Periodic Table Study Guide
advertisement

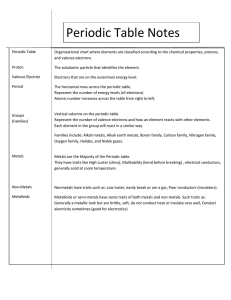
Periodic Table Study Guide 1. How did Dmitri Mendeleev arrange the elements on the periodic table? Atomic mass 2. How is the modern Periodic Table arranged? By increasing atomic number 3. Why are valence electrons significant? Where are they located? They bond with other atoms. Located in the outermost energy level. 4. What are the rows ( called? Rows = periods Columns = groups ) called on the periodic table? What are the columns ( ) 5. Where are metalloids located on the periodic table? Along the staircase 6. The numbers listed above the groups on the periodic table tell us what about those elements? Identifies the number of valence electrons 7. How do you identify an element by looking at a Bohr Model? (hint: what do you count?) Count the number of protons 8. Which subatomic particle identifies an element? Protons 9. How many electrons can the energy levels hold? 1st _______ 2nd _______ 3rd ________ 1st – 2 2nd – 8 3rd – 8 10. What can you predict about an element based on its location on the periodic table? Its chemical and physical properties 11. List the properties of metals: Luster (shiny), good conductor of heat/electricity, malleable, ductile 12. Where are metals, non-metals, and metalloids located on the Periodic Table? Metals – left side of the staircase Non-metals – right side of the staircase Metalloids – along the staircase 13. What kinds of properties do metalloids have? Properties of both metals and non-metals 14. What does ductile mean? Ability to be pressed into thin sheets of wire 15. Which group on the Periodic Table is unreactive (inert)? Why? Group 18 (noble gases). Their outermost energy level is full. 16. What is the name of groups 3 – 12? Transition metals 17. What do the period numbers indicate? The number of energy levels an atom has 18. Elements in the same _________________ have similar properties. List properties they might share: Group Physical and chemical properties: Luster Malleability Reactivity