The Great Plains - Ms Roache's Place
advertisement

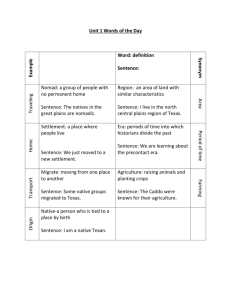
The Great Plains A quick tour Location The Great Plains are located just east of the Rocky Mountains. Physical Features Flatlands that rise gradually from east to west. Land eroded by wind and water. Grasslands with few trees. Climate The climate on the Great Plains is very harsh. Low rainfall. Many dust storms. Harsh winters. Before the Civil War People referred to the Great Plains as a treeless wasteland. Few people settled on the Plains, instead they passed through on the way west. Scenes from the Plains So, what changed people’s mind? Opportunities for land ownership The Homestead Act of 1862. For a $10 fee, homesteaders got 160 acres of land. They had to live on it and farm it for five years so they could own it. Technological advances Possibility of wealth New beginning for former slaves Adventure Inventions Barbed Wire Windmills Steel Plows Railroads Adaptations Sod Houses Wheat Farming Dry Farming Beef Cattle Longhorns Windmills A windmill is a machine that is operated by wind power. Windmills are used chiefly to pump water, grind grain and generate electric power. Windmills were used all over The Great Plains. They were used to pump water from the ground to the surface so the settlers could use it. This helped make The Great Plains more livable. Barbed Wire The widespread use of barbed wire fences changed life on the plains. Land that was once open to all was now being fenced off by ranchers and homesteaders. Homesteaders were better able to protect their crops and ranchers had better control over their herds. The American Indian was also affected by the wire that they referred to as “Devil’s rope”. Steel Plow Invented by John Deere, the steel plow was made to cut through the tough sod on the Great Plains without the dirt clogging up along the blade. This meant the farmer could plow without having to stop and clean his plow off every few yards. Dry Farming & Wheat Farming Dry farming is used in areas that have little rainfall. Basically, the farmer divides his fields in wide strips and then plants crops on every other strip. This allows the soil to gather moisture for two years. Wheat became popular on The Great Plains because it actually grows better this way, especially Red Wheat introduced by Russian Immigrants. Beef Cattle Raising Many ranchers started raising beef cattle on the Great Plains. It actually makes plenty of sense if you think about it…what big animal similar to a cow had been living on the plains for years? The longhorn was the choice of most as it was well suited to the harsh climate of the plains. Transcontinental Railroad The Transcontinental Railroad connected the Atlantic and Pacific coasts. It was made up of many small railroad lines. The railroad opened up the Great Plains area for people who wanted to settle there, and made trade easier from one area of the country to another. This encouraged industrial growth and economic growth. Sod Houses Sod Houses are exactly what they sound like. Houses made of sod. The settlers used sod because there were very few trees on the Great Plains.