Unit 1 - Economics w/ Financial Literacy
advertisement
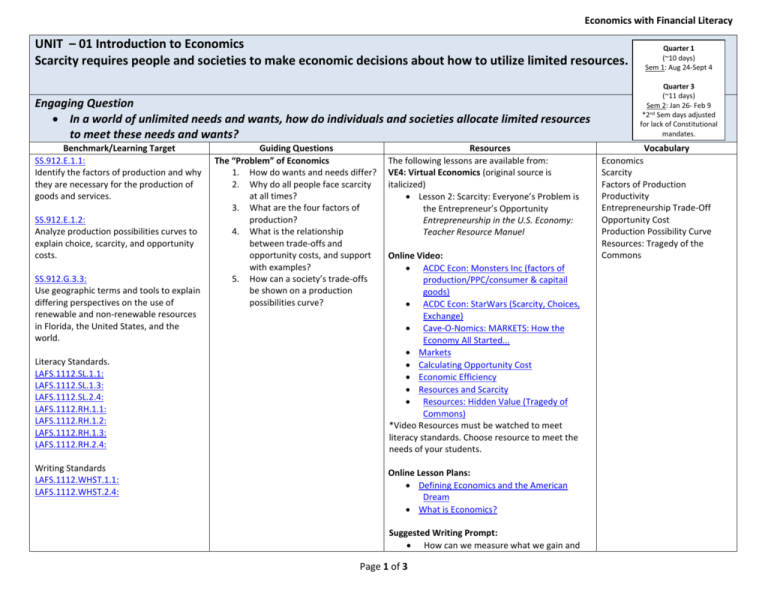
Economics with Financial Literacy UNIT – 01 Introduction to Economics Scarcity requires people and societies to make economic decisions about how to utilize limited resources. Engaging Question In a world of unlimited needs and wants, how do individuals and societies allocate limited resources to meet these needs and wants? Benchmark/Learning Target SS.912.E.1.1: Identify the factors of production and why they are necessary for the production of goods and services. SS.912.E.1.2: Analyze production possibilities curves to explain choice, scarcity, and opportunity costs. SS.912.G.3.3: Use geographic terms and tools to explain differing perspectives on the use of renewable and non-renewable resources in Florida, the United States, and the world. Literacy Standards. LAFS.1112.SL.1.1: LAFS.1112.SL.1.3: LAFS.1112.SL.2.4: LAFS.1112.RH.1.1: LAFS.1112.RH.1.2: LAFS.1112.RH.1.3: LAFS.1112.RH.2.4: Writing Standards LAFS.1112.WHST.1.1: LAFS.1112.WHST.2.4: Guiding Questions The “Problem” of Economics 1. How do wants and needs differ? 2. Why do all people face scarcity at all times? 3. What are the four factors of production? 4. What is the relationship between trade-offs and opportunity costs, and support with examples? 5. How can a society’s trade-offs be shown on a production possibilities curve? Resources The following lessons are available from: VE4: Virtual Economics (original source is italicized) Lesson 2: Scarcity: Everyone’s Problem is the Entrepreneur’s Opportunity Entrepreneurship in the U.S. Economy: Teacher Resource Manuel Online Video: ACDC Econ: Monsters Inc (factors of production/PPC/consumer & capitail goods) ACDC Econ: StarWars (Scarcity, Choices, Exchange) Cave-O-Nomics: MARKETS: How the Economy All Started... Markets Calculating Opportunity Cost Economic Efficiency Resources and Scarcity Resources: Hidden Value (Tragedy of Commons) *Video Resources must be watched to meet literacy standards. Choose resource to meet the needs of your students. Online Lesson Plans: Defining Economics and the American Dream What is Economics? Suggested Writing Prompt: How can we measure what we gain and Page 1 of 3 Quarter 1 (~10 days) Sem 1: Aug 24-Sept 4 Quarter 3 (~11 days) Sem 2: Jan 26- Feb 9 *2nd Sem days adjusted for lack of Constitutional mandates. Vocabulary Economics Scarcity Factors of Production Productivity Entrepreneurship Trade-Off Opportunity Cost Production Possibility Curve Resources: Tragedy of the Commons Economics with Financial Literacy lose when making choices? SS.912.G.3.3: Compare how the various economic systems (traditional, market, command, mixed) answer the questions: (1) What to produce?; (2) How to produce?; and (3) For whom to produce? SS.912.E.2.12: Construct a circular flow diagram for an open-market economy including elements of households, firms, government, financial institutions, product and factor markets, and international trade. Literacy Standards. LAFS.1112.SL.1.1: LAFS.1112.SL.1.3: LAFS.1112.SL.2.4: LAFS.1112.RH.1.1: LAFS.1112.RH.1.2: LAFS.1112.RH.1.3: LAFS.1112.RH.2.4: Writing Standards LAFS.1112.WHST.1.1: LAFS.1112.WHST.2.4: Economic Systems and Characteristics of the American Economy 1. What three questions must all economic systems answer? 2. What are the major types of economic systems, their advantages/disadvantages, and their goals? 3. What are the roles of government in our free enterprise economy? 4. 5. 