Financial Check Up
advertisement

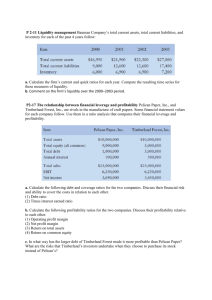
Financial Check Up Agribusiness Finance LESE 306 Fall 2009 Seen the Doc Lately? Benefits from an annual financial checkup. Treadmill stress test your financial strength. Get your vision examined. What is the status of your…. Liquidity? Solvency? Profitability? Efficiency? Debt repayment capacity? Survivability? Key Financial Indicators Generally accepted Financial Indicators Focus today on a few key indicators of liquidity, solvency, profitability, financial efficiency, debt repayment capacity and the implications for survivability. Measures of Liquidity 1. Current ratio: • Current assets divided by current liabilities. • Demonstrates ability to cover scheduled current liabilities for the coming year out current assets and still have “cash” left over. • Should exceed 1.0 to be technically liquid. • Some firms fail despite exceeding this hurdle. Measures of Liquidity 1. Current ratio: • Current assets divided by current liabilities. • Demonstrates ability to cover scheduled current liabilities for the coming year out current assets and still have “cash” left over. • Should exceed 1.0 to be technically liquid. • Some firms fail despite exceeding this hurdle. 2. Working capital: • Current assets minus current liabilities. • Expresses liquidity in dollars rather than ratio. • Should be positive. • Cash is King! Liquidity Trends Current Ratio Survived 4.00 3.50 3.00 2.50 2.00 1.50 1.00 0.50 0.00 Failed 1 2 3 4 5 Year Before Failure Source: W. H. Beaver, “Financial Ratios and Predictors of Failure”, Journal of Accounting Research Liquidity Trends Current Ratio Survived 4.00 3.50 3.00 2.50 2.00 1.50 1.00 0.50 0.00 Failed Minimum 1 2 3 4 5 Year Before Failure Source: W. H. Beaver, “Financial Ratios and Predictors of Failure”, Journal of Accounting Research Liquidity Trends Working Capital-to-Total Assets Survived 0.45 0.40 0.35 0.30 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 Failed 1 2 3 4 5 Year Before Failure Source: W. H. Beaver, “Financial Ratios and Predictors of Failure”, Journal of Accounting Research Measures of Solvency 1. Debt ratio: • Total debt divided by total assets. • Demonstrates ability to liquidate the firm, cover all liabilities out of all assets, and still have “cash” left over. • Should not exceed 0.50 to minimize financial risk exposure. • Some firms fail however at lower levels. Measures of Solvency 1. Debt ratio: • Total debt divided by total assets. • Demonstrates ability to liquidate the firm, cover all liabilities out of all assets, and still have “cash” left over. • Should not exceed 0.50 to minimize financial risk exposure. • Some firms fail however at lower levels. 2. Leverage ratio: • Total debt divided by equity or net worth. • Often a credit standard in loan approval decisions. • Should not exceed 1.0 to minimize financial risk exposure. • Effects of rising interest rates. Solvency Trends Total Debt-to-Total Assets 0.90 0.80 0.70 0.60 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 0.10 0.00 Failed Survived 1 2 3 4 5 Year Before Failure Source: W. H. Beaver, “Financial Ratios and Predictors of Failure”, Journal of Accounting Research Solvency Trends Total Debt-to-Total Assets 0.90 0.80 0.70 0.60 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 0.10 0.00 Failed Maximum Survived 1 2 3 4 5 Year Before Failure Source: W. H. Beaver, “Financial Ratios and Predictors of Failure”, Journal of Accounting Research Measures of Profitability 1. Rate of return on assets: • Net income plus interest divided by total assets. • Demonstrates the after-tax return to the total capital invested in the firm. • Should be positive; the higher the better. Measures of Profitability 1. Rate of return on assets: • Net income plus interest divided by total assets. • Demonstrates the after-tax return to the total capital invested in the firm. • Should be positive; the higher the better. 