Macromolecule Chart Ch.6 packet - Bryn Mawr School Faculty Web
advertisement

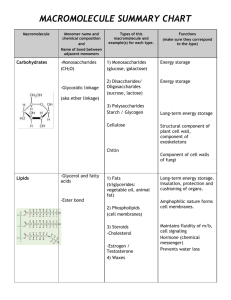
Elements include carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. There are always 2 H for every O Monomers are fatty acids Elements include carbon, Elements include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen hydrogen and sometimes oxygen. The hydrogens are in no set ratio. This macromolecule contains Polypeptides are an example an amino and a carboxylic acid group You get this macromolecule originally from your parents Chitin found in exoskeletons is an example Starches (Glycogen) found in animals are an example Enzymes are one of these macromolecules Need to eat fruits and veggies for this macromolecule Need to eat plant oils for this macromolecule Cellulose found in plants is an example Needed for immune system activity Can get this macromolecule from dairy and meat Need to eat legumes for this macromolecule especially if you are a vegetarian Peptide bonds join the monomers of this macromolecule Can be found in saturated and non-saturated forms Needed for steroid types of hormones Needed to regulate metabolic reactions throughout living cells DNA and RNA are examples of Needed for immediate energy this type of macromolecule These macromolecules are hydrophobic These macromolecules are also used for structural support Nucleotides are the monomer for macromolecule Monomers are amino acids Needed for long term energy storage Needed for insulation and padding Carbohydrates Nucleic Acids Proteins Lipids Carbohydrates Nucleic Acids Proteins Lipids