Biology Midterm Review Stations
advertisement

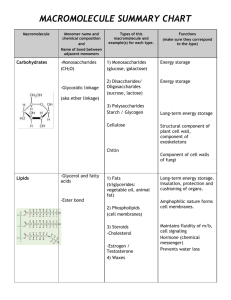
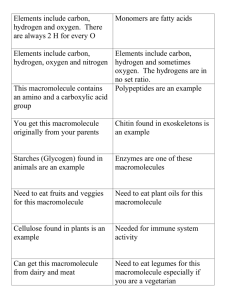
Biology Midterm Review Stations For this review, you may use all of your available materials from notebook, textbook, and your interactive reader. WRITE DOWN YOUR ANSWERS FOR EACH! STATION 1 – SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. Choose one of the following observations or purpose: a. I want to know if a bean plant will grow more quickly outside or inside. b. I want to know if water freezes faster on its own or with sugar added 2. On the handout provided, complete the following information: a. FOCUS QUESTION b. HYPOTHESIS (If – then) c. What will you manipulate or vary? *INDEPENDENT VARIABLE d. CONTROL SET-UP and EXPERIMENTAL SET-UP e. CONSTANTS f. What will you measure? *DEPENDENT VARIABLE g. Make a DATA TABLE, but leave blank as you are not completing the experiment. h. Assume that the data which you collected means that you were completely wrong with your hypothesis. WRITE YOUR CONCLUSION. STATION 2 – GRAPHING, DATA TABLES 1. DATA TABLE: Make a 3-column data table to organize the following weekly temperatures for Palmetto, FL between 1/7-14/14; the first number is the daily high and the second number is the projected daily low temperature. Remember to write an informative title and labels for each column and row! 1/7 – 48o, 35o; 1/8 – 67o, 57o; 1/9 – 77o, 61o; 1/10 – 82o, 65o; 1/11 – 82o, 64o; 1/12 – 72o, 62o; 1/13 – 72o, 66o; 2. Make a two-line line graph with key showing high and low temperatures. Use the data table’s title. Label the dependent and independent variables. STATION 3 – BIOCHEMISTRY A. ATOMIC THEORY: 1. Draw a Bohr atomic model diagram of a carbon atom. 2. Label the protons and neutrons in the nucleus and place the electrons properly in their orbitals. 3. List the atomic number and the atomic mass of carbon on the side of your diagram. 4. Answer the question: Why is carbon the basic building block for biomolecules and life? B. MACROMOLECULES: You go to Wendy’s and get a bacon cheeseburger (with lettuce, tomato, ketchup), medium fries, and a small lemonade. 1. Copy the following chart. A WENDY’S FASTFOOD CHEESEBURGER MEAL BROKEN DOWN macromolecules food and water components protein lipid carbohydrate nucleic acid water what this does in monomer for your body macromolecule 2. List each of the meal’s components into its macromolecule category. Be careful, as some components will go into more than one (example: cheese – lipid, protein). 3. Describe what each macromolecule does in your body. 4. List the monomer (building block) for each macromolecule. STATION 4 – WATER 1. Draw a diagram of two water molecules. Indicate the hydrogen and oxygen atoms. Label the oxygen side negatively charged and the hydrogen side positive. Indicate the hydrogen bonds between the two molecules. 2. Briefly describe why each of the following properties of water is vital to life: a. polarity b. hydrogen bonding c. universal solvent d. adhesion e. cohesion 3. Which property of water causes the ocean water around us to stay warmer in the winter and thus the coastal land temperatures are warmer than inland? STATION 5 – CELL MEMBRANE AND TRANSPORT 1. TRANSPORT You are adrift in a lifeboat for two days and run out of water. You vaguely remember that you should not drink ocean water… In one or two sentences, explain what drinking ocean water would do to your cells using at least one term from each of the following groups: a. HYPOTONIC or HYPERTONIC or ISOTONIC b. OSMOSIS or DIFFUSION or FACILITATED DIFFUSION c. SWELL AND LYSE or SHRIVEL AND CRENATE d. ACTIVE or PASSIVE TRANSPORT. 2. BULK TRANSPORT You are flying back to Florida after a fabulous two-week vacation, but are unlucky enough to be seated next to a man who coughs for the next three hours. Yikes! You are desperately hoping that your immune system is working well and that your macrophages can take care of the wee, little beasties spewed out by this inconsiderately ill person. Draw a labeled diagram of your white blood cells engulfing these foreign particles in your system to destroy. Use one term from each category: a. endocytosis or exocytosis b. endoplasmic reticulum or vacuole c. cell membrane or nuclear membrane d. centriole or lysosome STATION 6 – CELL STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS 1. Draw a prokaryotic cell and label all structures. 2. List what this cell has in common with all eukaryotic cells.