2. Rate of return on equity: • Net income divided equity. • Demonstrates the after-tax return on owner equity invested in the firm. • Should be positive; the higher the better. Profitability Trends Rate of Return on Assets 0.15 0.10 Survived 0.05 0.00 -0.05 1 2 3 4 5 -0.10 -0.15 Failed -0.20 -0.25 Year Before Failure Source: W. H. Beaver, “Financial Ratios and Predictors of Failure”, Journal of Accounting Research Profitability Trends Rate of Return on Assets 0.15 0.10 Survived 0.05 Minimum 0.00 -0.05 1 2 3 4 5 -0.10 -0.15 Failed -0.20 -0.25 Year Before Failure Source: W. H. Beaver, “Financial Ratios and Predictors of Failure”, Journal of Accounting Research Measure of Debt Repayment Capacity 1. Term Debt and Capital Lease Coverage Ratio: • Cash available from operations to cover scheduled payments (net income plus depreciation and interest payments less withdrawals) divided by scheduled principal and interest payments on term loans and capital leases. • After provision for taxes and withdrawals. • Should be greater than 1.0. • Non-farm income often factored in by lenders. Measure of Debt Repayment Capacity 1. Term Debt and Capital Lease Coverage Ratio: • Cash available from operations to cover scheduled payments (net income plus depreciation and interest payments less withdrawals) divided by scheduled principal and interest payments on term loans and capital leases. • After provision for taxes and withdrawals. • Should be greater than 1.0. • Non-farm income often factored in by lenders. 2. Debt Burden Ratio: • Total debt outstanding divided by net income. • Number of years required to retire total debt if net income remains constant and used entirely for this purpose • Should be low; the lower the better. Debt Repayment Capacity Inverse of debt burden ratio assuming use of depreciation allowances to retire debt. Net Cash Income-to-Total Debt 0.60 Survived 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 0.10 0.00 -0.10 1 -0.20 2 3 4 5 Failed -0.30 Year Before Failure Source: W. H. Beaver, “Financial Ratios and Predictors of Failure”, Journal of Accounting Research Some Conclusions…. Indicators of growth/survival: Increasing liquidity Increasing solvency Increasing debt repayment capacity Increasing profitability Some Conclusions…. Indicators of potential failure: Declining liquidity Declining solvency Decreasing debt repayment capacity Decreasing profitability Some Conclusions…. Indicators of growth/survival: Increasing liquidity Increasing solvency Increasing debt repayment capacity Increasing profitability Indicators of potential failure: Declining liquidity Declining solvency Decreasing debt repayment capacity Decreasing profitability Tale of Two Cities… Working Capital-to-Total Assets 0.45 0.40 0.35 0.30 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 Failed 1 2 3 4 5 Year Before Failure Source: W. H. Beaver, “Financial Ratios and Predictors of Failure”, Journal of Accounting Research Tale of Two Cities… Total Debt-to-Total Assets Working Capital-to-Total Assets 0.45 0.40 0.35 0.30 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 0.90 0.80 0.70 0.60 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 0.10 0.00 Failed 1 2 3 Year Before Failure 4 5 Failed 1 2 3 4 5 Year Before Failure Source: W. H. Beaver, “Financial Ratios and Predictors of Failure”, Journal of Accounting Research Tale of Two Cities… Total Debt-to-Total Assets Working Capital-to-Total Assets 0.45 0.40 0.35 0.30 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 0.90 0.80 0.70 0.60 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 0.10 0.00 Failed 1 2 3 4 5 Failed 1 2 3 4 5 Year Before Failure Year Before Failure Rate of Return on Assets 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 -0.05 1 2 3 4 5 -0.10 -0.15 -0.20 Failed -0.25 Year Before Failure Source: W. H. Beaver, “Financial Ratios and Predictors of Failure”, Journal of Accounting Research Tale of Two Cities… Total Debt-to-Total Assets Working Capital-to-Total Assets 0.45 0.40 0.35 0.30 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 0.90 0.80 0.70 0.60 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 0.10 0.00 Failed 1 2 3 4 Failed 1 5 2 5 Net Cash Income-to-Total Debt Rate of Return on Assets 0.15 0.60 0.10 0.50 0.05 0.40 0.30 0.00 2 3 -0.10 4 5 