Muscle Contraction: Structure & Function Worksheet
advertisement
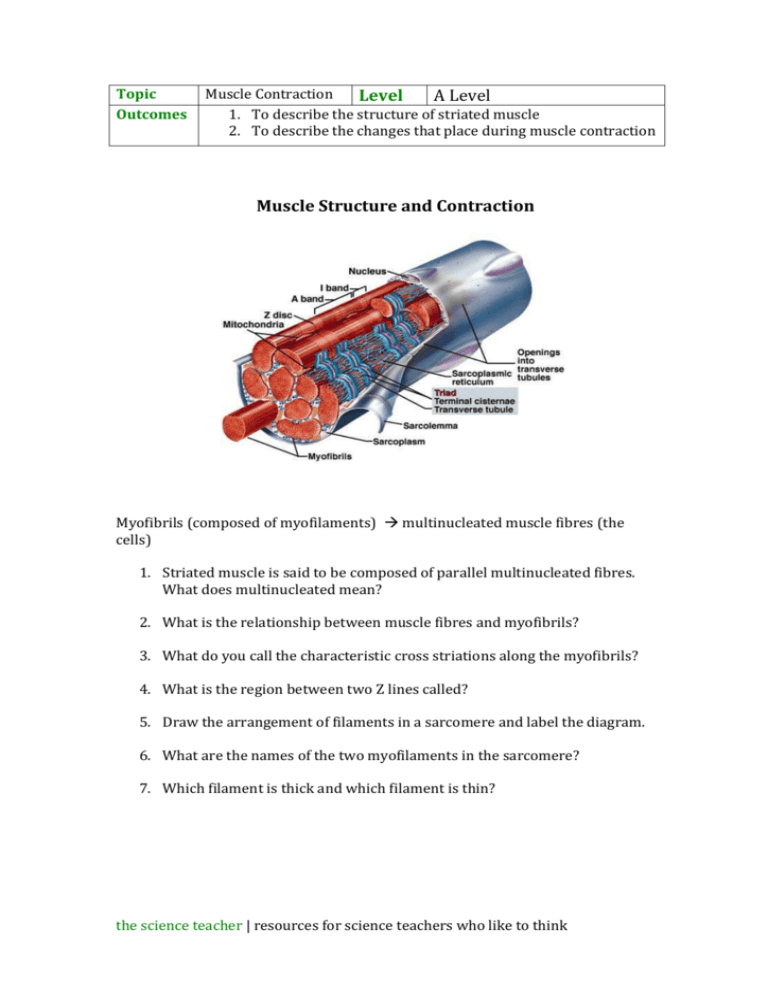
Topic Outcomes Muscle Contraction Level A Level 1. To describe the structure of striated muscle 2. To describe the changes that place during muscle contraction Muscle Structure and Contraction Myofibrils (composed of myofilaments) multinucleated muscle fibres (the cells) 1. Striated muscle is said to be composed of parallel multinucleated fibres. What does multinucleated mean? 2. What is the relationship between muscle fibres and myofibrils? 3. What do you call the characteristic cross striations along the myofibrils? 4. What is the region between two Z lines called? 5. Draw the arrangement of filaments in a sarcomere and label the diagram. 6. What are the names of the two myofilaments in the sarcomere? 7. Which filament is thick and which filament is thin? the science teacher | resources for science teachers who like to think Muscle contraction: 8. When muscle contraction occurs what filaments are pulled in between the myosin filaments? 9. Match the following chemicals to their function in muscle contraction. Myosin binds to actin molecules in a way that prevents myosin head from forming a cross bridge Actin supplies energy for the flexing of the myosin ‘head’ Ca ions has a moveable head that provides a power stroke when activated Troponin- two protein molecules twisted in a helix shape that form a thin filament Tropomyosin ATP bind to the blocking molecules, causing them to move and expose the myosin binding site the science teacher | resources for science teachers who like to think