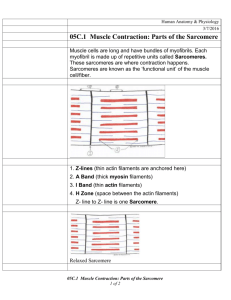
PPT#6.muscle physiology
advertisement

MUSCULAR SYSTEM Structure and Function Skeletal Muscle Properties 1. Excitability = ability to receive and respond to a stimulus 2. 3. 4. Also called irritability or responsiveness Contractility = ability to shorten when stimulated Extensibility = ability to be stretched Elasticity = ability to recoil and resume resting length Organization of Skeletal Muscle muscle cell = muscle fiber A “muscle” is composed of many muscle fibers arranged in bundles called fascicles Fascia = connective tissue that separates muscles; also forms tendons Organization of Skeletal Muscle Three layers of connective tissue: Muscle fiber endomysium perimysium epimysium Organization of Skeletal Muscle Three layers of connective tissue: 1. 2. 3. Epimysium outermost layer; surrounds the entire muscle Perimysium surrounds a bundle of muscle fibers (fascicle) Endomysium surrounds individual muscle fibers All three layers of connective tissue come together to form a tendon which attaches the muscle to bone Organization of Skeletal Muscle epimysium perimysium endomysium Organization of Skeletal Muscle Hierarchy of organization: Muscle fascicle fiber myofibrils myofilaments (actin/myosin) Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Sarcolemma = plasma membrane of muscle cell Sarcoplasm = cytoplasm of muscle cell Sarcoplasmic reticulum = stores calcium for contraction Transverse tubules = network of narrow tubes that form passageways through a muscle fiber Myofibrils = protein filaments (myofilaments) Actin and myosin Skeletal Muscle Anatomy nucleus sarcolemma mitochondria sarcoplasm myofibril Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Sarcomere = functional unit of skeletal muscle There may be thousands of sarcomeres in one fiber aligned end to end Myofilaments Form dark and light bands which gives skeletal muscle a striped appearance Interaction between these myofilaments within each sarcomere causes the sarcomere to shorten during contraction Actin (thin filament) The most abundant protein in eukaryotic cells Forms the light band of the sarcomere Each actin molecule has an active site capable of interacting with myosin At rest, active sites are blocked Myosin (thick filament) Motor protein Forms the dark band of the sarcomere Each myosin molecule has a globular head and a long fibrous tail Myosin head interacts with actin active site during contraction LABEL THIS DIAGRAM IN YOUR NOTES!!! Sarcomere Structure DArk band = A band = Myosin (thick) LIght band = I band = actin (thin) Sarcomere structure Z line = marks the boundaries of each sarcomere M line = middle of the sarcomere Sarcomere structure H zone = region of sarcomere where thick filaments do not overlap with thin filaments Zone of overlap = region of sarcomere where thick filaments overlap with thin filaments Sarcomere Structure sarcomere Thin filament Z line I band Animation H zone A band Thick filament Z line I band M line Microscopes…Skeletal Muscle In your lab notebook, create a new Lab titled “Skeletal Muscle” Part I. Microscopic observations Draw a picture of skeletal muscle under HIGH POWER Identify patterns and label multiple nuclei, muscle fibers, banding Label…A, I, M, Z, H animation Label…A, I, M, Z, H Changes to the sarcomere I band gets smaller Z lines move closer together H zone decrease Zones of overlap get larger Width of A bands doesn’t change animation Sliding Filament Theory (model) The theory of how muscle contracts Contraction occurs as the thin filament “slides” past the thick filament Involves 5 different molecules and calcium Myosin Actin Tropomyosin Troponin ATP Role of Nervous System in Muscle Contraction Skeletal muscles contract only under nervous system control Neuromuscular junction = association of nerve fiber with muscle fiber Acetylcholine = the neurotransmitter that acts on skeletal muscle by triggering calcium release Calcium is the “key” to allowing actin and myosin to interact during contraction Before contraction begins… Muscle at rest Troponin is bound to actin filaments Tropomyosin binds to the troponin Blocks Myosin active site preventing contraction from occuring heads (cross bridges) are “primed” for contraction Signal from nervous system (impulse) triggers the release of calcium animation What do you know about a muscle at rest? The contraction cycle 1. Calcium binds to troponin, shifting tropomysoin, exposing actin active site The contraction cycle 2. Myosin head binds to actin active site (cross-bridge forms) The contraction cycle Attached myosin head pivots toward center of sarcomere 3. This step requires energy that was stored in myosin head prior to contraction The contraction cycle 4. Cross-bridges detach; myosin binds another ATP The contraction cycle 5. Myosin is reactivated. The entire cycle can now be repeated The contraction cycle Ends when calcium ion concentration returns to normal Accomplished reticulum Contraction animation by active transport of calcium into sarcoplasmic Sketches in your lab book 1. Skeletal muscle If you do not, get a microscope and do this first! 2. Actin Filament Label actin molecules, troponin, tropomyosin and an active site 3. Myosin Filament Should contain multiple myosin molecules Label head and tail 4. Sarcomere (at rest vs. contracted) Without detail of individual filaments Label A band, I band, M line, Z line, H zone Describe changes to these structures during contraction Sketches The Contraction Cycle BIG PICTURE Skeletal muscle fibers shorten as thin filaments interact with thick filaments and sliding occurs The trigger for contraction is calcium Calcium ions are released when the muscle fiber is stimulated by an impulse from a motor neuron Contraction is an active process Relaxation and return to normal are passive processes Rigor Mortis Upon death, circulation stops and skeletal muscles are deprived of nutrients Muscle fibers run out of ATP Calcium ions cannot be cleared Sustained contraction occurs All body muscles are involved Individual becomes “stiff”