The 5 KINGDOMS of Classification
advertisement

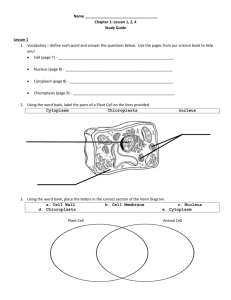
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS 1 WARM UP (15 minutes) Line up around the room. You need to place yourself in order of your birthdays, but you cannot speak to one another. - Class is organized into groups according to birthday. How else could the class have been divided into groups? - Why might you want to group or classify objects? 2 Who Needs a Classification System? How is your life organized? When you go to the grocery store, how do know how to find the milk? When you go to the clothing store, how do you know where to look for your favorite brand? 3 Why do Scientists Classify? Did you know that there are almost 2 million kinds of organisms on Earth? How could we possibly keep them all straight or study them without some form of organization? 4 CLASSIFICATION What is does the word classification mean? Classification means the act of grouping living things by using a set of rules and similarities. The “SCIENCE” of classification is called taxonomy. Taxonomy is the field of biology that study how living things are 5 classified. Who first developed a system to classify organisms? As early as 350 B.C., the Greek Philosopher Aristotle created guidelines for grouping living things. Aristotle grouped organisms based on four characteristics: •Body parts •Life histories •Activities •Character 6 The Modern Classification System The modern classification system was developed by the Swedish scientist, Carolus Linnaeus, in the mid 1700’s. His system was based upon classifying organisms according to the organism’s physical and structural similarities. Some characteristics he used to classify organisms were outside appearance, internal organs, and how body systems worked. Modern scientists are still using most of Linnaeus’s classification system. 7 Linneaus’ System of Scientific Names Binomial Nomenclature is a two word classification naming system developed by Linneaus. Each species of a living thing is given a DOUBLE NAME EX: Just like your first and last name First Name (Genus) Tells which group of similar species the living thing belongs to. Genus is ALWAYS capitalized. Second Name (Species) Tells the name of the one particular species in that genus. Species is 8 NEVER capitalized. How Living Things Are Classified? Organisms are ranked in a “Taxa” according to their characteristics. Taxa is a further broken-down level of classification found within each kingdom according to similarities. The broader the Taxa the more general its characteristics & the more species it contains. 9 How Are Living Things Classified? •There are 7 levels in the classification system of organisms Broadest Level •As one goes from the Kingdom to the Species (DOWNWARD)…An increase in the similarity between organisms occur •There are fewer numbers of different kinds of organisms Most Specific 10 How Are Living Things Classified? Kingdom: The highest level Phylum: A subdivision of a kingdom Class: Each phylum is divided into classes Order: Each class is divided into orders Family: Each order is divided into families Genus: Each family is divided into genera Species: Lowest level (represents a single type of organism) 11 CLASSIFICATION OF CARS CLASSIFICATION KINGDOM PHYLUM CLASS ORDER FAMILY GENUS SPECIES CAR 1 Mechanical Transportation Automobile SUV Ford Explorer Eddie Bauer All Wheel Drive 12 How Are Living Things Classified? Homework: Write an original catch phrase for the categories of classification so that each word in the phrase begins with the letter of the category in their correct order from largest to smallest Example: Kids Play Cards On Fat Green Stools Phyllum Kingdom Order Class Species Family Genus 13 The Classification Game!! In the following few slides, you will find 14 different organisms, each of them labeled with a letter. In your groups, write down two main classification (example red/green). Then place the corresponding letters under the correct classification. 14 For Example These organisms have been classified by their color. Green Red 15 ARE YOU READY 16 B E A D C F G K L J I H M N 17 One Possible Solution Animals Plants C D A G I J M ???? B K E N F L H 18 Did You Have Problems?? There were actually several different ways to go about classifying these 14 organisms. You might have done color, shape, size, number of legs… the possibilities are endless. You might have encountered one or two that really did not fit into either of your two classifications, what should you do when this happens? Make a new classification of course! And this is what scientist have done as well through the years. 19 The 5 KINGDOMS of Classification A Kingdom is the largest group in the Classification system. It encompasses all the related species. 20 The 5 KINGDOMS of Classification In all, there are 5 Kingdoms of Life… 1.Monera 2.Protista 3.Fungi 4.Plantae 5.Animalia 21 The 5 Kingdoms of Classification The Kingdom, Monera consists of all Bacteria. Examples of Bacteria include: Cyan bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus Escherichia coli. This picture is of E. coli 22 The 5 Kingdoms of Classification The Kingdom, Protista consists of simple eukaryotes (multi-cellular organisms). Examples of Protista include: majority of molds such as Saprolegnia (Water mold) Dictyostelium diccoideum (Slime Mold). 23 The 5 Kingdoms of Classification The Kingdom, Fungi consists of fungus & yeasts members. These break down organic materials to obtain food. Examples of different types of fungus include: Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Yeast) Amanita muscaria (Fly Agaric). 24 The 5 Kingdoms of Classification The Kingdom, Plantae houses all the plant members. Examples of plants include: Flowers Corn Moss Ferns Trees 25 The 5 Kingdoms of Classification The last Kingdom, Animalia consists of Humans and ALL animals. Examples of Animalia include: Insects Mammals Reptiles Birds Amphibians. 26 Using the Classification System Field guides help identify organisms. -they highlight differences between similar organisms (like trees) Taxonomic Key / Dichotomous Key) is a paired statements that describe the physical characteristics of different organisms 27 Taxonomic Key Norns belong to the genus Norno and can be divided into eight species that are generally located in specific regions of the world. Use the dichotomos key to identify the norns below. A 1. 1’ Has pointed ears .................................... go to 3 Has rounded ears ....................................go to 22. 2 2’ Has no tail ............................................. Kentuckyus Has tail .................................................. Dakotus 3 3’ Ears point upward .................................. go to 5 Ears point downward ............................. go to 4 4 4’ Engages in waving behavior .................. Dallus Has hairy tufts on ears .........................Californius 5 5’ Engages in waving behavior .................. WalaWala Does not engage in waving behavior.......go to 6 6 6’ Has hair on head ..................................... Beverlus Has no hair on head (may have ear tufts) .......go to 7 7 7’ Has a tail ................................................. Yorkio Has no tail, aggressive ............................ Rajus D G B C E F H 28 REVIEW Classification means the act of grouping living things by using a set of rules and similarities. Taxonomy is the field of biology that study how living things are classified. The modern classification system was developed by Carolus Linnaeus. His system is based upon classifying organisms according to physical and structural similarities. Binomial Nomenclature is a two word classification naming system. Each species of a living this is give a double name. First name (Genus) is ALWAYS capitalized. The second name (Species) is NEVER capitalized. Organisms are ranked in a “Taxa” according to their characteristics. Taxa is a further broken-down level of classification found within each kingdom according to similarities. The broader the Taxa the more general its characteristics & the more species it contains. 29 REVIEW (Cont’d) Broadest Level There are 7 levels in the classification system Most Specific 30 REVIEW (Cont’d) The 5 Kingdoms Monera – all bacteria Protista – all simple eukaryotes (multi-cellular organisms, i.e. molds) Fungi – all fungus and yeasts (i.e. mushrooms) Plantae – all plants Animalia – all animals, reptiles, insects, birds Taxonomic Key / Dichotomous Key) is a paired statements that describe the physical characteristics of different organisms 31