11.2 Movement assessment statements

Potential command term assessment statements
Topic 11: Animal Physiology
11.2 Movement
Essential Idea: The roles of the musculoskeletal system are movement, support and protection.
Nature of science: Developments in scientific research follow improvements in apparatus— fluorescent calcium ions have been used to study the cyclic interactions in muscle contraction.
State that bones and exoskeletons provide anchorage for muscles and act as levers.
State the synovial joints allow certain movements but not others.
Outline how movement of the body requires muscles to work in antagonistic pairs.
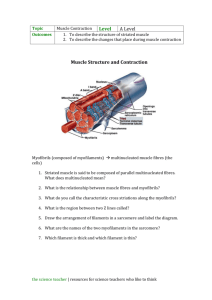
Annotate a diagram of the human elbow including the structures and functions of:
Cartilage
Synovial fluid
Joint capsule
Humerus
Radius
Ulna
Biceps
Triceps
Describe the action of antagonistic pairs of muscles in an insect leg.
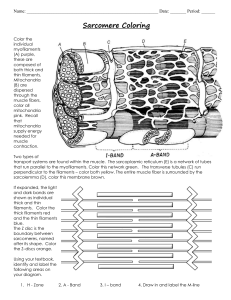
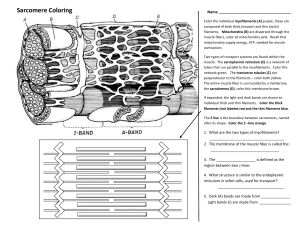
Draw and label diagrams of the structure of a sarcomere including:
Z lines
actin filaments
myosin filaments with heads
the resultant light and dark bands.
Describe the structure of skeletal/striated muscle fibres (muscle cell).
Multinucleate
Specialized endoplasmic reticulum = sarcoplasmic reticulum
Muscle fibres contain many myofibrils
Each myofibril is made up of contractile sarcomeres.
Explain how the contraction of the skeletal muscle is achieved by the sliding of actin and myosin filaments.
The release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and
the proteins tropomyosin and troponin control muscle contractions.
The formation of cross bridges
the sliding of actin and myosin
the breaking of cross bridges
the role of ATP hydrolysis.
Analyse electron micrographs to find the state of contraction of muscle fibres.
Outline the use of grip strength data loggers to assess muscle fatigue.
Explain muscle action from the use of animations to visualize contraction.