Management of PUD, H. pylori infection
advertisement

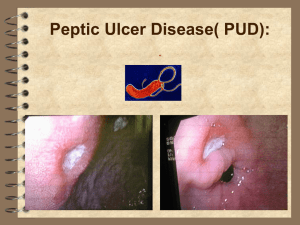
Management of PUD, H. pylori infection 4th Med Pharmacology 27/10/05 Introduction PUD = ulceration of gastroduodenal mucosa (usually extending through muscularis mucosa) Prevalence 5-10% 50% of these have recurrence within 5 yrs Discovery of H. pylori of great importance diagnostically & therapeutically in PUD (Nobel prizeMarshall & Warren) H. pylori cultured from stomach of ~90% DU pts & ~80% GU pts Eradication of H. pylori ↓ recurrence of PUD by ~7590% Pathogenesis of PUD Not fully understood, but 3 major factors identified Factor Treatment approach Infection with gram-negative H. pylori Eradication of H. pylori infection, e.g. triple tx ↑ gastric HCl secretion ↓ HCl secretion or neutralizing it, e.g. H2 antagonists, pirenzepine, antacids Inadequate mucosal defence against gastric HCl Agents that protect gastric mucosa, e.g. sucralfate Importance of treating PUD Gastric ulcers: 5% malignant Endoscopic biopsy at time of initial diagnosis recommended & repeat endoscopy after 6-8 wks tx Surgical tx for nonhealing GU Duodenal ulcers: Usually not malignant If pt asymptomatic do not need to prove ulcer healing Many heal without tx H2-receptor antagonists, sucralfate & high dose antacids shown to ↑ rate of healing and % of ulcers that heal. Drug tx has 7085% incidence ulcer healing at 6 wks cf placebo (~40%) Importance of treating PUD (contd) Complications of PUD 1) GI bleeding Gastric outlet obstruction Perforation Penetration into pancreas Intractability 2) 3) 4) 5) Stomach Stomach Duodenum Non-pharmacological measures to treat PUD Diet Stop smoking Avoid aspirin/NSAIDs. Enteric coating or anti-ulcer tx may ↓ mucosal damage from aspirin. In pts with strong indications for NSAID tx treating with PPI, H2-R antagonists, sulcralfate or misoprostil may relieve symptoms. Tx with a COX 2 selective NSAID [CI CVS problems] Avoid C2H5OH Drugs used to treat PUD Antimicrobial H2-Histamine Prostaglandins Agents R Blockade Amoxicillin Bismuth Clarithromycin Metronidazole Tetracycline Cimetidine Famotidine Nizatidine Ranitidine Misoprostol PPI Lansoprazole Omeprazole Antimuscarinic Agents Pirenzepine Antacids Al(OH)3 [Mg(OH)2] CaCO3 Mucosal Protective Agents Bismuth Sulcralfate H. pylori Eradication 1) 2) 3) 4) If GU/DU identified by upper endoscopy/radiographic study need to determine if H.pylori present Diagnostic tests include: Serologic testing C-13 urea breath test Urease assay (Clotest) Culture/histological analysis of endoscopic biopsy Majority of PU can be healed with H2-antagonists/PPI alone, but relapse of sx occur in up to 80% pts within 1 yr cf 8% if treated with H.pylori eradication tx. Current recommendations for tx of H. pylori Test for H.pylori before starting eradication tx If H. pylori test is positive, use eradication tx If H. pylori test is negative, treat with lansoprazole (Zoton) 30mg OD. Use for 4 wks for DU, 8 wks for GU. May use lansoprazole 15mg OD to prevent relapse Eradication of H. pylori Eradication defined as negative tests for the bacterium 4 wks or more after the end of tx Current recommendations for tx of H. pylori 1st line eradication tx for H. pylori 2nd line tx Preferred tx= PPI PO + Clarithromycin 500mg BD PO + Amoxicillin 1 gm BD PO for 7 days PPI + Bismuth 120mg QDS PO + Metronidazole 500mg TDS PO + Tetracycline 500mg QDS PO for 7 days If Penicillin allergic= PPI + Clarithromycin 500mg BD PO + Metronidazole 400mg BD PO for 7 days E.g. of PPI: Lansoprazole 30mg BD PO Subsequent failures handled on individual basis with advice from gastro/micro H. pylori eradication 1 week triple-therapy regimens eradicate H.. Pylori in >90% cases. Usually no need for continued antisecretory tx unless ulcer complicated by bleeding/perforation 2 week triple-therapy offer higher eradication rates cf 1 week but SE common & poor compliance 2-week dual-therapy with PPI & antibacterial produce low rates of H. pylori eradication & not recommended H. pylori eradication Treatment failure may be due to - Resistance to antibacterial drugs - Poor compliance Drug Side effects Bismuth n&v, unpleasant taste, darkening of tongue & stools, caution in renal disease Metronidazole n&v, unpleasant taste, ↓effectiveness OCP, care with lithium/warfarin Amoxicillin & tetracycline GI side effects, ↓ effectiveness OCP, pseudomenbranous colitis Lansoprazole ↓ effectiveness OCP H2-receptor antagonists MOA: Competitively block binding of histamine to H2 R, ↓ intracellular cAMP & secretion of gastric acid. Reversible Egs: Cimetidine, ranitidine, famotidine & nizatidine Effective for acute/chronic DU & benign GU. Recurrence common after tx with H2-R antagonists alone is stopped. Mainly renal excretion H2-receptor antagonists Drug Side effects Cimetidine -reversible impotence, gynaecomastia & ↓ sperm count (high doses) (nonsteroidal antiandrogen) -mental status abnormalities-confusion, hallucinations (elderly/renal impairment) -leukopenia & thrombocytopenia (rare) -cytochrome P450 inhibitor (e.g. impairs metabolism of warfarin, theophylline & phenytoin) Ranitidine, fanotidine, nizatidine -Impotence, gynaecomastia & confusion less frequently than cimetidine. -Little interference with cytochrome P450 -Reversible drug-induced hepatitis with all H2-antagonists Proton-pump Inhibitors (PPI) • MOA: blocks parietal cell H+/K+ ATPase enzyme system (proton pump) ↓ secretion of H+ ions into gastric lumen • Heals erosive oesophagitis more effectively than H2antagonists. Used in antimicrobial regimens to eradicate H. pylori • SE: n&v, diarrhoea, dizziness, headaches, gynaecomastia & impotence (rare), thrombocytopenia, rashes • Dose: 20mg/day omeprazole in acute tx of DU Mucosal Protective Agents 1) Sulcralfate MOA: Binds to positively charged proteins present on damaged mucosa forming a protective coat Useful in “stress ulceration” As effective as H2-R antagonists/high dose antacids in healing of DU SE: Constipation ↓absorption of cimetidine, digoxin, phenytoin & tetracycline 2) Bismuth MOA: Antimicrobial action. Also inhibit pepsin activity, ↑mucus secretion & interact with proteins in necrotic mucosal tissue to coat & protect the ulcer crater Antacids • MOA: Weak bases that react with gastric acid to form H20+salt. ↓pepsin activity as pepsin inactive at pH>4 • Symptom relief, liquids>tablets • E.g. Maalox = [Mg(OH)2] + Al(OH)3 Drug Side effect [Mg(OH)2] severe osmotic diarrhoea (therefore combined with AlOH) Al(OH)3 ↓phosphate, ↓absorption of tetracycline, thyroxine & chlorpromazine, constipation CaCO3 ↑Ca in blood & urine (high doses) Antimuscarinic drugs • Not successful b/c of general unwanted antimuscarinic effects • Muscarinic R stimulation ↑ GI motility & secretory activity • Pirenzipine: Some selectivity due to affinity for & blockade of M1-receptors in autonomic ganglia (low affinity for M2-receptors of smooth muscle of ileum & bladder) In stomach appears to inhibit transmission in parasympathetic enteric ganglia. Used as adjunct in refractory PUD & Zollinger-Ellison syndrome Poorly absorbed from GIT and excreted mainly unchanged in urine & bile Doesn’t cross BBB SE: Dry mouth, visual disturbances, agranulocytosis & thrombocytopenia Prostaglandin analogues • Endogenous prostaglandins (PGE2 & I2) contribute to GI mucosa integrity by -stimulation of mucus & bicarbonate secretion -maintenance of blood flow (allows removal of luminal H-ions) -prevention of luminal H-ions from diffusing into the mucosa (e.g. in response to C2H5OH) -↓ of gastric acid secretion -helping to repair damaged epithelium • Gastric & duodenal mucosal damage & chronic PU associated with the use of NSAIDs may derive from interference with the cytoprotective action of prostaglandins • Misoprostol = synthetic prostaglandin E1 analogue Prevents NSAID induced ulcers & heals chronic GU & DU SE: Abdo pain, n&v, diarrhoea, abortifacient (produces uterine contractions) NSAID-associated ulcers • GI bleed & ulceration can occur with NSAIDs. If possible withdraw NSAID if ulceration. Consider alternative analgesia • If at risk of ulcer a PPI, H2-R antagonist or misoprostol may be considered for protection against