protist
advertisement
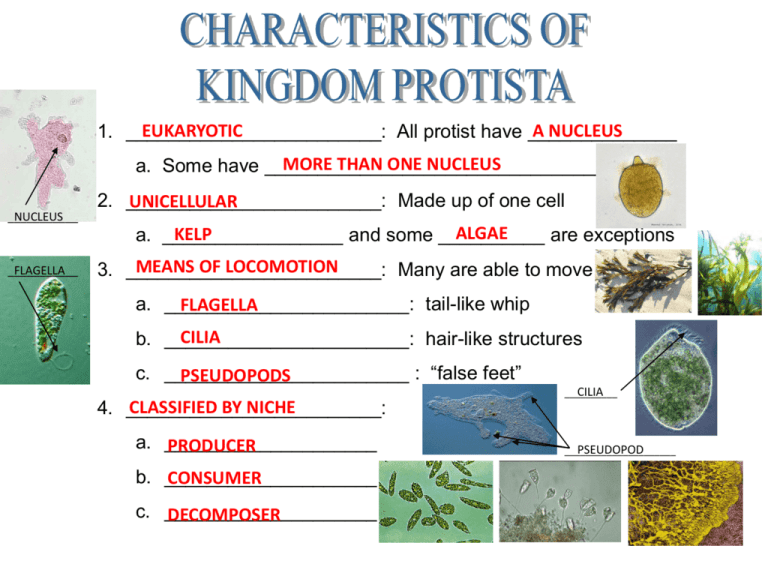
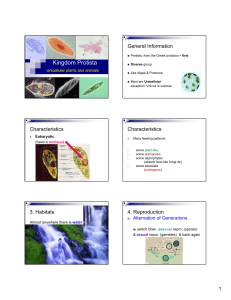
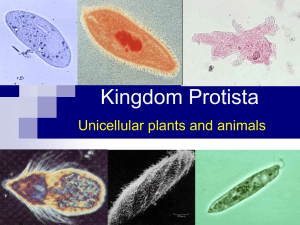
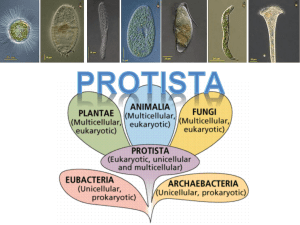
EUKARYOTIC A NUCLEUS 1. ________________________: All protist have ______________ MORE THAN ONE NUCLEUS a. Some have _________________________________ ___________ NUCLEUS 2. ________________________: Made up of one cell UNICELLULAR ALGAE KELP a. _________________ and some __________ are exceptions ___________ FLAGELLA MEANS OF LOCOMOTION 3. ________________________: Many are able to move a. _______________________: tail-like whip FLAGELLA CILIA b. _______________________: hair-like structures c. _______________________ : “false feet” PSEUDOPODS CLASSIFIED BY NICHE 4. ________________________: a. ____________________ PRODUCER b. ____________________ CONSUMER c. ____________________ DECOMPOSER CILIA __________ PSEUDOPOD _____________________ 1. __________________________: CONSUMERS a. Also known as ___________________ First Animal 2. __________________________: PRODUCERS 3. __________________________: DECOMPOSERS AMOEBA Observations: PARAMECIUM Observations: STENTOR Observations: VORTICELLA Observations: TRYPANOSOMA Observations: PLASMODIUM Observations: EUGLENA Observations: VOLVOX Observations: DINOFLAGELLATES Observations: DIATOM Observations: SPIROGYRO Observations: BROWN ALGAE Observations: 1. _____________________ number of species in Kingdom Protista LARGEST SIMILARITIES 2. Many ___________________ are shared between animal-like protist and animals. The KEY difference is their ___________________________ BODY ORGANIZATION a. All animals are _____________________ MULTICELLULAR b. All animal-like protist are ________________ UNICELLULAR 3. ___________________-term often used to describe animal-like PROTOZOA protist. a. PROTOZOA FIRST ANIMAL PARAMECIUM VORTICELLA DIDINIUM AMOEBA ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ CONSUMERS 1. All are ________________________: a. CAN NOT make their own ____________ FOOD MOBILITY 2. Most have methods of ____________________ a. _____________________:Long “tail-like” projection FLAGELLA CILIA HAIR-LIKE b. _____________________:Tiny _______________ extensions FALSE FEET PSEUDOPODS c. _____________________:“________________” * ______________ extension from the main cell CYTOPLASMIC 1. All producers contain __________________ and can make their CHLOROPHYLL own _________________. FOOD 2. Serveral differences between plants and plant-like protist: MULTICELLULAR a. All plants are _____________________ b. Animal-like protist can beMULTICELLULAR _____________ or _____________ UNICELLULAR ROOTS, STEMS, LEAVES c. Plants have specialized tissues for _____________________ d. Plant-like protists do not have the same _______________ or TISSUES THE SAME REPRODUCTIVE __________________________ parts as plants 3. Many “phytoplankton” are a huge ______________________ for FOOD SOURCE ACQUATIC most _____________________ animals. 4. Produce __________________ as a bi-product of photosynthesis OXYGEN ________________ ________________ ________________ ________________ ECOSYSTEM 1. Play an important role in the ______________________ as ________________. DECOMPOSERS CARBON NITROGEN a. Recycle ________________ and _______________ back into the soil for __________________ use. PLANTS 2. Difference between fungi and fungus-like protist is that fungus-like protist can __________________ during part of their life cycle MOVE CAN NOT MOVE while fungi ___________________________. PROTIST EUKARYOTIC _______________________________ ANIMAL-LIKE _________________________________ NICHE: CONSUMER ________________ _________________ Characteristics of Kingdom Protista: UNICELLULAR _______________________________ _______________________________ PLANT-LIKE _________________________________ ________________ PRODUCER _________________ (AUTOTROPH) NICHE: (HETEROTROPH) _________________ CELL ORGANIZATION: CELL ORGANIZATION: ________________ UNICELLULAR UNICELLULAR OR ________________ FUNGUS-LIKE __________________________ NICHE: ________________ DECOMPOSER _________________ (HETEROTROPH) CELL ORGANIZATION: ________________ UNICELLULAR MULTICELLULAR _________________ MOBILITY: MOST ________________ METHODS OF LOCOMOTION: FLAGELLA ______________ SOME ________________ MOBILITY: METHODS OF LOCOMOTION: ________________ FLAGELLA MOBILITY: ________________ DURING CERTAIN ________________ POINTS IN _____________ LIFECYCLE METHODS OF LOCOMOTION: ______________ PSEUDOPODS PSEUDOPODS _______________ _______________ FLAGELLA CILIA _______________ EXAMPLES: __________ AMOEBA _____________ PARAMECIUM EXAMPLES: EUGLENA VOLVOX DIATOM _________________________ EXAMPLES: _______________ SLIME MOLD