Cell Structures and Functions 10-12 and 10-13

Welcome to Class! 10-13 and 10-14
Complete the following:
New entry
“Specialized Cell Structure and Functions”
Draw a T-Chart or Venn Diagram compare and contrast Plant and
Animal cell below:
Agenda
1.
Discuss the STARTER (two cells)
2.
Cornell Notes on Cell Structure and Function
3.
Coloring Cells
4.
Conga Line
Homefun:
Coloring Cells Due Friday 10/16
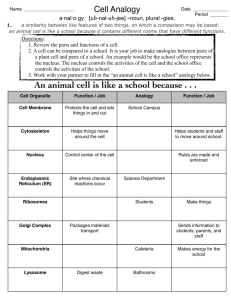
Cell Wall
Description:
Rigid outer layer
Outside of cell membrane
Function:
Support
Protection
Helps cell maintain its shape
Analogy
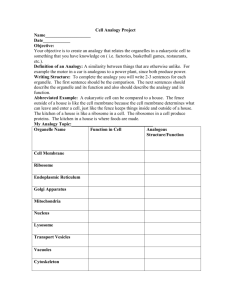
Cell Membrane
Description:
Outside covering of cell made of lipid bilayer
Function:
Barrier between cell and its environment
Controls what substances can enter or leave the cell
Provides support and protection, especially in cells without a cell wall
Analogy
Ribosomes
Description:
Made of protein and RNA
Very small, spherical shaped
Function:
Make proteins
Analogy
Cytoplasm
Description:
Jelly-like substance that fills the cell and surrounds the organelles
Function:
Fills space between organelles
Contains materials needed by the organelles
Analogy
Flagella
Description:
Long, thread-like extension of a cell
Function:
Helps cell move
Analogy
Cilia
Description:
Short, hair-like projection on the cell surface
Function:
Used to sweep away things from the cell surface or help the cell move through fluid
Analogy
Nucleus
Description:
Core, central portion of cell
Function:
Contains genetic information (DNA)
Directs cell activities
Analogy
Nuclear Membrane
Description:
Double-layer membrane surrounding the nucleus
Function:
Separates nucleoplasm from cytoplasm
Analogy
Nucleolus
Description:
Round structure within nucleus
Made of protein and RNA
Function:
Makes ribosomes
Analogy
Chloroplast
Description:
Oval or bean shaped structure with green color
Function:
Helps capture sunlight to produce food (energy) for plants
Analogy
Golgi Apparatus
Description:
Flattened sacs called cisternae
Function:
Modifies and packages materials created in the cell for transport (inside or outside of the cell)
Analogy
Lysosome
Description:
Small sacs
Function:
Use digestive enzymes to breakdown old/worn-out organelles, viruses or bacteria, and/or food particles
Analogy
Mitochondrion
Description:
Spherical or rod-shaped
Inner and outer membranes
Function:
Converts sugars into ATP (energy) for the cell
Analogy
Plastid
Description:
Double-membrane bound organelle
Function:
Involved in food storage; function depends mostly upon which pigments are present
Analogy
Rough Endoplasmic
Reticulum
Description:
System of membranous tubes and sacs with ribosomes on the surface (making it appear rough)
Function:
Helps make and transport new proteins to Golgi apparatus or outside of the cell
Analogy
Smooth Endoplasmic
Reticulum
Description:
System of membranous tubes and sacs
Function:
Makes lipids
Creates and stores steroids
Stores ions that cells might need
Metabolizes carbohydrates
Analogy
Vacuole
Description:
Sacs: smaller in animal cells, larger in plant cells
Function:
Store a variety of things such as water, nutrients, or waste products
Analogy
Vesicle
Description:
Small sacs
Function:
Stores, transports, or digests materials within the cell
Analogy