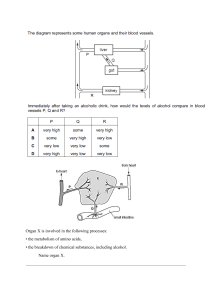
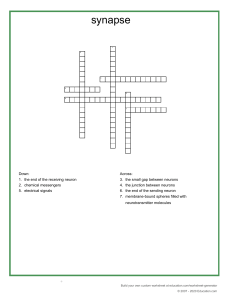
The Synapse The place where the axon of one neuron meets the dendrite of another is called a synapse. Synapses are also found between neurons and other types of cells; such as muscle cells. The axon of the sending neuron does not actually touch the dendrite of the receiving neuron. There is a tiny gap between them, the synapse. Voluntary action: When an action is produced with the involvement of thoughts, they are called voluntary action. It involves actions like walking, eating, jumping and running. These actions are produced consciously. Involuntary action: Actions which take place without consciousness or willingness of an individual are called the involuntary action. Digestion, heart beating, sneezing, etc are few examples of involuntary actions. EFFECTS OF INJURY TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM If the sensory nerve is damaged impulses will not be transmitted to the CNS If the motor neuron is damaged the effector muscle will be unable to respond to impulses. Damage to the brain and spinal cord may be caused by blows, infections, cerebral hemorrhage, stroke and if a blood vessel rapture. Damages like this can lead to 1. Loss of muscle control 2. Paralysis 3. Loss of speech 4. Impaired mental ability THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine system deals with long-term changes in the body. It is responsible for maintaining a constant internal environment in the body. This is called homeostasis. The messages are transmitted by chemicals called hormones that are released in the blood stream from a specific gland. Each hormone targets a specific organ where they stimulate the required change. An important hormones released into the bloodstream include ADH (anti-diuretic hormone), adrenaline and insulin. Source Organ(s) Role Effects ADH Pituitary gland Kidneys Controlling the Increases reabsorption of water content of water by the collecting the blood ducts Adrenaline Adrenal glands Several targets including the Preparation for 'fight or flight' Increases breathing rate, heart rate, flow of blood Source Organ(s) Role respiratory and circulatory systems Insulin Pancreas Liver Effects to muscles, conversion of glycogen to glucose Controlling blood glucose levels Increases conversion of glucose into glycogen for storage Control systems that keep such conditions constant are examples of homeostasis; this is the maintenance of constant internal conditions in an organism. A negative feedback mechanism is an important type of control that is found in homeostasis. A negative feedback control system responds when conditions change from the ideal or set point and returns conditions to this set point. There is a continuous cycle of events in negative feedback. General stages in negative feedback In general, this works by: if the level of something rises, control systems reduce it again if the level of something falls, control systems raise it again Negative feedback flowchart An example of negative feedback is the control of body temperature. Body temperature is controlled by the hypothalamus in your brain, and if your body gets too hot, your body begins to sweat to try and reduce it. Conversely if the body gets too cold, it begins to shiver to try and raise the temperature. INTEGRATED SCIENCE NAME: ____________________ SENSE AND COORDINATION CLASSWORK COMPLETE THE TABLE BELOW. HORMONE Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) Follicle Stimulating Hormone(FSH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) Growth hormone Thyroxine Adrenaline Oestrogen Progesterone Testosterone Glycogen Insulin GLAND TARGET ORGAN FUNCTION NAME: _________________________________________ MATHEMATICS MATRICES REVIEW 4 2 A =[ ] 3 1 −1 2 B= [ ] 5 −3 1. Calculate or solve for the following: a. A – B b. 3C c. -4B d. AB e. 𝐴2 FORM: 5-4 C= [ 2 3 ] −1 −2 f. 𝐵 − 2𝐶 2. Find the inverse of matrix a. A I. Determinant II. Adjoint III. Inverse FAMILY RESOURCES MANAGEMENT Use the school laptops and research on the topic “The importance of play to children”. A. In groups of three students are to write a paragraph discussing the topic. “The importance of play to students”, in no more than 600 words. 10 marks B. In groups of three (3) students design and create a game they would use to teach an 8-year-old. The game can be centered around any subject area. C. Write a paragraph describing the game and how it will be played.