Topic 2.3 - Eukaryotic Cells
advertisement

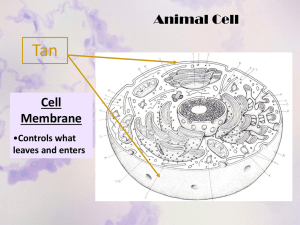
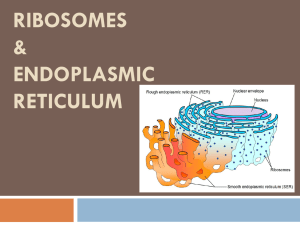
1 Topic 2.3 - Eukaryotic Cells 2.3.1 Draw and label a diagram to show the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell. 2.3.2 Annotate the diagram with the functions of each named structure. 2.3.3 The ribosomes are the main site for protein synthesis. The proteins made by free ribosomes can be used inside the cell. Rough endoplasmic reticulum is the portion of the endoplasmic reticulum that is studded with ribosomes. The proteins made in these ribosomes are packaged in the rough ER (rER) and are usually sent outside of the cell. A lysosome uses hydrolytic enzymes to digest macromolecules. The Golgi apparatus receives many of the products of the rough endoplasmic reticulum and it modifies them. Later these proteins are transported to other destinations in packages of membrane. A mitochondrion is the site of cellular respiration. The nucleus contains the DNA which controls and contains the genotype for the cell. Identify structures in electron micrographs of liver cells. 2 2.3.4 Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells Naked DNA DNA in cytoplasm No mitochondria 70s ribosomes No membrane-bound organelles Smaller cells (Size: 1 - 10 µm ) Eukaryotic cells DNA associated with proteins DNA enclosed in a nuclear envelope mitochondria 80s ribosomes Have internal membranes that compartmentalize functions Larger cells (Size: 2 - 1000 µm ) 2.3.5 State three differences between plant and animal cells. Plant cells contain a cell wall while animal cells do not. Plant cells have chloroplasts while animal cells do not. Most animal cells do not contain large central vacuoles while most plant cells do. 2.3.6 Outline two roles of extracellular components. The plant cell wall contains maintains the cell shape, preventing excessive water uptake and holds the whole plant up against the force of gravity. Animal cells secrete glycoproteins that form the extracellular matrix. This functions in support, adhesion and movement.