Algoritma, hayat*n her alan*nda, herhangi bir i*i yapmak için tan
advertisement
What is Algorithm ?
Algorithm, is a work plan that shows the sections of a duty.
Example
• Join Hacettepe Robotics Community.
• Study hard.
• Join Robot Projects.
• Graduate from Hacettepe.
• Find a Job with high salary.
• Enjoy ! ☻
How to make an Algorithm ?
• Flowcharts
• Pseudocodes
Flowcharts
Start
Tap
Temperature
No
Temp.
<25 ?
Print ‘hot’.
Yes
Print ‘Cold’.
End
Types of Flowcharts
• Sequence
• Selection
• Loop
Start
Start
Process
Decision
Process
Process
Start
Process
Decision
Process
End
Sequence
Process
End
Selection
End
Loop
Pseudocodes
• Have a usage like routine speaking.
• No syntax.
• Aims to understand how program works.
Example
•
•
•
•
•
1
2
3
4
5
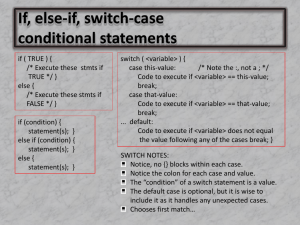
if
students grade > 60
print ‘PASSED’
else
print ‘FAILED’
Introduction to C Programming
• Standart libraries
• Standart input/output functions
• Data types
• Variable declarations
• Operators
Standart Libraries
• Stdio.h ( Standart input/output) :
• Defines variable types
• Various functions for performing input / output
• Stdlib.h ( Standart Library) :
• Various functions for performing general functions
Standart Libraries
• Define Library;
• #include<stdio.h>
• #include<stdlib.h>
Standart Input / Output Functions
• Printf
• Scanf
Printf
1)Single Text;
• printf("Hello World !");
Printf
2)Control Characters;
Character
Meaning
\n
New line
\a
Alert
\t
TAB
Printf
3)Conversion Specifier(Place Holder);
Conversion Specifier
Character
Meaning
Data Type
%c
Single character
Char
%s
String
Char
%d
Integer
İnt
%f
Reel number
float
%lf
Double
double
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Welcome to Hacettepe Robotics Community!\n");
}
Scanf
• scanf("%Conversion_specifier",&Variable _name);
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x,y,sum;
printf("Insert x and y>> !\n");
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
sum=x+y;
printf("Sum is >> %d",sum);
}
Data Type
Information
Size kept in the memory
Char
Single character or string
1
int
Integer
2
Float
Fractional numbers (7 digits)
4
Double
Fractional numbers (15 digits)
8
For a single character
Data Type
For a string
char
%c ve %s
int
%d
float
%f
double
%lf
Conversion Specifier
Aritmetic Operators
Operator
Information
Example
Meaning
+
Addition
x+y
Sum of x and y
-
Subtraction
x–y
Difference of x and y
*
Multiplication
x*y
Product of x and y
/
Division
x/y
Quotient of x and y
%
Mod
x%y
Remainder of x/y
Assignment Operators
Operator
Information
Example
Meaning
=
Assignment
x=7;
x=7;
+=
Assignment with additon
x+=3;
x=x+3;
-=
Assignment with subtraction
x-=4;
x=x-4;
*=
Assignment with multiplication
x*=5;
x=x*5;
/=
Assignment with division
x/=3;
x=x/3;
%=
Assignment of remainder from a division
x%=9;
x=x%9;
++
One increasing
x++; or ++x;
x=x+1;
--
One decreasing
x--; or --x;
x=x-1;
Compare Operators
Operator
Information
Example
Meaning
>
Greater than
x>y
Is x, greater than y ?
<
Less than
x<y
Is x, less than y ?
==
Equal
x==y
Is x, equal to y ?
>=
Greater than or equal to
x>=y
Is x, greater than or equal to y ?
<=
Less than or equal to
x<=y
Is x, less than or equal to y ?
!=
Not equal
x!=y
Is x, not equal to y ?
&&
Logical and
x>2 && x<y
Is x, greater than 2 and less than
y?
||
Logical or
x>2 || x<y
Is x, greater than 2 or less than
y?