Cell - structure and function
advertisement

Cell - structure and function
Instructional Objectives
1. The students will be able to recognize unicellular and multi cellular organism.
2. The students will be able to able to recognize different types of cell.
3. The students will be able to predict the functions performed by unicellular and
multicellular organisms.
4. The students will be able to differentiate organisms based on number of cells.
5. The students will be able to cite illustration of unicellular organisms
6. The students will be able to apply knowledge and understanding to detect errors
in the figure.
7. The students will be able to draw diagrams of amoeba, paramecium
Concepts
Variation in number, unicellular and multicellular
Functions of unicellular and multicellular organismS
Variation in size, microscopic and macroscopic
Previous Knowledge
The students have knowledge of certain basic functions occurring in living
organisms
The students knows that cell is smallest unit of an organism
Instructional materials
Set Induction: Worksheet I
Development of lesson: Chart of Amoeba, Paramecium, Onion peel cell, Human
Cheek cell.
Sequential Teaching Learning activities
Expected Behavioural Outcome
1. SET INDUCTION
Teacher Greets students
St6udents also greets teacher
Activity I
Teacher asks following questions to the
students:
Tr : what does our body is made up of?
How many cells are present in our
body?
Organism made up of more than one
cell are called multicellular organism.
Tr; what do you understand by term
unicellular organism?
Ss:Cells
Ss:many cells
Ss:organism with one cell
Tr:very good. Organism made up of
single cell is called as unicellular
organism.
Ss: multicellular
Tr: Is plant is unicellular or
multicellular?
Tr:very good. Egg of hen is it
unicellular or multicellular?
Tr: good.{teacher gives worksheet to
each group} you have to put tick mark
in correct box.
Tr; whether unicellular organism can
breathe ?
Tr: which organism reproduce ,is it
unicellular or multi cellular?
Ss: Unicellular
Ss: unicellular animal take breath
Ss: Both reproduce
Tr: what about other functions, are they
performed by both unicellular and
multicellular?
Ss: both performs the all necessary
functions
Tr: thus in each case all necessary
functions are performed but in
multicellular organisms it is carried out
by groups of cell Forming different
tissues.
2] STATEMENT OF THE TOPIC
So now let us see what is the cell
structure which makes them to perform
all these functions in both type of cell.
Thus today we are going to learn about
“cell Structure”
3]DEVELOPMENT OF THE LESSON
What must be the size of the cell?
Students respond saying microscopic.
Tr: Yes .the smallest cell is 0.1 to 0.5
micrometer in bacteria. The largest cell
measuring is 170mm x 130mm is the
egg of an Ostrich
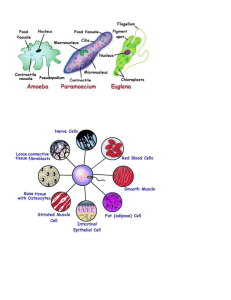
(teacher shows the chart of amoeba and
paramecium)
Tr: what shape do they have ?
The organism in picture unicellular
organism. Amoeba and Paramecium.
Amoeba does not have a definite shape.
it keeps on changing its shape.
Projection of varying length protruding
Students respond their answer
out of its body, they are called as
pseudopodia. These projections appear
and disappear as amoeba moves or
feeds.
Tr: so, thus the most of the cells are
microscopic in size and we observe
them under the microscope. Amoeba
and paramecium are example of
unicellular organism.
Teacher shows the chart of cell structure
of onion peel cells diagram
Tr: what is present inside the cell?
Tr: teacher shows the chart of human
cheek cells.
Tr : what is present inside the cell of
human cheeks?
Ss:responds saying nucleus and
cytoplasm
Ss:responds saying nucleus and
cytoplasm
Ss: responds saying cell membrane.
Tr: what separates one cell from other
cell?
Tr: Correct. Cell membrane gives shape
to the cell. The cytoplasm and nucleus
are enclosed within the cell membrane
also called as the plasma membrane. It
is porous and allows movement of
substances both inward and outward. In
plant cell there is an outer thick layer or
covering called the cell wall.
Students respond saying cytoplasm
Tr: What is present more in cell?
Tr: yes. It is a jelly like substance
between nucleus and membrane.
Tr: in cytoplasm various other
components are present called the
organelles,
Students respond saying nucleus
Tr: which is the important component of
cell?
Tr: yes. It is generally spherical and
located in the centre of the cell. Nucleus
is separated from cytoplasm by a
membrane called nuclear membrane.
Teacher summarizes the topic.
4)EVALUATION
I] state whether the statement are true
or false
I)A multicellular organism is made up
of one cell.
ii) Cells exist in different shapes
iii)Amoeba is a unicellular organism
iv)Largest cell is the egg of ostrich.
II]Make a sketch of Amoeba.
III] Make a sketch of human cheek cell.
5]HOMEWORK
Find the difference and similarities
between plant cell and animal cells.
i] False
ii] True
iii] True
iv] True
Worksheet I
Which all function can unicellular and multicellular organism can performs. Put
tick mark at appropriate places:
Organism
Breathe
Unicellular
Multicellular
Eat
Moves
Reproduce Excretes Grow