Unit 6 vocab 2015 - McEachern High School
advertisement
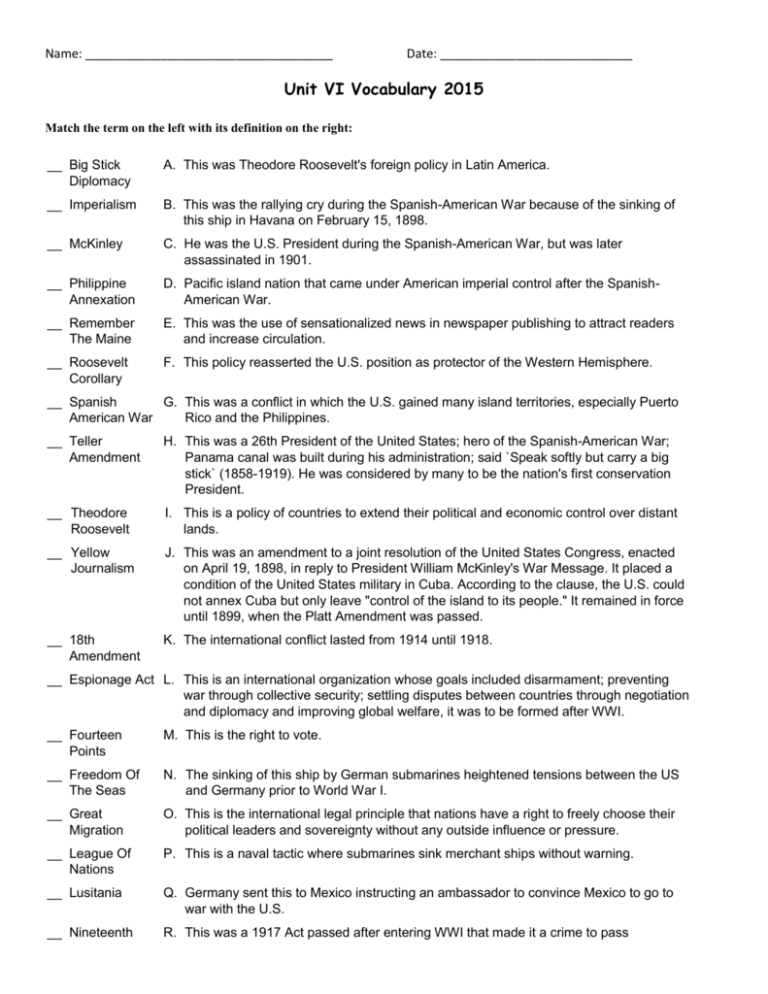
Name: ____________________________________ Date: ____________________________ Unit VI Vocabulary 2015 Match the term on the left with its definition on the right: __ Big Stick Diplomacy A. This was Theodore Roosevelt's foreign policy in Latin America. __ Imperialism B. This was the rallying cry during the Spanish-American War because of the sinking of this ship in Havana on February 15, 1898. __ McKinley C. He was the U.S. President during the Spanish-American War, but was later assassinated in 1901. __ Philippine Annexation D. Pacific island nation that came under American imperial control after the SpanishAmerican War. __ Remember The Maine E. This was the use of sensationalized news in newspaper publishing to attract readers and increase circulation. __ Roosevelt Corollary F. This policy reasserted the U.S. position as protector of the Western Hemisphere. __ Spanish G. This was a conflict in which the U.S. gained many island territories, especially Puerto American War Rico and the Philippines. __ Teller Amendment H. This was a 26th President of the United States; hero of the Spanish-American War; Panama canal was built during his administration; said `Speak softly but carry a big stick` (1858-1919). He was considered by many to be the nation's first conservation President. __ Theodore Roosevelt I. This is a policy of countries to extend their political and economic control over distant lands. __ Yellow Journalism J. This was an amendment to a joint resolution of the United States Congress, enacted on April 19, 1898, in reply to President William McKinley's War Message. It placed a condition of the United States military in Cuba. According to the clause, the U.S. could not annex Cuba but only leave "control of the island to its people." It remained in force until 1899, when the Platt Amendment was passed. __ 18th Amendment K. The international conflict lasted from 1914 until 1918. __ Espionage Act L. This is an international organization whose goals included disarmament; preventing war through collective security; settling disputes between countries through negotiation and diplomacy and improving global welfare, it was to be formed after WWI. __ Fourteen Points M. This is the right to vote. __ Freedom Of The Seas N. The sinking of this ship by German submarines heightened tensions between the US and Germany prior to World War I. __ Great Migration O. This is the international legal principle that nations have a right to freely choose their political leaders and sovereignty without any outside influence or pressure. __ League Of Nations P. This is a naval tactic where submarines sink merchant ships without warning. __ Lusitania Q. Germany sent this to Mexico instructing an ambassador to convince Mexico to go to war with the U.S. __ Nineteenth R. This was a 1917 Act passed after entering WWI that made it a crime to pass information that would interfere with the success of the US Armed Forces. __ Prohibition S. This amendment prohibited the sale and use of alcoholic beverages. __ Self T. He was 28th President of the United States; led the United States in World War I and Determination secured the formation of the League of Nations. __ Suffrage U. This was a movement to give females the right to vote. __ Unrestricted Submarine Warfare V. This was the outlawing of the sale, production, or transportation of alcoholic beverages. __ Women's Suffrage W. This was a major component of Woodrow Wilson's 'Fourteen Points,' especially since unrestricted submarine warfare was a major component of World War I. __ Woodrow Wilson X. This was the content of a speech given by U.S. President Woodrow Wilson describing his plan for European reconstruction after WWI. __ World War I Y. This was the large movement of African Americans from the Southern U.S. to the Northern U.S. in the early-20th century. __ Zimmerman Note Z. This amendment guaranteed that all women in the United States would have the right to vote.