The Periodic Table of Elements
advertisement

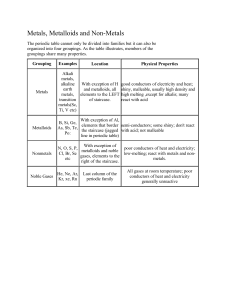
The Periodic Table The Organization of the Periodic Table • The Periodic Table of Elements is organized by Atomic number (the number of PROTONS in an element) • Dmitri Mendeleev ( 1834- 1907) created the periodic table of elements • The Periodic Table of Elements is a visual presentation of the elements in groups according to their physical and chemical properties. The Periodic Table of ElementsColumns • The table has been organized by the number of VALENCE electrons ( Electrons in the outer most energy level) • The table has also been organized into columns or FAMILIES ( up and down) • Each FAMILY contains elements with the same number of VALENCE electrons • The amount of VALENCE electrons determines their chemical properties... How they are going to react Groups and Families of the Periodic Table • How many VALENCE electrons does Lithium (Li), Sodium (Na) and Potassium (K) have? • They belong to the same group/family because they all have one valence electron Family Names • Certain groups/families have specific names • We have the • • • • Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth Metals Halogens Noble Gases The Alkali Metals • All elements in the first column EXCEPT hydrogen • (Li, Na,K, Rb, Cs,Fr) • Characteristics of ALKALI metals • • • • These elements all have 1 VALENCE electron These elements are all shiny and soft metals These elements will react with water EXPLOSIVELY!! Because of their high reactivity these elements are not found in their elemental state but instead exist as COMPOUNDS The Alkaline Earth Metals • All elements in the second column • (Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra) • Characteristics of Alkaline Earth Metals • These elements all have 2 valence electrons • These elements are highly malleable and reactive and they burn easily in the presence of heat • Because of their high reactivity these elements are not found in their elemental state but instead exist as COMPOUNDS • They form many compounds found in rocks and earth… The Halogens • All Elements in the second to last column (Group 7) • Characteristics of Halogens • • • • These elements have 7 VALENCE electrons These elements are all non-metals The word HALOGEN means “salt-former” All compounds that contain Halogen elements are called SALTS ex: NaCl • Halogens also kill germs when they are dissolved in water The Noble Gases • All elements in the last column ( Group 8) • Characteristics of Noble Gases • These elements are special because their outer energy shell is completely full • These elements will not easily combine with other elements to form compounds • When electricity is passed through these gases, light is released and these gases are often used in lights. • Argon comes from the Greek argos, meaning “lazy” or “inactive” The Periodic Table of Elements • All of the elements can be classified into three categories 1) Metals 2) Non- Metals 3) Metalloids • The staircase shaped line that crosses the right side of the table helps to locate and identify these categories Metals • Good conductors of electricity and heat • Often ductile and malleable which means they are easily made into wires or flattened into sheets... THINK ALUMINUM FOIL... • Usually shiny • All METALS are solid at room temperature except MERCURY which is liquid • Many Metals react with Acids • Found to the LEFT of the STAIRCASE on the Periodic Table Non- Metals • Poor conductors of electricity and heat • Many non-metals are gases at room temperature • The solid non-metals can easily be made into powders • Found to the RIGHT of the STAIRCASE • Except for HYDROGEN Metalloids • Seven elements with properties of both METALS and NON-METALS • Ex: Some METALLOIDS are good conductors of electricity and some are poor conductors depending on conditions • METALLOIDS are found on both sides of the staircase Activity • On your Periodic Table • Label and define the parts of the periodic table – – – – Square Atomic Number Group Staircase • Color in the metals, non-metals and metalloids each in a different color