Work Study: Methods, Measurement, and Productivity
advertisement

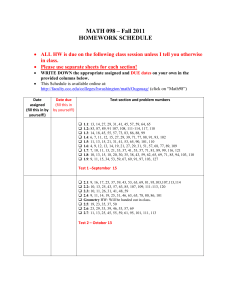
Work Study Prof. Dr. Orhan TORKUL Arş. Gör. M. Raşit CESUR Arş. Gör. Furkan YENER Work Design and Organizational Success • • Elementally, the ability of an organization to convert form input to output. Productivity = Effectivity Output Input Innovation Profitability Efficiency Productivity Quality Quality of business life (Organizational success) Method Study • Method study is a systematic approach to find out easier and better ways in order to be success in a task. • 5 steps for systematic approach in Method study; 1. 2. 3. Select the work: Highest cost or lovest productivity works are prefered in generally. Obtain and save the facts: Datas should save such as actual method and frequency of work Examine the details: Actual method should examined, Some elemants could be removed or modified. Method Study • 4. 5. 5 steps for systematic approach in Method study; Improve better method and make tests: New method should be improved based on changes and make tests. Establish and sustain of the improvement: Improved method should be enhanced and implemented. Flow Process Diagrams/Charts • Flow work diagram contains all activities(operations, storages, inspection, carrying and delays) in a process. Process Start Specialist Actual_____Proposed______ Steps Man____ or Material _______ Stop Date Symbols 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. .. Flow Process Charts Explanations Two Handed Process Charts • Two Handed Process Chart could be used for analyze of work made by someone at the spesific work center . Two Handed Process Charts Two Handed Process Charts Operation________ Name _________ Date ___________ Actual _______________ Proposed ____________ Work place layout and product drawing (if it is necessary) Left hand Activities Symbols Right Hand Activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. .. Two Handed Process chart Two Handed Process Charts Operation: (one) hand makes some efficient operation, Transport: (one) hand moves from one place to another, Delay : Hand does nothing, waits, Hold : Hand keeps an object. Other Schemas • • • • • Flow process chart : A flow diagram is basically a process flow diagram of the facility was drawn with the goal of the configuration. Multiple activity Schema: Multi - activity Schema shows at least two or more objects, man and machine activities simultaneously. Work Distrubition Schema: the list of everybody’s activities and responsibilities in a departmant or group. Operation Process Chart: Inessential work, inspection or storage are eliminated and to obtain proper sequences of the these. Gantt Schema: Gantt Schema is a horizontal timeline diagram which is used in scheduling and it shows relative timeline of various activities. Principles of Movement’s Economy • • 1. 2. 3. 4. Thoughts and notions are proved of benefits when effective work procedure is planning. The following principles of movement’s economy list is taken from Mundel. Remove Combining Redesign Simplification Human Engineering • • • Workers and machines can work together as a system to ensure more effective and efficient human-machine interface design. Today, thanks to human engineering, machinery may lowered or set up higher position or completely re-designed and thus the worker and the machine can be provided as a single system work better. A good example of Human engineering is aircraft cockpit design. Work Measurement Under normal operating conditions and at a normal pace, and trained an average person working 8 hours per day, a measure of the time required for the fulfillment of the task. 1. Normal Time 2. Normal tempo 3. Actual Time 4. Tolerances • Standart Time Calculation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Directly Time study Time study’s standart datas Pre-determined Time systems Pre-determined Time systems standart datas Work sampling Direct Time Study • The actual time required to do a job, taking into account the tolerance measure of the time directly. Time Study Form Performance Evaluation Calculations OPERATION AVERAGE 1 15 2 7 3 5 4 8 Total Actual Time Success Evaluation =%115 Normal Time Tolerances Standart Time =15+7+5+8=35 =(35)(1,15)=40,25 =%12 =(40,25)(1,12)=45,08 Normal Time = Actual Time X Success Evaluation If operator performance is %90 or less than %10 from normal expectations, Normal time colculates as following solution. Normal Time = (35)(0,90) = 28,50 To suppose doing a study and personal needs constitute work days %4 and tiredness effects the performance %5 and unavoidable delays accure %3 at time. Tolerances = %4 + %5 + %3 = %12 We needs to add Tolerances to the Normal time in order to calculate the Standard time we may find Standart time as follows. Standart Time:(40,25)(1,12) = 45,08 Time Study’s Standart Datas • Time study’s standart data’s using the worths which are obtained from normal time schedule previously. Y X 6 cm 8 cm 10 cm 12 cm 6 cm 0,025 0,026 0,026 0,027 8 cm 0,026 0,026 0,027 0,027 10 cm 0,027 0,028 0,028 0,029 12 cm 0,027 0,028 0,029 0,030 Pre-determined Time Table • • Leave any parts of the job detail, various factors (weight, distance and etc.) previously created by taking into consideration, when utilized as reference values table is called a pre-determined time table. Giving an object from one hand to another; weight > 2 lb. X 0,454 kg. Distance Time 4 inch x 2,54 cm 0,00412 min 8 inch 0,00591 min Work Sampling Rate for the time spent on a specific type of activity, instantaneous measurements made using the calculation of random variables is called work sampling. Percentage of Occurrence A Facility Accumulated percentage • = 𝑅𝑒𝑝𝑒𝑡𝑡𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝐴 𝐹𝑎𝑐𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑁𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑂𝑏𝑠𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑠 10 8 Accumulated Percentage 6 4 Standard 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Number of observations 9 10 Productivity Measurement • • O𝑟𝑔𝑎𝑛𝑖𝑧𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑙 = O𝑟𝑔𝑎𝑛𝑖𝑧𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝑂𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡 O𝑟𝑔𝑎𝑛𝑖𝑧𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝐼𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡 𝑃𝑟𝑜𝑑𝑢𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑖𝑡𝑦 D𝑦𝑛𝑎𝑚𝑖𝑐 𝑃𝑟𝑜𝑑𝑢𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝐼𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑥 = 𝑇ℎ𝑖𝑠 𝑦𝑒𝑎𝑟′ 𝑠 𝑂𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡 𝑇ℎ𝑖𝑠 𝑦𝑒𝑎𝑟′ 𝑠 𝐼𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡 𝐵𝑎𝑠𝑖𝑐 𝑦𝑒𝑎𝑟′ 𝑠 𝑂𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡 𝐵𝑎𝑠𝑖𝑐 𝑦𝑒𝑎𝑟′ 𝑠 𝐼𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡 Normal Productivity Measurement Model 1. 2. 3. 4. Quiet contemplation Cyclically to express thoughts Intra-group netting Voting Multi-Factor Productivity Measurement Model Basically, MFPMM have two ways that may affect the profitability of an organization. 1. Re-pricing 2. Productivity Variation THANKS