Body and behavior
advertisement

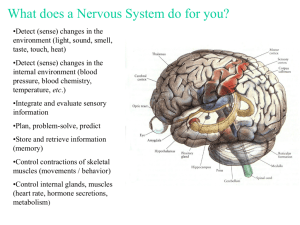
Body and behavior Chapter 6 Standards Standard II: Biopsychological Biological basis of behavior IIA-1.1 Structure and function on neuron IIA- 2.1 Organization of the nervous system The nervous System Controls your movement, emotions, thinking, and behavior (almost all you do) Never at rest Divided into 2 parts: Central Nervous System (CNS) – the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – nerves branching beyond the spinal cord Nervous System All parts are protected: Brain – skull and layers of sheathing (coating) Spinal cord – the vertebrae Peripheral – layers of sheathing - nerves about as thick as a pencil Extremities – nerves get smaller and smaller Neurons Strips of long cells that carry messages to and from the brain Carry messages by chemical-electrical signals Neuron can “fire” over and over again Messages are sent from neuron to neuron Body contains millions Parts of a neuron 4 Basic Parts: Dendrites The cell body (contains the nucleus) An axon Axon terminals Dendrites Short, thin fibers that protrude from the cell body Receive impulses (messages) from other neurons and sends them to the cell body Axon Single extension Carries impulses from cell body to the axon terminals Usually short, but can be several feet long Myelin sheath (white fatty substance) insulates and protects the axon; can speed the transmition Axon Terminal Branch out at the end of the axon Release neurotransmitters to stimulate dendrites of the next neuron Positioned opposite of the dendrite of another neuron Synapse & Neurotransmitters Synapse – space between the neurons; transmits messages to the next neuron Neurotransmitters – chemicals released by neurons - locks or excites receptors Ex: endorphin – inhibits pain norepinephrine – involved with memory and learning Afferent, Efferent, and Interneurons Afferent neuron (sensory neurons) – relay messages from the sense organs (eyes, nose, skin) to the brain Efferent neuron (motor neurons) – send signals from the brain to the glands and muscles Interneurons – processes signals only to other neurons Voluntary vs involuntary activites Somatic Nervous System (SNS) – the part of peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary activities (skeletal muscles) Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) – part of the nervous system that controls involuntary activities Ex: heartbeat, breathing, digestion, etc. The brain Composed Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain of 3 parts: Hindbrain Rear base of the skull; controls basic processes of life Includes: Cerebellum (behind spinal cord) – controls posture, balance and voluntary movements Medulla – controls heart rate, breathing, and reflexes Pons – bridge between spinal cord and brain and produces chemicals needed for sleep Midbrain Small, above the pons Integrates sensory information and sends it upwards Medulla and pons extends upward into the midbrain Reticular Activating System (RAS)- spans across medulla, pons, and midbrain - Alerts brain of incoming signals and involved in sleep/wake cycle Forebrain Brains central core Includes: Thalamus – integrates sensory information Hypothalamus – controls hunger, thirst, and changes in temperature Cerebral Cortex & Cerebrum Cortex - Outer layer of forebrain Cerebrum – inner layer Higher thinking processes Gives you ability to learn and store complex and abstract information Site of conscious thinking processes Limbic System Core of forebrain Regulates our emotions and motivations Includes: Hypothalamus, thalamus, hippocampus, and amygdala Amygdala - controls violent emotions such as rage and fear Hippocampus: - formation of memories Lobes of the Brain Cerebrum – 2 hemispheres Connected by: Corpus callosum Each hemisphere has deep grooves = regions or lobes Occipital lobe – vision Parietal lobe – body sensations Temporal lobe – hearing, memory, emotion, speaking Frontal lobe – organization, planning, creative thinking Hemispheres (Left & Right) Corpus callosum – carries messages back and forth between the 2 hemispheres Right: Controls left side of body - Nonverbal, spatial, and holistic Left: Controls right side of body - Verbal, Mathematical, Analytic Corpus Callosum Can be severed = Split-Brain Operation Now have “2” brains; operate independently, no communication between the two sides How Psychologists Study the Brain Record electrical activity in brain – EEG - wires and electrodes attached to a machine Stimulation – “make” neurons fire on certain parts of brain and record; determine function Lesions – cutting or destroying part of brain to see if animal behaves differently Accidents – learn from brain trauma and tragedies Images CT scans – pinpoint injuries and deterioration PET scans – capture picture of brain as different parts are being used MRI – able to see/study activity and structures - combines benefits of CT and PET scans