NSAID-associated ulcers. Colic & diarrhoea may limit use of misoprostol • If NSAID treatment needs to continue -treat ulcer with PPI & on healing of ulcer continue with PPI -treat ulcer with PPI & on healing switch to misoprostol for maintenance tx Caution COX-2 inhibitors & CVS events Because of concerns re CVS safety, COX-2 inhibitors should only be used in preference to standard NSAIDs only when specifically indicated & after assessment of CVS. Pts receiving COX-2 inhibitor & who have IHD or cerebrovascular disease should be switched to alternative asap Associated Gastric Conditions Zollinger-ellison syndrome Rare gastrin-secreting, non-ß islet cell tumour of the pancreas or duodenum →gastric acid hypersecretion 2/3rd Zollinger-ellison tumours malignant MEN-1 associated with Zollinger-ellison syndrome in ¼ cases Presents with DU (single/multiple) + diarrhoea Tx: Control of ↑acid with H2-R antagonists & PPI at much higher doses than those used for PUD Non-ulcer dyspepsia Syndrome of persistent ulcer-like symptoms in absence of radiographic & endoscopic abnormalities May be explained by motor abnormalities, microscopic inflammation, H. pyloriassociated gastritis & associated psychiatric disease Tx: Empiric. Some may benefit from psychoactive agents e.g. TCADs GORD GORD = Symptoms of “heartburn” General advice includes AVOIDING Drug Tx Meals antacids=+/-alginic at night, lying down after meals Elevate head of bed Heavy lifting, tight clothing, bending Being overweight Smoking (nicotine relaxes lower oesophageal sphincter) Aggravating substances (spicy foods, C2H5OH) Drugs which encourage reflux (e.g. antimuscarinic, smooth muscle relaxants, theophylline) acid Pro-kinetic agent, e.g. metoclopramide H2-antagonist PPI If severe sx when tx stopped, or bleed from oesophagitis or stricture maintenance tx with PPI or surgery may be necessary GI haemorrhage Risk factors for ↑ morbidity/mortality 1) Age > 60yrs 2) Additional co-morbid illness/es 3) Bright red haemetemesis & ↓ BP 4) Large (>2 cm ulcers) 5) Shock 6) Recurrent bleed Need to maintain adequate circulatory volume in order to localise bleeding site and institute tx Management of upper GI haemorrhage 1) Resuscitation and stabilisation Assess haemodynamic status Frequent vital signs HR & BP Blood for FBC, coag, grp & cross-match GI haemorrhage (contd) 2) Tx IVF. Hypovolaemia is usually the cause of the ↓BP so should initiate restoration of intravascular volume. Vasopressors generally not indicated. Blood transfusion if bleeding massive, ongoing or severe Coagulopathy may require FFP Thrombocytopenia may require platelet transfusion ET intubation to prevent aspiration CVP monitoring to guide fluid replacement Early consult with gastroenterologist, surgeon, or invasive radiologist when significant haemorrhage, continued instability or active bleeding 3) Upper GI bleeding diagnosed by • OGD (diagnostic &/or therapeutic) • Arteriography • Upper GI barium study Treatment of different lesions Peptic ulcer haemorrhage Most stop bleeding spontaneously 1) Endoscopy – thermal coagulation, injection tx, haemostatic clips 2) Surgery – e.g. if failure of endoscopic tx, haemodynamic instability despite resuscitation, recurrent haemorrhage, shock, continued bleed requiring > 3 units/day. Tx include oversewing of artery + truncal vagotomy + pyloroplasty, antrectomy, gastrojejunostomy (Billroth procedure), highly selective vagotomy 3) Arterial angiotherapy (arterial vasopressin/embolisation) 4) Intravenous PPI. Better able to maintain gastric pH > 6 & protect ulcer clot from fibrinolysis 5) H2-antagonists. Not in active bleed. ?effective in ↓recurrent bleed Treatment of different lesions Mallory-Weiss tear: Mucosal tear at GO junction. Most stop spontaneously. May need therapeutic endoscopy or arterial angiography Aortoenteric fistula: Usually aorto-duodenal. Usually hx previous aortic graft surgery. Tx: surgery Stress ulceration: Pts with head injuries, burns, major trauma, shock, sepsis, respiratory failure, coagulopathy. Prophylactic tx with H2-R antagonists, sucralfate & antacids in pts at risk