6. How do freedom of enterprise and freedom of choice apply to the American economy? What roles do private property, the profit incentive, and competition play in the American economy? How can people balance economic rights with economic responsibilities? The following lessons are available from: VE4: Virtual Economics (original source is italicized) Lesson 10 - The Circular Flow of Economic Activity Economics in Action: 14 Greatest Hits for Teaching High School Economics Online Lesson Plans: Economic Systems Pencils or Candies? Born on Third Base Online Video: FED Reserve: Circular Flow Diagram *Video Resources must be watched to meet literacy standards. Choose resource to meet the needs of your students. Suggested DBQ: (1 DBQ or CISM per 9 weeks required) DBQ: Capitalism vs. Communism Suggested Writing Prompt: Consider how the element of prediction in economics might be important in their own lives. Is there a trend in the region toward a growth or decline in the overall number of jobs? How might such economic predictions be important for their futures? Choose two of the economic systems that you have learned about and compare and contrast the two. Be sure to include positives and negatives of each. In conclusion, synthesize what system you believe is the best for our nation to engage in. Be sure to give concrete examples to support your answer. How do Mixed Economies divide the Page 2 of 3 Economic System Traditional Economy Command Economy Market Economy Circular Flow of Economic Activity Mixed Economy Capitalism Laissez-Faire Free Enterprise System Profit Incentive Competition Economic Efficiency Standard of Living Economics with Financial Literacy decision making? What are the key characteristics of the American economic system and how are they demonstrated throughout our society? Online Resource (look for your own lesson): http://www.econedlink.org/lessons/econ omic-lessonsearch.php?type=educator&gid=4 SS.912.E.2.3: Research contributions of entrepreneurs, inventors, and other key individuals from various gender, social and ethnic backgrounds in the development of the United States. SS.912.E.3.6: Differentiate and draw conclusions about historical economic thought theorized by economists. Literacy Standards. LAFS.1112.SL.1.1: LAFS.1112.SL.1.3: LAFS.1112.SL.2.4: LAFS.1112.RH.1.1: LAFS.1112.RH.1.2: LAFS.1112.RH.1.3: LAFS.1112.RH.2.4: Writing Standards LAFS.1112.WHST.1.1: LAFS.1112.WHST.2.4: What do Economists do? 1. How do economists use models to study the real world? 2. Why are there different schools of economic thought? 3. What individuals have contributed historical economic thought significant to society? Microeconomics Macroeconomics Economic Model Online Lesson Plans: Is Capitalism Good for the Poor? Suggested Writing Prompts: What principles guide an economic way of thinking? Your principles should show that you understand how people make choices and how those decisions affect others. Economists use the scientific method to analyze economic events and predict outcomes. Explain and show how they use graphs to analyze the relationship between two sets of date. Use an economic model to help explain how the world works. Models can take various forms such as diagrams, equations or descriptions. ESE/ESOL Strategies: Pairs Check Cornell Notes Thinking Maps Ticket out the Door 3-2-1 Mix-Pair-Share Literacy Circles Advanced/Honors Classes: For all advanced/honors classes the expectation is to increase the rigor, research and writing expectations, along with the speed at which the curriculum is taught. Student Misconceptions: Students need to understand the difference between opportunity cost and trade-offs. An individual may have several trade-offs but only one opportunity cost. In reality, there is only one other “thing” that can be done with your time/money, etc. Students must understand the production possibility curve, and that in order to move along the curve, one of the two items are being given up to produce the other. Walk students through this. Use easy numbers to make the example a reality for students. Give them examples from their own life. Students need to understand the difference between scarcity and shortage. Shortage is temporary, whereas scarcity is an ongoing challenge. Page 3 of 3