Virus
advertisement
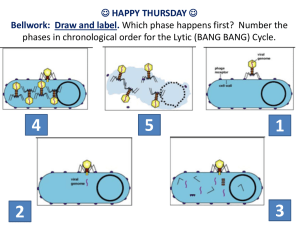
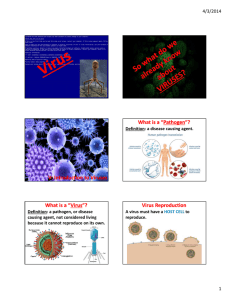
V: Introduction to Viruses What is a “Pathogen”? Definition: a disease causing agent. What is a “Virus”? Definition: a pathogen, or disease causing agent, not considered living because it cannot reproduce on its own. Virus Reproduction A virus must have a HOST CELL to reproduce. Structure of a “Virus” Capsid: outer protein coat. Genetic Material: DNA or RNA. V: Invasion of the Virus “Lytic Cycle” Definition: process in which a virus enters a cell, makes a copy of itself, and causes the cell to burst. “Lytic Cycle” (Viral Reproduction) “Stage A (1)” The virus lands on the host cell and then injects its genetic material into the host cell. “Stage B (2)” The virus using the host cell to synthesize, or make, viral proteins (capsids) and nucleic acids (genetic material-DNA or RNA). “Stage C (3)” The virus assembles (puts together) capsids and nucleic acids to prepare for release. “Stage D (4)” The host cell breaks open (lysing) and the newly assembled viruses begin to be released. V: Bacteriophage Lytic Cycle “Lysogenic Cycle” Definition: process by which a virus embeds its DNA into the DNA of the host cell and is replicated along with the host cell's DNA. Lysogenic cycle is a viral reproduction cycle in which the virus is dormant until it enters the lytic cycle. “Lysogenic Cycle” What is a “Retrovirus”? Definition: a virus that contains RNA as its genetic material instead of DNA. Viruses cause “Disease” How: by disrupting the body’s normal equilibrium. In many viral infections, viruses attach and destroy certain cells in the body, causing the symptoms of the disease. “HIV” (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) Definition: retrovirus that destroys white blood cells called helper T cells and causes the disease known as AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome). “Influenza” (Flu or Grippe) Definition: a highly infectious respiratory disease. Your best defense against this virus is to receive an annual vaccination (according to the Mayo Clinic). What is a “Vaccine”? Definition: a preparation of weakened or killed pathogens. When injected into the body, a vaccine sometimes prompts the body to produce immunity to the disease. V: How Vaccines Work What is “Immunity”? Definition: the body's ability to destroy new pathogens. What are “Antibiotics”? Definition: compounds that block the growth and reproduction of bacteria. DO NOT work on viral infections! Who is a “Immunologist”? Definition: a person who specializes in the immune system, to study the mechanism used by the virus to infect cells. If a company wants to develop antiviral drugs, they would need to ask a research immunologist.