FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
advertisement

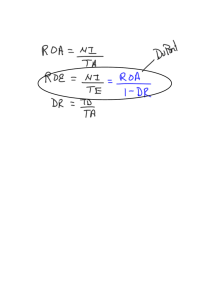
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS Accounting and Finance The Balance Sheet The Income Statement The Statement of Cash Flows Accounting Practice & Malpractice Taxes Financial Statements reflect the financial resuts of the firm. The Balance Sheet Definition Financial statements that show the value of the firm’s assets and liabilities at a particular point in time (from an accounting perspective). The Balance Sheet The Main Balance Sheet Items Current Liabilities Payables Short-term Debt Current Assets Cash & Securities Receivables Inventories + Fixed Assets Tangible Assets Intangible Assets = + Long-term Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity Market Value vs. Book Value Book Values are determined by GAAP Market Values are determined by current values Equity and Asset “Market Values” are usually higher than their “Book Values” Market Value vs. Book Value Example According to GAAP, your firm has equity worth $6 billion, debt worth $4 billion, assets worth $10 billion. The market values your firm’s 100 million shares at $75 per share and the debt at $4 billion. Q: What is the market value of your assets? A: Since (Assets=Liabilities + Equity), your assets must have a market value of $11.5 billion. Market Value vs. Book Value Example (continued) Book Value Balance Sheet Assets = $10 bil Debt = $4 bil Equity = $6 bil Market Value Balance Sheet Assets = $11.5 bil Debt = $4 bil Equity = $7.5 bil The Income Statement Definition Financial statement that shows the revenues, expenses, and net income of a firm over a period of time (from an accounting perspective). The Income Statement Earnings Before Income & Taxes (EBIT) EBIT = Total Revenues - COGS - DEPRECATION The Income Statement Pepsico Income Statement (year end 2001) Net Sales (-) Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit (-) Selling, G&A expenses (-) Depreciation expense EBIT (-) Net interest expense Taxable Income (-) Income Taxes Net Income 26,935 (10,754) 16,181 (10,918) (1,082) 4,181 (152) 4,029 (1,367) 2,662 Profits vs. Cash Flows Differences “Profits” subtract depreciation (a non-cash expense) “Profits” ignore cash expenditures on new capital (the expense is capitalized) “Profits” record income and expenses at the time of sales, not when the cash exchanges actually occur “Profits” do not consider changes in working capital The Statement of Cash Flows Definition Financial statement that shows the firm’s cash receipts and cash payments over a period of time. The Statement of Cash Flows Pepsico Statement of Cash Flows (excerpt - year end 2001) Net Income Non-cash expenses Depreciation Changes in working capital 2,662 1,082 (41) A/R=(13) A/P=26 Inv=(118) other=64 Cash Flow from operations Cash Flow from investments Cash provided by financing Net Change in Cash Position 3,703 (1,784) (1,775) 144 Taxes Taxes have a major impact on financial decisions Marginal Tax Rate is the tax that the individual pays on each extra dollar of income. Average Tax Rate is the total tax bill divided by total income. Taxes Example - Taxes Taxes and and Cash Cash Flows Flows can can be be changed by the use of debt. Firm A pays part of its profits as debt interest. Firm B does not. EBIT Interest Pretax Income Taxes (35%) Net Income Firm A 100 40 60 21 39 Firm B 100 0 100 35 65 Taxes FOOD FOR THOUGHT - If you were both the debt and equity holders of the firm, which would generate more cash flow to you? (assume Net Income = Cash Flow) EBIT Interest Pretax Income Taxes (35%) Net Income Firm A 100 40 60 21 39 Firm B 100 0 100 35 65 ? Taxes FOOD FOR THOUGHT - If you were both the debt and equity holders of the firm, which would generate more cash flow to you? (assume Net Income = Cash Flow) Net Income + Interest Net Cash Flow Firm A Firm B 39 65 40 79 0 65 ? Corporate Tax Rates (2002) Taxable Income ($) 0-50,000 50,001-75,000 75,001-100,000 100,001-18,333,333 over 18,333,333 Tax Rate (%) 15 25 34 34-39 35 Personal Tax Rates (2002) Single Taxable Income ($) 0-6,000 6,000-27,950 27,950-67,700 67,700-141,250 141,250-307,050 over 307,050 Married Taxable Income ($) 0-12,000 12,000-46,700 46,700-112,850 112,850-171,950 171,950-307,050 over 307,050 Tax Rate (%) 10 15 27 30 35 38.6 FİNANSAL ORANLAR Kaldıraç Oranları: Faaliyet Kaldıracı = Toplam Borçlar / Toplam Valıklar Borç/Özkaynak = Toplam Borçlar / Öz Kaynaklar Likidite Oranları: Cari Oran = Dönen Varlıklar / Kısa Vadeli Borçlar Nakit Oranı = (Kasa + Pazarlanabilir Menkul Kıymetlar) / Kısa Vadeli Borçlar Faaliyet Oranları: Alacak Devir Hızı = Ortalama Alacaklar / Ortalama Günlük Satışlar Stok Devir Hızı = Satılan Malların Maliyeti / Ortalama Stoklar FİNANSAL ORANLAR Karlılık Oranları: Net Kar Marjı = Net Kar / Satışlar Öz Sermaye Karlılığı = Net Kar / Ortalama Özkaynak Pazar Değeri Oranları: Fiyat / Kazanç Oranı = Hisse Fiyatı / Hisse Başına Kazanç Kar Payı Verimi = Hisse Başına Kar / Hisse Fiyatı