US History
advertisement

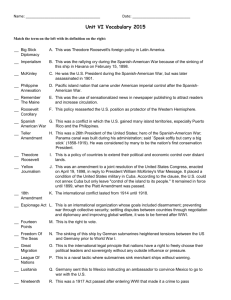
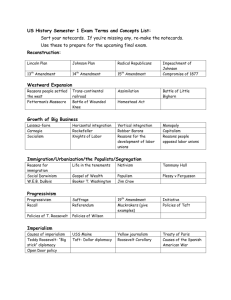
EOC REVIEW Unit 1: West and Gilded Age Defining Characteristics Late 1800’s Factory system Population shift to cities Inventions/industrialism Immigration Urbanization Political corruption and political machines Entrepreneurship (growth of big business) Philanthropy Indian policies Labor unions Growth of railroad (transcontinental) Cattle industry boom Westward movement and the Homestead Act Laissez-faire Key Terms Dawes Act Tammany Hall Boss Tweed Populism Homestead Strike Pullman Strike Haymarket Riot Andrew Carnegie John D. Rockefeller Labor Unions Chisholm Trail “Robber Barons vs Captains of Industry” Chinese exclusion Act Nativism Urbanization Settlement Houses Gospel of Wealth Klondike Gold Rush Homestead Act Bessemer Process You should know: 1. Indian policies during this era 2. Civil Service reforms during this era 3. Understand the growth of business and industrialization a. Factories b. Railroad 4. Understand the growth of labor unions 5. Cattle industry boom 6. Social issues during the time a. Nativism b. Growing poor c. Social Gospel movement 7. Causes and effects of settlement in the Great Plains 8. The effects of the Transcontinental Railroad 9. Scientific discoveries of the era a. Electricity, Telephone, Petroleum-based products, Steel production Unit 2: Freedom Week Defining Characteristics Freedom Liberty Key Terms Declaration of Independence Executive Orders Alexis de Tocqueville You Should Know 1. The structure of the US Government a. Branches b. Checks and Balances c. Powers and responsibilities of each branch 2. Alexis de Tocqueville's five values crucial to America's success as a constitutional republic: liberty, egalitarianism, individualism, populism, and laissez-faire. 3. The significance of E Pluribus Unum Unit 3: Progressive Era Defining Characteristics Progressive Era (1890-1920) Opposed corruption and waste in government Concerned with social injustice Interested in government reform at all levels Civil Service Reform Anti-trust acts Populism Interested in government reform at all levels Muckrakers Reform 16th, 17th, 18th and 19th Amendments Suffrage Prohibition Pure Food and Drug Act Federal Reserve Social Gospel Movement Key Terms 16th amendment 17th amendment 18th amendment 19th amendment Initiative Referendum Recall The Jungle Susan B. Anthony Ida B. Wells Social Gospel Movement W.E.B duBois Booker T. Washington Muckrakers *Populist Party/Populism laissez-faire Sherman Anti-Trust Act Interstate Commerce Commission Pure Food and Drug Act Lobbying You should know: 1. The impact of Progressive Era reforms (how it helped Americans participate in government more) 2. President Teddy Roosevelt’s policy on land conservation (and how he established the National Park system) 3. 4. Technological innovations and business practices of the era (electricity light bulb, patents, etc.) Understand how technology improves the standard of living in the United States a. Electricity b. Automobiles c. Telegraph d. Radio Unit 4: Rise of World Power Defining Characteristics (1890’s-1920) Spanish American War and Expansionism – acquisitions of land (Guam, Hawaii, Philippines, and Puerto Rico) Latin America – Panama Canal World War I (1914-1918) – Woodrow Wilson, League of Nations, total war, technological advances, Treaty of Versailles Key Terms Spanish-American War Henry Cabot Lodge Alfred Thayer Mahan Rough Riders Sanford B. Dole Panama Canal Platt Amendment Open Door Policy Dollar Diplomacy Zimmerman Telegram General John J. Pershing Espionage Act 1917 Selective Service Act Battle of Argonne Forest Wilson’s “Fourteen Points” Treaty of Versailles (after WWI, there are many others!) You should know: 1. What was the Spanish-American War, and how did it help transform the United States into a world power 2. Why and how the United States expanded as an imperial power 3. The causes of WWI, and for United States entry into the war 4. The US’s need/want for the Panama Canal 5. The impact of technology in warfare during WWI a. Poison gas, trench warfare, first tanks 6. America’s policy of isolationism before WWI 7. The basic outline and intention of Wilson’s “Fourteen Points” 8. The economic effects of the Spanish-American War and WWI 9. Technological innovations and scientific discoveries as a result of the Spanish-American War and WWI (antibiotics, vaccines, new weapons, etc.) Unit 5: Transition to Modern America Defining Characteristics Twenties 1920-1929: Isolationism Immigration Red Scare Jazz Age Social Darwinism Eugenics Nativism Changing role of