Muscular System SG
advertisement

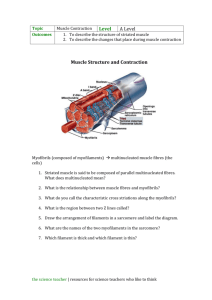
Muscular System SG: 1. Describe the structure of skeletal muscle (p.185) 2. List and describe the functions of skeletal muscle (maintains, posture, generates heat, stabilizes joints, movement). 3. Describe the microscopic structure of skeletal muscle – know the following terms: sarcolemma, myofibrils, light bands, dark bands, sarcomeres, myofilaments, thick filaments, thin filaments, myosin, actin, myosin heads). 4. How do sarcomeres shorten and what are cross bridges? 5. What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum, what does it store and release, and what is its function in muscle contraction. 6. Describe how a nerve stimulus initiates an action potential in a muscle fiber (189) 7. Describe how an action potential leads to the contraction of a muscle fiber. 8. What is the function of calcium in muscle contraction? Where does it bind? 9. Describe how a muscle fibers returns to a relaxed state. (i.e. neurotransmitter broken down, ion movement restores membrane to the resting state, calcium returns to the sarcoplasmic reticulum, myosin heads detach, and the muscle lengthens). 10. List and describe the three pathways for regeneration of ATP. 11. Compare anaerobic and aerobic respiration. 12. Define motor unit. 13. Define muscle tone. Focus less on - some of the parts of the sarcomere – H zone, Z disk, M-Line (should still know light and dark bands, actin and myosin, and how a sarcomere causes muscle contraction) - twitch vs. tetanus - labeling muscles