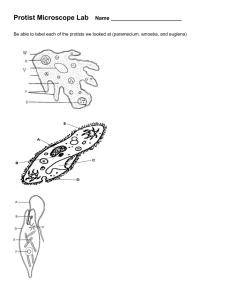
Terms Used in Part 1 Microbes
advertisement

Terms Used in Part 1 Microbes Amoeba: an animal-like protist Bacteria: unicellular organisms that lack membrane-bound structures; a common term used to describe prokaryotes. Cilia: a short hair-like appendage used by microorganisms for motion. Eukaryote: either unicellular or multi-cellular organism that contains membrane-bound organelles and genetic material within a nucleus. Flagellum: a whip-like structure on unicellular organisms that aids with movement. Microbe: any organism or near life form that cannot be seen with the naked eye. Paramecium: a protist. Parasite: an organism that derives nourishment or habitat from the tissues or fluids of another organism. A eukaryotic pathogen can be unicellular or multi-cellular. Prokaryote: a unicellular organism that lacks a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelle. Protist: generally, a single-celled organism with a nucleus and organelles, including amoebas, euglenas, paramecia and volvox. Pseudopod: an extension of the cytoplasm used for movement in some organisms. A means of locomotion for an amoeba; literally, “false foot.” Virus: a particle consisting of DNA encased in a protein coat that must inject its DNA into a living cell in order to reproduce. A microbe that consists of nucleic acid enclosed within a protein shell that requires a living cell in order to reproduce. Scientists consider the virus to be not alive