Cellular-Structure2
advertisement

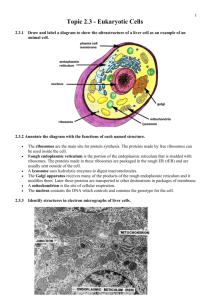
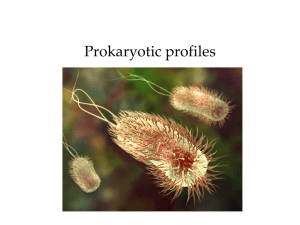
Cellular Structure Chapter 4 Eubacteria Eukarya Archaea Monera (defunct) Eubacteria Eukarya Archaea Animalia Fungi Plantae Protista Bacterial Structure Outwardly, there is little to go by in bacterial structure Bacteria may be of various shapes (morphologies) Coccus = Spherical Bacillus = Rod Spiral = Spiral Pleomorphic = Varied, Undefined On a microscopic level there are layers of structure. Glycocalyx = Outer Coating. Flagella = Motive structures Fimbriae and Pili = Attachment Bacteria are divided into two large groups based on overall cellular structure Gram Positive vs. Gram Negative Gram Identity is about cell structure more than staining Gram Positive = Single Membrane Gram Negative = Double Membrane EXCEPTION Mycobacterium EXCEPTION Mycoplasma Even exceptions to normal Gram staining can be classified by their overall structure and genetics. Internal structure in bacteria is limited, but organized. Specialized internal structures are found in some bacteria. Endospores G+ structure to go dormant. Magnetosomes Magnetite crystals for alignment Storage Granules PHB Energy Storage Eukarya Structure Eukarya externally lack the complexity of Bacteria but are more internally structured There are three classes of organelles. Non-membrane Bound Ribosomes, flagella, etc. Endomembrane System Nuclear Membrane, ER, etc. NonEndomembrane Membrane-Bound Mitochondria and Plastids Non-Membrane Organelles A Note on Evolution Ribosomes Public Domain - PDB Cytoskeleton Endomembrane System Nucleus Cell Nuclei in HeLa Cells Public Domain Image-Wikipedia The Nucleus has numerous functions Contains the DNA of the Cell Controls access to the DNA Regulates division of the DNA Endomembrane System Wikimedia Commons Mitochondria and Plastids Mitochondria Chloroplasts These organelles share a number of unique characteristics Internal DNA Each possess a small circular piece of DNA Ribosomes Each possess ribosomes internal to their structure Binary Fission Both reproduce independent of the cell cycle. Endosymbiotic Theory Aerobic Eubacteria Photosynthetic Eubacteria Protoeukaryote Aerobic Eukaryote Photosynthetic Eukaryote Various lines of evidence support this theory. Organelle ribosomes more closely resemble bacterial ribosomes than eukaryotic ribosomes. DNA of Mitochondria is closely related to Rickettsia bacteria. DNA of Chloroplasts is closely related to blue-green photosynthetic bacteria.