Week 10-14 study Guide
advertisement

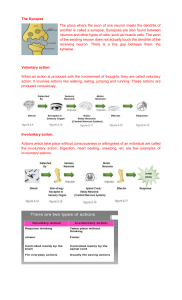
Major Concepts - Describe a neuron and myelin sheath, explaining the formation and transmission of an action potential and the transmission of a signal across a synapse and the main chemicals and transmitters involved. (Textbook Section 13.1 and 13.2) - Label parts of Neuron - Explain function of the parts - Structure and purpose of myelin sheath - Action Potential - how it happens (ion flow) - all or nothing - salutatory conduction - NT (know the main ones and how they affect the synapse) - Identify structures of the central and peripheral nervous systems and explain their functions in regulating the voluntary (somatic) and involuntary (autonomic) systems. (13.1, 13.3, 13.4) - CNS - Structures - Brain (Structure and Function) -PNS - Somatic - Autonomic - Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic - Describe the organization of neurons into nerves and simple reflex arcs. (13.1) - Describe the structure and function of the human eye (ie: cornea, lens, sclera, choroid, retina, rods & cones, pupil, iris, and optic nerve) (14.2) - pathway light travels - accommodation - colour vision - vision problems - Describe the structure and function of the human ear (ie: pinna, auditory canal, tympanum, ossicles, cochlea, organ of Corti, auditory nerve, utricle and saccule, semicircular canals, and Eustachian tube) (14.3) - pathway sound travels - equilibrium - static and dynamic - Explain other ways that human organisms sense their environment and spatial orientation (ie: touch, smell, taste, pressure, balance, etc.) (14.1, 14.3) - Identify the principal endocrine glands of the human organism (15.1, 15.2, 15.3) - The ten from quiz diagram - Describe the function of the hormones of the principal endocrine glands (15.1, 15.2, 15.3, 15.4) - The chart in your notes (*text has more detail on each of those!) - Explain the metabolic roles hormones may play in homeostasis (15.2, 15.3, 15.4, 15.5) - Thyroxine, triiodothyronine, calcitonin, PTH, hGH (main ones) - Explain how the endocrine system allows human organisms to sense their internal environment and respond appropriately. (15.1, 15.2, 15.3, 15.4, 15.5) - how hormones maintain homeostasis - negative and positive feedback -specific examples for hormones - Compare the endocrine and nervous control systems and explain how they act together (ex: stress and the adrenal gland). (15.2, 15.3, 15.5) - Describe, using an example, the physiological consequences of hormone imbalances (ex: diabetes, hyperthyroidism). (15.2, 15.3, 15.4) Vocabulary Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Glial Cell Neuron Dendrite Axon Myelin Sheath Schwann Cell Nodes of Ranvier Neurilemma Sensory Neuron Sensory Receptor Ganglion Interneuron Motor Neuron Effector Reflex Arc Action Potential Resting Potential Facilitated Diffusion Gated Ion Channel Sodium-Potassium Pump Active Transport Polarized Membrane Depolarization Repolarization Hyperpolarization Refractory Period Saltatory Conduction Threshold Level All-or-None Response Synapse Neurotransmitter Presynaptic Neuron Postsynaptic Neuron Acetylcholine Cholinesterase Summation Addiction Meninges Cerebrospinal Fluid Cerebrum Cerebral Cortex Corpus Callosum Thalamus Hypothalamus Olfactory Bulb Cerebellum Pons Medulla Oblongata Sympathetic Nervous System Parasympathetic Nervous System Vagus Nerve Sensory Adaptation Sclera Cornea Aqueous Humour Choroid Layer Iris Retina Rods Cones Fovea Centralis Rhodopsin Accommodation Glaucoma Cataract Astigmatism Nearsightedness (Myopia) Farsightedness Pinna Auditory Canal Tympanic Membrane Ossicles Oval Window Eustachian Tube Vestibule Semicircular Canals Cochlea Organ of Corti Basilar Membrane Otoliths Homeostasis Dynamic Equilibrium Negative Feedback Positive Feedback Hormones Endocrine Hormones Insulin Human Growth Hormone Epinephrine (Adrenaline) Pituitary Gland Releasing Hormone Inhibiting Factor Islets of Langerhans Glucagon Diabetes Adrenal Medulla Adrenal Cortex Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) Glucocorticoid Mineralocorticoid Sex Hormone Cortisol Adrenocorticotropic Hormone Tropic Hormone Aldosterone Thyroid Gland Parathyroid Glands Thyroxine Triidothyronine Calcitonin Goiter Parathyroid Hormone Antidiuretic Hormone Prostaglandins Anabolic Steroids Osmoreceptors