Ideal Gas Law
advertisement

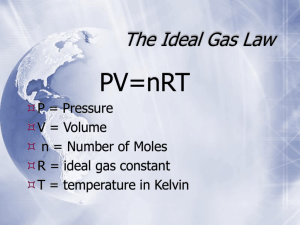
Ideal Gas Law PV = nRT Brings together gas properties. Can be derived from experiment and theory. Ideal Gas Equation Volume Pressure PV=nRT No. of moles R = 0.0821 atm L / mol K R = 8.314 kPa L / mol K Kelter, Carr, Scott, Chemistry A Wolrd of Choices 1999, page 366 Universal Gas Constant Temperature PV = nRT P V T n R = = = = = pressure volume temperature (Kelvin) number of moles gas constant Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP) T = 0 oC or 273 K P = 1 atm = 101.3 kPa = 760 mm Hg 1 mol = 22.4 L @ STP Solve for constant (R) PV nT Recall: 1 atm = 101.3 kPa Substitute values: (1 atm) (22.4 L) = R (1 mole)(273 K) R = 0.0821 atm L / mol K R = 0.0821 atm L mol K or (101.3 kPa) ( 1 atm) = 8.31 kPa L mol K R = 8.31 kPa L / mol K Ideal Gas Law What is the volume that 500 g of iodine will occupy under the conditions: Temp = 300oC and Pressure = 740 mm Hg? Step 1) Write down given information. mass = 500 g iodine T = 300oC P = 740 mm Hg R = 0.0821 atm . L / mol . K Step 2) Equation: PV = nRT Step 3) Solve for variable V = nRT P Step 4) Substitute in numbers and solve (500 g)(0.0821 atm . L / mol . K)(300oC) V = 740 mm Hg V= What MISTAKES did we make in this problem? What mistakes did we make in this problem? What is the volume that 500 g of iodine will occupy under the conditions: Temp = 300oC and Pressure = 740 mm Hg? Step 1) Write down given information. mass = 500 g iodine Convert mass to gram; recall iodine is diatomic (I2) x mol I2 = 500 g I2(1mol I2 / 254 g I2) n = 1.9685 mol I2 T = 300oC Temperature must be converted to Kelvin T = 300oC + 273 T = 573 K P = 740 mm Hg Pressure needs to have same unit as R; therefore, convert pressure from mm Hg to atm. x atm = 740 mm Hg (1 atm / 760 mm Hg) P = 0.8 atm R = 0.0821 atm . L / mol . K Ideal Gas Law What is the volume that 500 g of iodine will occupy under the conditions: Temp = 300oC and Pressure = 740 mm Hg? Step 1) Write down given information. mass = 500 g iodine n = 1.9685 mol I2 T = 573 K (300oC) P = 0.9737 atm (740 mm Hg) R = 0.0821 atm . L / mol . K V=?L Step 2) Equation: PV = nRT Step 3) Solve for variable V = nRT P Step 4) Substitute in numbers and solve (1.9685 mol)(0.0821 atm . L / mol . K)(573 K) V = 0.9737 atm V = 95.1 L I2 Ideal Gas Law What is the volume that 500 g of iodine will occupy under the conditions: Temp = 300oC and Pressure = 740 mm Hg? Step 1) Write down given information. mass = 500 g iodine T = 300oC P = 740 mm Hg R = 0.0821 atm . L / mol . K Step 2) Equation: PV = nRT Step 3) Solve for variable V = nRT P Step 4) Substitute in numbers and solve (500 g)(0.0821 atm . L / mol . K)(300oC) V = 740 mm Hg V= What MISTAKES did we make in this problem?