women/"flappers" Economic boom/consumerism Prohibition/18th Amendment Key Terms Social Darwinism Eugenics Nativism Red Scare Prohibition The Great Migration Clarence Darrow William Jennings Bryan Scopes Monkey trial Henry Ford Assembly line manufacturing Marcus Garvey Charles Lindbergh Teapot Dome Scandal 18th Amendment* 19th Amendment* Harlem Renaissance You should know: 1. That the stock market crashed in 1929 2. The causes and effects of immigration and race relations during this era 3. The changing role of women during this era 4. The causes and effects of Prohibition 5. The causes and effects of the Great Migration 6. How Americans tried to naturalize Native Americans Unit 6: The Great Depression and the New Deal Defining Characteristics Depression (1929-1941) o Crash of stock market o Great Depression o Dust Bowl New Deal o Expansion of the Federal government o Relief, Reform, Recovery Key Terms The New Deal The Dust Bowl Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) Security and Exchange Commission (SEC) Social Security Administration (SSA) Agriculture Adjustment Act (AAA) Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) Federal Housing Administration (FHA) You should know: 1. Causes of the Great Depression a. Bank failures, over-speculation/stock market crash, tariffs, policies of the “Fed” 2. Effects of the Great Depression 3. The causes and effects of the Dust Bowl 4. Arguments against the New Deal 5. Why Franklin D. Roosevelt tried to “pack” the Supreme Court, and the criticisms against him for it Unit 7: America reacts to a World at War Defining Characteristics Totalitarianism Alliances Pearl Harbor Internment Home front (volunteerism, victory gardens and war bonds) Mobilization Key Terms Pearl Harbor Fascism Communism Adolf Hitler Joseph Stalin Winston Churchill Lend-Lease Act Executive Order 9066 Victory Garden War Bonds Vernon J. Baker You should know: 1. Reasons for US involvement in WWII a. Rise of dictatorships (know where and how) b. Dictatorships expanding territory (Japan, Germany, and Italy) 2. American responses to fighting WWII as a result of Patriotism a. Victory Gardens, Women and Minority employment, war bonds, high levels of enlistment 3. The effects of WWII on the home front a. Ending the Depression (and why), rationing, changes in manufacturing, Unit 8: World War II Defining Characteristics: Axis Powers and Allied Powers Multiple-front war Military leaders Significant contributions of groups Key Terms Holocaust Higgins Boat M1 Garand Manhattan Project Battle of Midway Bataan Death March D-Day/Invasion of Normandy Omar Bradley Dwight D. Eisenhower Joseph MacArthur George Patton Tuskegee Airmen Double-V Campaign Navajo Code Talkers Flying Tigers Potsdam Conference You Should Know 1. President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s relationship with Churchill and Stalin, compared to President Truman’s 2. How technological innovations changed warfare a. M1 Garand, Tanks, Higgins boat, submarines, torpedo’s etc. b. Atomic weapons 3. The effects of fighting a war on multiple fronts 4. The effects of concentration camp liberation Unit 9: Onset of Cold War Defining Characteristic: Ideological war against Communism HUAC Truman Doctrine Marshall Plan Berlin Airlift NATO Domino Theory/containment Korean Conflict McCarthyism Space Race Cuban Missile Crisis Key Terms: HUAC Sen. Joseph McCarthy McCarthyism Truman Doctrine Marshall Plan Sputnik NATO Containment Berlin Airlift Cuban Missile Crises Beat Generation Iron Curtain Berlin Wall Venona Papers Space Race Arms Race Korean War Baby Boom GI Bill NDEA You should know: 1. 2. How the United States responded to Soviet Aggression after WWII a. Truman Doctrine b. Containment c. Marshall Plan d. NATO e. Berlin Airlift f. Cuban Missile Crises How/why Cold War tensions were escalated a. Arms Race b. Space Race c. McCarthyism d. Venona Project 3. 4. 5. 6. The reasons for US involvement in the Korean War The Outcomes of the Korean War The effects of population growth/distribution in the United States (i.e. effects of the Baby Boom, the GI Bill, and Suburbanization) The positive and negative results of the Beat Generation and Rock n’ Roll (i.e. Elvis) Unit 10: Civil Rights Movement Defining Characteristics: Political organizations Civil Rights Acts (1957 and 1964) Voting Rights Act of 1965 Various approaches to advocacy Significant Supreme Court cases Presidential actions and congressional votes Significant leaders Key Terms Civil Rights Acts (1957 and 1964) Voting Rights Act of 1965 13th amendment 14th amendment *19th amendment 24th amendment NAACP *W.E.B. duBois *Booker T. Washington Rosa Parks Martin