Virus & Bacterial Genetics Study Guide: Key Terms & Concepts
advertisement

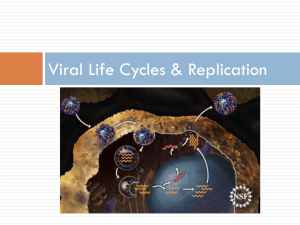
CH. 18 STUDY GUIDE: Virus and Bacterial Genetics KEY TERMS VIRUSES plasmids capsid transposons("jumping genes") nucleic acid core structural gene lytic cycle regulator gene lysogenic cycle operator bacteriophage operon vectors promoter provirus inducer BACTERIA repressor bacterial chromosome activator transformation repressible enzymes transduction inducible enzymes conjugation cAMP-CAP complex prion restriction enzymes viriod retrovirus 1 WORD ROOTS capsa - = a box (capsid: the protein shell that encloses the viral genome). conjug - = together (conjugation: in bacteria, the transfer of DNA between two cells that are temporarily joined) lyto - = loosen (lytic cycle: a type of viral replication cycle resulting in the release of new phages by death or lysis of the host cell). - oid = like, form (nucleoid: a dense region of DNA in a prokaryotic cell) - phage = to eat (bacteriophages: viruses that infect bacteria). pro - = before (provirus: viral DNA that inserts into a host genome) retro - = backward (retrovirus: an RNA virus that reproduces by transcribing its RNA into DNA and then inserting the DNA into a cellular chromosome) trans - = across (transformation: a phenomenon in which external DNA is assimilated by a cell). virul - = poisonous (virulent virus: a virus that reproduces only a lytic cycle). QUESTIONS 1. Using a diagram describe the lytic and lysogenic cycles of viral replication. Use the following terms in your description: virulent, temperate, lysogenic cells, lytic cycle, provirus and vegetative virus. 2. Describe the bacterial chromosome. How does it differ from a eukaryotic chromosome? 3. Describe the nature of bacterial plasmids and discuss their role in recombinant DNA studies. 4. Using a diagram describe the process of transduction by bacteriophages and tell of the implications and uses of this process. 2 5. Describe prokaryotic gene induction. Explain the role of inducer, operator, promoter and repressor, the regulator gene and the structural genes. 6. Using a diagram, describe the function of a repressible operon and explain how it differs from an inducible operon. 7. Using a diagram, describe how the cAMP-CAP complex facilitates transcription. 3