Muscles and Movement Worksheet: Anatomy & Physiology

11.2 -MUSCLES AND MOVEMENT
1.
Label the following features and state their function in movement. a. b. c. d. e. f.
Joints
‘moment’ or pivot for movement
2.
The elbow.
Name:
3.
Outline the antagonistic nature of the action of muscles in the human body, using the elbow as an example.
Biceps
Triceps
Flexing (bending)
4.
Compare the action of the hip and knee joints.
Extending
Type of joint
Range of movement
Bones
Lever
Flex/ effort
Extend/ effort
Femur
Hip (similar to shoulder)
Ball and socket
Knee
Image
5.
Label these structures of a muscle cell. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j.
6.
Outline the need for large numbers of mitochondria in muscle cells.
7.
Muscle cells contract as a result of nerve impulses. a.
State the part of the motor neuron which connects to the muscle cells
b.
Identify the neurotransmitter used at the neuromuscular junction.
8.
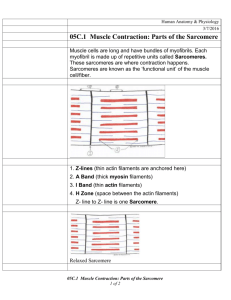
Label the structures of the sarcomere: a.
b.
c.
d. e.
9.
Identify the number of complete number of sarcomeres in this EM image:
Sarcomeres =
10.
Explain the contraction of skeletal muscle.
Sliding Filament Theory
Complete the flow chart below
A nerve impulse is sent from the brain through the …………… ………………… to stimulate muscle contraction
The nerve impulse travels down the
………………. , generating an action potential which causes calcium ions to be released from the ………………………. ………………………
Ca+ ions diffuse into the sarcomere and attach to …………. which changes shape.
As …………….. changes shape it pulls
……………….. away from the myosin binding sites on the actin – which are now exposed!
When the nerve impulse stops, Ca 2+ ions are…………………….. and ………………returns to its normal shape
Myosin heads use ………… to pull themselves along the actin molecule, forming an …………………. …………………. at each binding site before breaking and …………… stroking to the next one.
The sarcomere shortens as the actin filaments are pulled towards the ………………. of the sarcomere
…………..… covers the myosin binding sites and the muscle relaxes
11.
Compare these two electron micrographs of a skeletal muscle sarcomere.
Contracted or relaxed?
Sarcomere length
Z-bands
H-bands
Light bands
Dark bands
PAST PAPER QUESTION
No change
No change
Shorter
Closer