Luther King Jr. Malcolm X Orval Faubus Thurgood Marshall Gov. George Wallace Caesar Chavez Black Panther Party LULAC “I have a Dream” speech “Letter from Birmingham Jail” *Plessy v Ferguson Brown v. Board of Education “Great Society” Affirmative Action Title IX You should know: 1. How Civil Rights developed and changed throughout American history 2. Significant leaders of the Civil Rights movement 3. The differences and similarities between non-violent and militant protest in the Civil Rights movement 4. How Americans participate in the political process a. Lobbying b. Non-violent protest c. Court decisions d. Litigation e. Amending the Constitution UNIT 11: New Frontiers and Familiar Enemies Defining Characteristics New Frontier – John F. Kennedy Great Society – Lyndon B. Johnson Economic Changes o Cold war fueled business o Policy Changes o Cold war fueled need for Math and Science fields (NDEA) Key Terms Tet Offensive Vietnamization Fall of Saigon * ”Great Society” Draft 26th Amendment Credibility Gap Silent Majority National Defense Education Act (NDEA) Gulf of Tonkin incident War Powers Resolution Tinker v Des Moines You Should Know: 1. Reasons for US involvement in the Vietnam War 2. The outcomes of the Vietnam War 3. Major events in the Vietnam War 4. Responses to the Vietnam War by Americans Unit 12: 1970-1990 Defining Characteristics Nixon’s relationship with China Reaganomics: supply-side economics, trickle-down economics (reduce government spending, reduce federal income tax and capital gains tax, reduce government regulation, and tighten money supply to reduce inflation) “Peace through Strength”: peace comes through showing we have strength but hopefully not using it Involvement in the Middle East Conservative resurgence Key Terms Reaganomics Camp David Accords Iran Hostage Crises The Iran-Contra Affair Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) founded to manage oil supply General Agreement of Tariff and Trade (GAAT) passed after WWII to regulate world trade to aid economic recovery following the war The Heritage Foundation—American conservative think tank in leading role of conservative movement 1973 (Reagan) Watergate The Moral Majority: associated with Christian right and Republican party 1970s-1980s The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) protecting human health and the environment by writing and enforcing regulations (Nixon 1970s) You Should Know: 1. How President Nixon normalized the relationship between China and the United States 2. Domestic and International policies of President Reagan 3. US involvement in the Middle East a. Relationship with Israel (support) b. 4. 5. Camp David Accords (signed by Egypt and Israel following 12 days of secret negotiations for peace here—Jimmy Carter President) c. Iran Hostage Crises 1979-1981 Carter president; 52 American diplomats held by Iranian students who took over Embassy in Tehran; failed attempts to get them; released when Reagan president) d. Marines in Beirut under Reagan 1983 299 Americans died from bombing “Islamic Jihad” claimed responsibility e. Iran-Contra affair 1980s secret arrangement to fund Nicaragua contra rebels from profits gained by selling arms to Iran; Reagan president Causes and effects of Americans moving from the Rust Belt to the Sun Belt The effects of scientific discoveries and inventions on the United States a. Satellite Communication b. Computers c. How Space exploration improves the quality of life Unit 13: 1990-Present Defining Characteristics U.S. Involvement in world affairs Persian Gulf War (Operation Desert Storm) 1990-1991 Iraq’s invasion of Kuwait (America has victory over Iraq) Balkans Crisis (Yugoslav Wars) ethnic conflicts fought from 1991-2002 inside territory of Yugoslavia September 11, 2001 Long term effects of government entitlement programs 2008 Presidential election Key Terms: 5th Amendment North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) agreement by Canada, Mexico, and US 1994 concerning trade blocs in North America Patriot Act 2001 signed by GHWB allows investigators tools to intercept and monitor organized crime and drug trafficking You should know: 1. The United States’ involvement in world affairs a. End of the Cold War b. The Persian Gulf War c. The Balkans Crises d. 9/11 attacks e. Global War on Terror 2. The impact of third parties on Presidential elections (Ralph Nadar) 3. The causes and effects of Hurricane Katrina 4. Causes and effects of immigration to the United States 5. Why/how President Clinton was impeached 6. The impact of the relationship between the branches of government in the 2000 Presidential elections