuwkoop Center, cortical rotation, Spemann Organizer, sperm entry) 6. What is the grey crescent, and what major portion of the developing blastula does it ultimately become? 7. What structure determines the anterior/posterior polarity of the blastula? 8. Label each of the following tissues/cells with their germ layer of origin: Ectoderm, Mesoderm, or Endoderm. Neurons __________ Intestinal Epithelia __________ Vertebrae__________ Astrocytes __________ Blood __________ Cardiac muscle __________ Epidermis __________ Kidney __________ 9. The Spemann organizer is located at the (dorsal / ventral) lip of the blastopore. 10. Which two germ layers involute during gastrulation? 11. Draw a representative blastula and gastrula representing the positions of the germ layers before and after this involution. 12. How does the ectoderm that is apposed against the interior mesoderm ultimately differ from ectoderm that has no contact with the mesoderm after gastrulation? 13. What are diffusible morphogens and how do they regulate cell fate on a molecular level? 14. The “default” fate of neuroectodermal cells is (neuronal / epidermal) lineage. 15. Chordin/Noggin/Fallistatin ( activate / inhibit ) BMP-4, which (induces / prevents) neuronal cell fate. 16. BMP-4 is secreted by (neuroectodermal / mesodermal) cells, while chordin/noggin/fallistatin are secreted by (neuroectodermal / mesodermal) cells. 17. What family of transcription factors operate downstream of transforming growth factor (TGF) morphogens? 18. What germ layer gives rise to the notochord? 19. Neural crest cells ultimately give rise to the (central / peripheral) nervous system, and originate from the (medial / lateral) most cells of the neural plate. 20. Formation of the neural floor plate is induced by what structure? 21. What is cephalization? On which end (anterior / posterior) of the neural tube does it occur? What does the other end become? 22. The lumen of the neural tube eventually becomes what anatomical region in the brain? 23. What does it mean to say that the cortex has a “laminar” structure? 24. The newest born neurons during development are found apposed to the (ventricular / pial) surface of the brain. 25. What are Bergmann Glia and what purpose do they serve during cortical development?