Vocabulary (Micro Life Continued)
advertisement

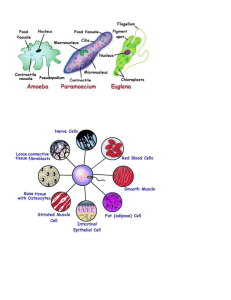
1 Vocabulary Selectively Permeable – when the cell membrane or cell wall only allows certain substances to pass through. Diffusion – the movement of substances from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. Osmosis - the diffusion of water across a membrane. Mitosis – the process by which the cell nucleus divides to form two new nuclei, each having a complete set of chromosomes. Meiosis – the process in which organisms produce gametes or sex cells. Eukaryote – an organism whose cells have a distinct membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Chloroplast – cell organelles that store chlorophyll and serve as the site for photosynthesis. Chlorophyll – the green pigment that captures the energy of the sun to drive photosynthesis. Photosynthesis – a process in which organisms use light energy (sun light) to join carbon dioxide and water to make nutrients. Euglena – unicellular protist with characteristics of both plants and animals. It moves and eats by using its flagellum (whip-like tail). It has a specialized organelle called an eyespot to sense light. It can feed on other organisms (animal-like) and make its own food (plant-like). Amoeba – unicellular protist with animal-like characteristics. It feeds on other organisms. It uses a pseudopod (which is an extension of its cytoplasm) for movement and to engulf its food. Paramecium – unicellular protist with animal-like characteristics. It feeds on other organisms. It is common in ponds and in slow-moving streams. It is almost completely covered with tiny hairs called cilia which it uses for movement. It uses two specialized organelles, an oral groove for feeding and a contractile vacuole that pumps water out of the cell to prevent the cell from bursting with excess water. Volvox – unicellular protist with plant-like characteristics. It makes its own food. It has chloroplasts and can carry out photosynthesis. It does not live alone, it lives in colonies. It uses flagella to propel (move quickly) the colony through water. Prokaryote – unicellular organism that lacks a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Microbe – tiny organism that can only be seen with a microscope. Virus – a particle that consists of a nucleic acid enclosed within a protein shell that requires a living cell in order to reproduce. Capsid – a protein shell that surrounds a virus. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – the nucleic acid responsible for carrying the genetic information of most organisms from one generation to the next. RNA (ribonucleic acid) – a particle that consists of nucleic acid enclosed within a protein shell that requires a living cell in order to reproduce. 2 Cellular Respiration – the process cell use to obtain energy from food. Bacteria - a large group of unicellular, prokaryote, microorganisms that exists everywhere on Earth including places where other forms of life cannot exist. They are spherical, spiral or rod-shaped organisms lacking chlorophyll that reproduce by fission. Contagion – an infectious disease that can be transmitted or spread from one organism to another. Mutagen – anything that changes the DNA of an organism Antimicrobial Product – is a substance that is designed to kill microbes before they can enter the body. Carrier – an organism that is infected with and can transmit a disease-causing microbe to another living thing, even though the carrier shows no symptoms of illness or disease. Parasite – an organism that derives nourishment or habitat from the tissues or fluids of another organism. Pathogen – an organism that causes a disease. Antibody – a chemical substance made by the body to help destroy an invading pathogen. Carcinogen – a chemical that causes cancer. Vector – a living thing that transmits a disease from one organism to another. Host – an organism that harbors a parasite such as a virus, a bacterium, a protozoa, or a fungus. Epidemic – a disease that spreads over a wide geographic area. Active Immunity – protection against a disease acquired by being infected with the pathogen that causes the disease. Passive Immunity – protection against a disease by receiving antibodies made in another individual. Antibiotic – a medicine or group of medicines used to kill or slow the growth of bacteria that cause disease. Dose – the amount of a chemical substance that one individual should take for the desired effect. Vaccine – a biological preparation that improves immunity to a particular disease. It usually has an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism, and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe. Noninfectious Disease – a disease that cannot be spread fro on e organism to another. Infectious Disease – any disease that is caused by a pathogen. Microscopic – a term used to describe objects too small to see with the “naked eye” and require a lens or microscope to see them clearly. Microbiologist – a scientist who studies microbes. Biotechnology – industrial use of living organisms, or parts of living organisms, to produce foods, drugs, or other products.