Check List for Concepts exam Level 1
advertisement
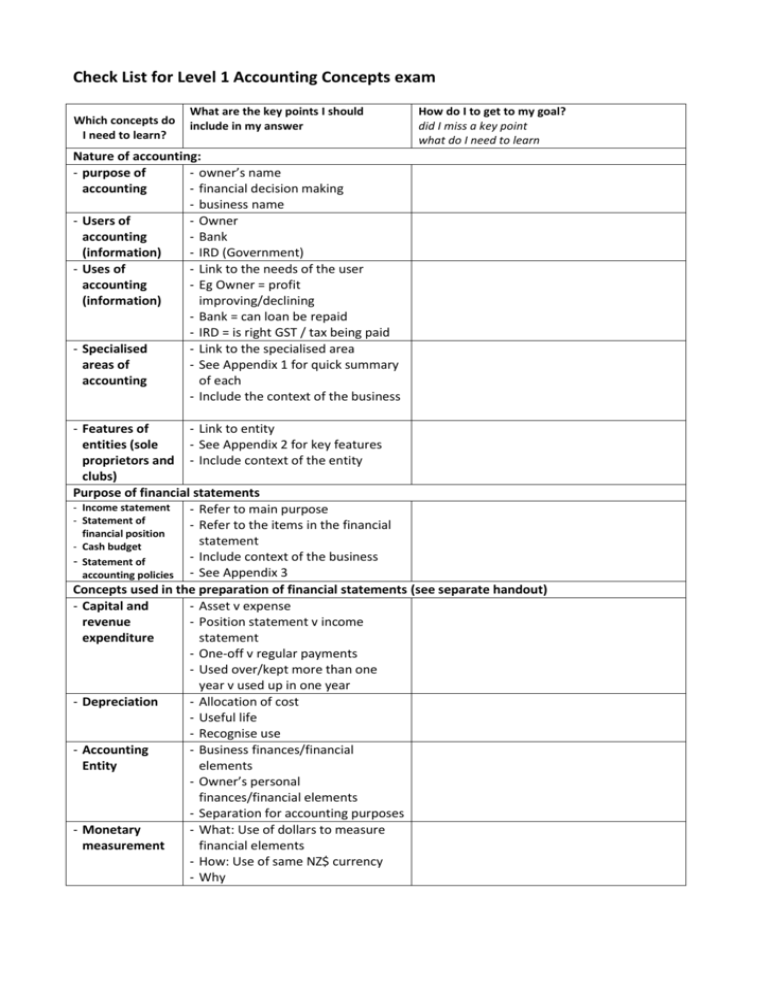
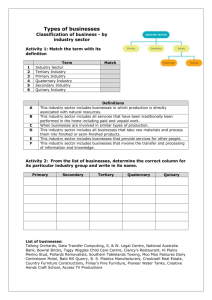
Check List for Level 1 Accounting Concepts exam Which concepts do I need to learn? What are the key points I should include in my answer How do I to get to my goal? did I miss a key point what do I need to learn Nature of accounting: - purpose of - owner’s name accounting - financial decision making - business name - Users of - Owner accounting - Bank (information) - IRD (Government) - Uses of - Link to the needs of the user accounting - Eg Owner = profit (information) improving/declining - Bank = can loan be repaid - IRD = is right GST / tax being paid - Specialised - Link to the specialised area areas of - See Appendix 1 for quick summary accounting of each - Include the context of the business - Features of - Link to entity entities (sole - See Appendix 2 for key features proprietors and - Include context of the entity clubs) Purpose of financial statements - Income statement - Refer to main purpose - Statement of - Refer to the items in the financial financial position statement - Cash budget Include context of the business - Statement of accounting policies - See Appendix 3 Concepts used in the preparation of financial statements (see separate handout) - Capital and - Asset v expense revenue - Position statement v income expenditure statement - One-off v regular payments - Used over/kept more than one year v used up in one year - Depreciation - Allocation of cost - Useful life - Recognise use - Accounting - Business finances/financial Entity elements - Owner’s personal finances/financial elements - Separation for accounting purposes - Monetary - What: Use of dollars to measure measurement financial elements - How: Use of same NZ$ currency - Why - Going concern - Period reporting - Accrual basis - Historical cost - What – business does as a going concern - How – continue into foreseeable future - Why – no need or reason to close - What (is it) - How (applied to the financial statement) - Why – link to decision making - What is the adjustment - How reported in income statement - How reported in position statement - Why reported in each statement - What – name item - How – refer to original cost - Why – transaction amount is reliable/recorded on a document Financial elements - Assets - Liabilities - Equity - Incomes Past with what Present with what and how Future with what, how and why Past with what Present with what and how Future with what, how and why Business assets less business liabilities - What the income is - What/who is providing the income - How and why increase in asset (bank) - How and why increase in equity (more profit) - Not owner contribution - Expenses - What the expense is - What/who is being paid - How and why decrease in asset (bank) - How and why decrease in equity (more profit) - Not owner contribution Accounting equation - A (+Ex) = L + E (+R) - Name specific financial element item - Provide specific dollar amount - State increase or decrease correctly Appendix 1 – specialised areas of accounting summary Auditor checks financial statements provide a true and fair view of financial performance and financial position Financial accountant/chartered accountant provides financial advice to the business owner to assist with business decisions Financial accountant/chartered accountant – provides financial advice to the business owner to assist him/her to make good financial decisions for his/her business Cost accountant involved in determining costs of production or other output of the business Management accountant involved in the overall management of the business particularly the financial management through the preparation of budgets Accounting technician involved in day-to-day operations of accounting systems so they operate efficiently and provide essential financial data and information for decision making Tax accountant involved in providing tax advice such as on GST, PAYE tax, business taxation requirements Appendix 2 – Features of entities summary - key points but answer must be in context Entity Features Sole Proprietor Community organisation/club Incorporated club Ownership One owner who makes all the decisions and keeps all the profit Liability of owners Unlimited liability – owner is personally liable to pay business debts if the business can’t pay those debts Advantages Owner is own boss, can make all the decisions, keeps all the profit Members are owners Incorporated organisations need at least 15 members Members have unlimited liability if the club/organisation is unincorporated Incorporated organisations Members have limited liability meaning members are only required to pay their subscription in full. Members are not personally liable to pay the debts of the incorporated club/organisation if the incorporated club/organisation can’t pay them – members only have to pay their subscription; all other personal assets are protected from being used to pay club debts. Unincorporated – only advantage is for very small clubs which don’t own assets or need to own assets such as local garden club Incorporated – advantage for members is limited liability; advantage for the club/organisation is that it is a separate legal entity so it can own assets and borrow money in its own right Disadvantages Limited access to capital – only the owners funds Unlimited liability as personal assets can be used to pay business debts if the business is in financial difficulty and can’t pay its debts because the business is not a separate legal entity Appendix 3 Purpose of financial statements summary Income statement Statement of financial position Cash budget Accounting policies Main purpose To determine profit for the year To help make decisions about improving profit through increasing income and/or decreasing expenses To report assets, liabilities and equity on balance day (a point in time) To help make decisions about the financial position – is the business financially stable/equity more than liabilities To help make decisions about cash flow in the future such as can the business afford new equipment/does the business need to borrow money To set out the policies used to measure the financial elements reported in the financial statements so users can make good decisions knowing how for example assets have been measured Items to write about Incomes Expenses Profit Current assets Current liabilities Non-current assets Non-current liabilities Equity Estimated receipts Estimated payments Estimated bank balance Measurement of assets at historical cost Accrual accounting used to determine profit and report assets and liabilities Method of depreciation Going concern assumption