0.20 0.10 0.00 -0.15 -0.20 4 Year Before Failure Year Before Failure -0.05 1 3 -0.10 1 -0.20 Failed -0.30 -0.25 Year Before Failure 2 3 4 5 Failed Year Before Failure Source: W. H. Beaver, “Financial Ratios and Predictors of Failure”, Journal of Accounting Research Multiple Uses of Financial Indicators #1:Historical Analysis A look backwards like the Beaver study. Comparison of current performance with past performance. Recommend doing this at the enterprise level as well as for the farm as a whole. Rate of Return on Assets 0.10 0.05 0.00 -0.05 1 2 3 -0.10 -0.15 -0.20 -0.25 Prior Years 4 5 #1:Historical Analysis A look backwards like the Beaver study. Comparison of current performance with past performance. Recommend doing this at the enterprise level as well as for the farm as a whole. Why is ROA falling? Rate of Return on Assets 0.10 0.05 0.00 -0.05 1 2 3 -0.10 -0.15 -0.20 -0.25 Prior Years 4 5 #2:Comparative Analysis Comparing current performance with similar operations like the Beaver study. Benchmark analysis at enterprise level when possible. Rate of Return on Assets 0.15 Benchmark 0.10 0.05 0.00 -0.05 -0.10 1 2 3 Your firm -0.15 -0.20 -0.25 Prior Years 4 5 #2:Comparative Analysis Comparing current performance with similar operations like the Beaver study. Benchmark analysis at enterprise level when possible. Address reasons why your firm is performing more poorly than other comparable operations before it is too late. Rate of Return on Assets 0.15 Benchmark 0.10 0.05 0.00 -0.05 -0.10 1 2 3 Your firm -0.15 -0.20 -0.25 Prior Years 4 5 #2:Comparative Analysis Comparing current performance with similar operations like the Beaver study. Benchmark analysis at enterprise level when possible. Address reasons why your firm is performing more poorly than other comparable operations before it is too late. Rate of Return on Assets 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 -0.05 1 2 3 -0.10 -0.15 -0.20 -0.25 Prior Years 4 5 #2:Comparative Analysis Comparing current performance with similar operations like the Beaver study. Benchmark analysis at enterprise level when possible. Address reasons why your firm is performing more poorly than other comparable operations before it is too late. Rate of Return on Assets 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 -0.05 1 2 3 -0.10 -0.15 -0.20 -0.25 Prior Years 4 5 #2:Comparative Analysis Comparing current performance with similar operations like the Beaver study. Benchmark analysis at enterprise level when possible. Address reasons why your firm is performing more poorly than other comparable operations before it is too late. Rate of Return on Assets 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 -0.05 1 2 3 -0.10 -0.15 -0.20 -0.25 Prior Years 4 5 #2:Comparative Analysis Comparing current performance with similar operations like the Beaver study. Benchmark analysis at enterprise level when possible. Address reasons why your firm is performing more poorly than other comparable operations before it is too late. Rate of Return on Assets 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 -0.05 1 2 3 -0.10 -0.15 -0.20 -0.25 Prior Years 4 5 #3:Pro Forma Analysis Stress testing current expected cash flows by varying prices, unit costs and yields. Look at implications of longer run price and unit cost trends on future financial health when making major decisions. Sources of Uncertainty Global trends in production and consumption Energy prices and core inflation trends Interest rates and exchange rates Changes in industry subsidies Reading the Signs What PV is Road designed to do... in Financial Management Demonstrate future consequences of existing and alternative concentrations Assess key external factors in strategic planning Facilitate proactive as opposed to reactive management Provide minimum 3-year pro forma financials required in Business Plan (FCA Reg. 12) Will export demand improve? Pro Forma Analysis When going down the road, use the windshield as well as the rear view mirror! Some Signs Are Confusing… Some Signs are Hard to Read... Ignoring Adverse Trends has its Consequences….